Immune Netw.
2016 Jun;16(3):195-199. 10.4110/in.2016.16.3.195.
Cross-Reactivity of Porcine Immunoglobulin A Antibodies with Fecal Immunoglobulins of Wild Boar (Sus scrofa) and Other Animal Species
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pathology, College of Veterinary Medicine, Konkuk University, Seoul 05029, Korea. lyoo@konkuk.ac.kr
- 2Animal and Plant Quarantine Agency, Gimcheon 39660, Korea.
- KMID: 2299794
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4110/in.2016.16.3.195
Abstract
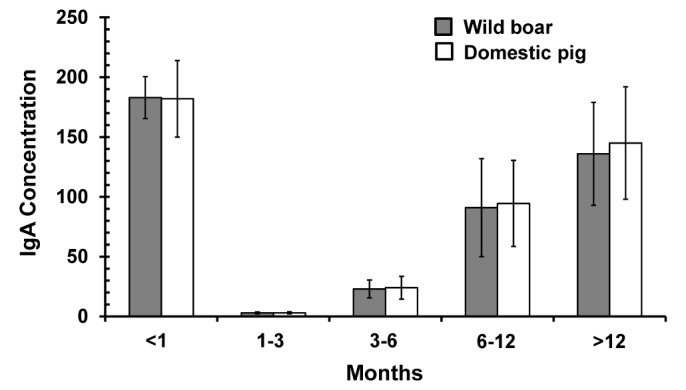
- Fecal samples obtained from wild boar habitats are useful for the surveillance of diseases in wild boar populations; however, it is difficult to determine the species of origin of feces collected in natural habitats. In this study, a fecal IgA ELISA was evaluated as a method for identifying the porcine species from fecal samples. Both domestic pigs (Sus scrofa domestica) and wild boars (Sus scrofa coreanus) showed significantly higher levels of fecal IgA than other animal species. Additionally, age dependent changes in the level of Ig A in wild boars and domestic pigs were identified; Titers of Ig A were highest in suckling period and lowest in weanling period.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Meng XJ, Lindsay DS, Sriranganathan N. Wild boars as sources for infectious diseases in livestock and humans. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2009; 364:2697–2707. PMID: 19687039.
Article2. Albina E, Mesplede A, Chenut G, Le Potier MF, Bourbao G, Le GS, Leforban Y. A serological survey on classical swine fever (CSF), Aujeszky's disease (AD) and porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome (PRRS) virus infections in French wild boars from 1991 to 1998. Vet Microbiol. 2000; 77:43–57. PMID: 11042399.
Article3. Jacobson M, Gerth LM, Holmgren N, Lundeheim N, Fellstrom C. The prevalences of Brachyspira spp. and Lawsonia intracellularis in Swedish piglet producing herds and wild boar population. J Vet Med B Infect Dis Vet Public Health. 2005; 52:386–391. PMID: 16283917.
Article4. Seo S, Sunwoo S, Hyun B, Lyoo YS. Detection of antibodies against classical swine fever virus in fecal samples from wild boar. Vet Microbiol. 2012; 161:218–221. PMID: 22841406.
Article5. Hsieh HM, Chiang HL, Tsai LC, Lai SY, Huang NE, Linacre A, Lee JC. Cytochrome b gene for species identification of the conservation animals. Forensic Sci Int. 2001; 122:7–18. PMID: 11587860.
Article6. Nikitin SV, Iudin NS, Kniazev SP, Aitnazarov RB, Kobzev VF, Bekenev VA, Savvina MA, Ermolaev VI. Frequency of chromosomes carrying endogenous retroviruses in the populations of domestic pig and wild boar. Genetika. 2008; 44:789–797. PMID: 18727389.
Article7. Franz J, Corthier G. Measurement of porcine faecal IgA, IgG and IgM levels by a competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981; 43:645–649. PMID: 7285397.8. Asada Y, Kawamoto Y, Shotake T, Terao K. Molecular evolution of IgG subclass among nonhuman primates: implication of differences in antigenic determinants among Apes. Primates. 2002; 43:343–349. PMID: 12426468.
Article9. Omatsu T, Ishii Y, Kyuwa S, Milanda EG, Terao K, Yoshikawa Y. Molecular evolution inferred from immunological cross-reactivity of immunoglobulin G among Chiroptera and closely related species. Exp Anim. 2003; 52:425–428. PMID: 14625410.
Article10. Nollens HH, Ruiz C, Walsh MT, Gulland FM, Bossart G, Jensen ED, McBain JF, Wellehan JF. Cross-reactivity between immunoglobulin G antibodies of whales and dolphins correlates with evolutionary distance. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2008; 15:1547–1554. PMID: 18768672.
Article11. Kern B, Depner KR, Letz W, Rott M, Thalheim S, Nitschke B, Plagemann R, Liess B. Incidence of classical swine fever (CSF) in wild boar in a densely populated area indicating CSF virus persistence as a mechanism for virus perpetuation. Zentralbl Veterinarmed B. 1999; 46:63–67. PMID: 10085775.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A survey of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome among wild boar populations in Korea
- Spargana in a Weasel, Mustela sibirica manchurica, and a Wild Boar, Sus scrofa, from Gangwon-do, Korea
- Seroepidemiological Survey of Aujeszky's Disease Virus in Wild Boar (Sus scrofa) and Raccoon Dogs (Nyctereutes procyonoides koreensis) in Korea
- Detection of Neutralizing Antibody Against Japanese Encephalitis Virus in Wild Boars of Korea
- Seroprevalence of Trichinella sp. in Wild Boars (Sus scrofa) from Yanggu-gun, Gangwon-do, Korea