Kosin Med J.
2012 Dec;27(2):99-103. 10.7180/kmj.2012.27.2.99.
Clinical Manifestations of 6 Cases of Septic Pulmonary Embolism at Increased Risk Recently
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, Dong-A University, Busan, Korea. sjum@dau.ac.kr
- 2Department of Radiology, College of Medicine, Dong-A University, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 2308517
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7180/kmj.2012.27.2.99
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
The aim of this study was to investigate the clinico-radiologic features and microbiologic data of patients with SPE in a tertiary care hospital in Busan.
METHODS
We retrospectively analyzed clinical and radiologic features of 6 cases with septic pulmonary embolism that occurred from March 2009 to March 2011 in Dong-A university medical center.
RESULTS
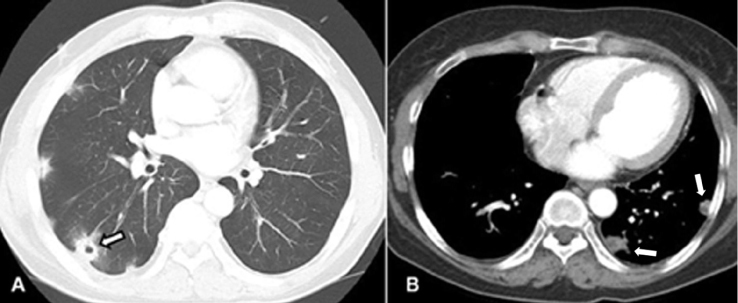
The mean age of the study population was 58 years, and two men and four women were included. Clinical symptoms included general weakness (5 patients), febrile sensation (4 patients) and pleuritic chest pain (2 patients). Underlying conditions were chemoport infection (4 patients), dental abscess (1 patients), and cellulitis of hip (1 patient). Chest computed tomography revealed bilateral multiple nodular opacities in most patients, and cavitation, central necrosis, feeding vessels were identified. All patients received parenteral antimicrobial therapy with or without central catheter removal, drainage of the extrapulmonary infection. Causative organisms were Pseudomonas aeruginosa (2 patients), Candida albicans (1 patient), Bacillus species (1 patient), and Klebsiella pneumonia (1 patient).
CONCLUSIONS
Clinical and radiologic features of septic pulmonary embolism were various and nonspecific. The diagnosis was usually suggested by the presence of a predisposing factor of septic pulmonary embolism and CT findings of bilateral multiple nodular opacities in patients with infectious signs and symptoms. Most important underlying condition was intravascular device infection.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Fat embolism syndrome: a review in cosmetic surgery
Hongil Kim, Bommie Florence Seo, Gregory Randolph Dean Evans
Kosin Med J. 2024;39(3):169-178. doi: 10.7180/kmj.24.126.
Reference
-
1. Fred HL, Harle TS. Septic pulmonary embolism. Am Fam Physician GP. 1970. 1:81–87.
Article2. Cook RJ, Ashton RW, Aughenbaugh GL, Ryu JH. Septic pulmonary embolism: Presenting features and clinical course of 14 patients. Chest. 2005. 128:162–166.3. Lee SJ, Cha SI, Kim CH, Park JY, Jung TH, Jeon KN, et al. Septic pulmonary embolism in Korea: Microbiology, clinicoradiologic features, and treatment outcome. J Infect. 2007. 54:230–234.
Article4. Araoz PA, Gotway MB, Harrington JR, Harmsen WS, Mandrekar JN. Pulmonary septic emboli: diagnosis with CT. Radiology. 1990. 174:211–213.
Article5. Rossi SE, Goodman PC, Franquet T. Nonthrombotic pulmonary emboli. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2000. 174:1499–1508.
Article6. Mylonakis E, Calderwood SB. Infective endocarditis in adults. N Eng J med. 2001. 345:1318–1330.
Article7. Sakuma M, Sugimura K, Nakamura M, Takahashi T, Kitamukai O, Yazu T, et al. Unusual pulmonary embolism: septic pulmonary embolism and amniotic fluid embolism. Circ J. 2007. 71:772–775.
Article8. Mermel LA, Farr BM, Sherertz RJ, Raad II, Grady NO, Harris JA, et al. Guidelines for the management of intravascular catheter-related infections. Clin Infect Dis. 2001. 32:1249–1272.
Article9. Lee HY, Kim NH, Kim JH, Kim DH, Kim YS, Jee YK, et al. A case of septic pulmonary embolism due to pyelonephritis. Korean J Med. 2009. 76:105–109.10. Lane RK, Matthay MA. Central line infections. Curr Opin Crit Care. 2002. 8:441–448.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Electrocardiographic Changes in a Patient With Pulmonary Embolism and Septic Shock
- Three Cases of Postpartum Pulmonary Embolism Following Cesarean Section
- Pulmonary Embolism Detected after Induction of the General Anesthesia: A Case Report
- Dyspnea Due to Candidal Septic Pulmonary Embolism Originated from Odontogenic Infection
- A Case of Emphysematous Pyelonephritis Complicated with Septic Pulmonary Embolism