Korean J Adult Nurs.
2013 Apr;25(2):170-182.
The Effects of Simulation Training With Hybrid Model for Nursing Students on Nursing Performance Ability and Self Confidence
- Affiliations
-
- 1Red Cross College of Nursing, Chung-Ang University, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Nursing, Ansan University, Ansan, Korea. susana21@ansan.ac.kr
Abstract
- PURPOSE
This study investigated the effectiveness of simulation training with a hybrid model of student nurses' performance ability and reported self confidence.
METHODS
A nonequivalent control group with pre-posttest was designed. Data collection was done during the first semester in 2012 at a college of nursing in Seoul. Nursing performance ability and reported self confidence related to taking care of patients with urinary problems were evaluated. The treatment group (n=96) received simulation training of a catheterization procedure with a hybrid model involving standardized patients and a mannequin. Nursing students in the comparison group (n=84) did not receive the simulation training but would receive it prior to their next clinical practicum's.
RESULTS
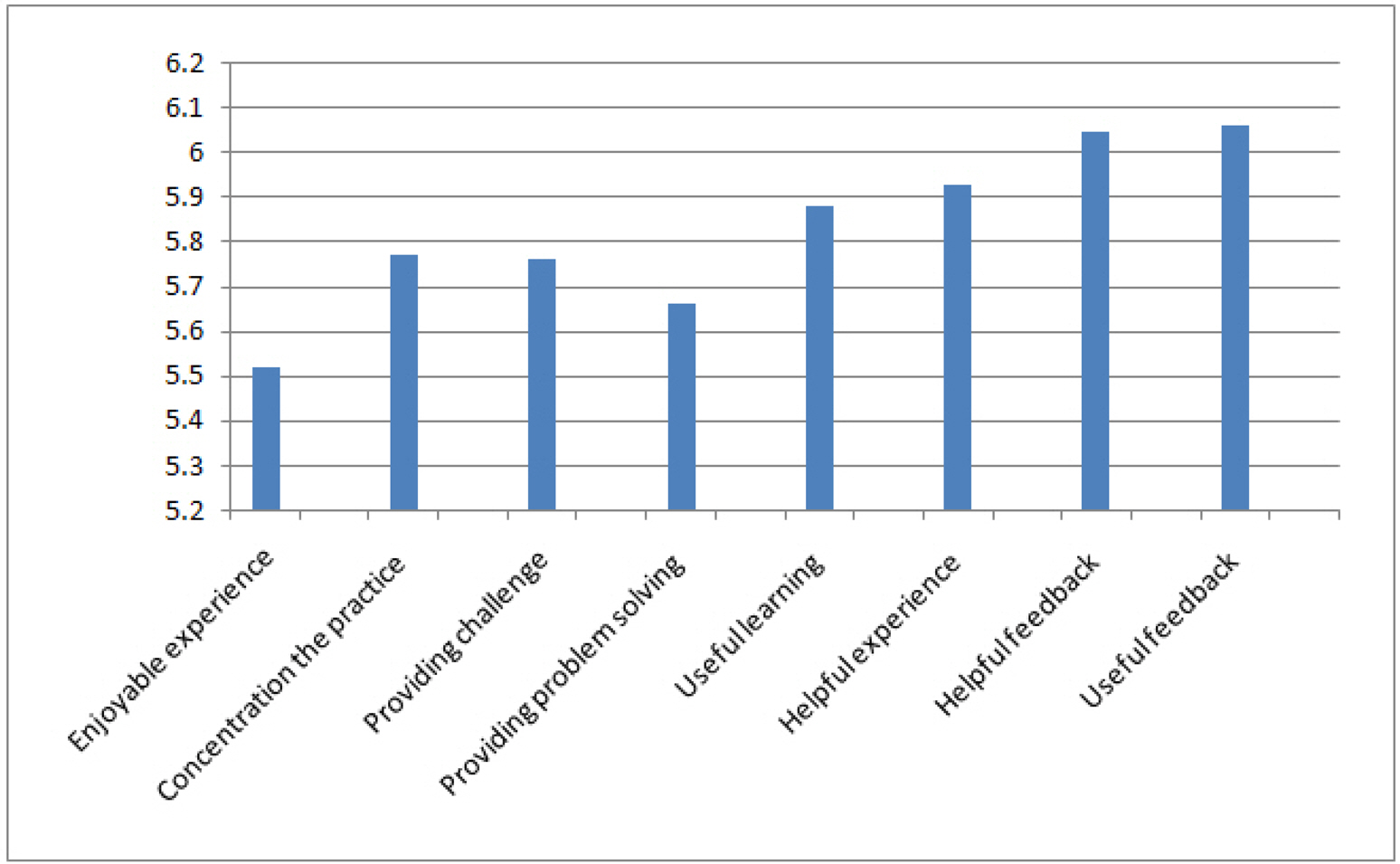
The treatment group showed a significantly higher performance ability and reported self confidence than that of the comparison group. The perceived helpfulness and contentment of the simulation training in experimental group was high.
CONCLUSION
The findings of this study demonstrated that simulation with a hybrid model was effective in teaching skills prior to the clinical experience which suggests that skill development is not dependent on the actual clinical situation. Nurse educators should consider simulation training as a tool beyond that of clinical practicum.
Figure
Reference
-
Ackermann A. D.2009. Investigation of learning outcomes for the acquisition and retention of CPR knowledge and skills learned with the use of high-fidelity simulation. Clinical Simulation in Nursing. 5(6):213–222. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ecns.2009.05.002.
ArticleAsghar A.2010. Reciprocal peer coaching and its use as a formative assessment strategy for first-year students. Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Education. 35(4):403–417. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/02602930902862834.
ArticleBlake K. D.., Gusella J.., Greaven S.., Wakefield S.2006. The risks and benefits of being a young female adolescent standardized patient. Medical Education. 40(1):26–35. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2929.2005.02343.x.Cho M. H.., Kwon I. S.2007. A study on the clinical practice experiences on nursing activities of nursing students. The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education. 13(2):143–154.Choi J. Y.., Jang K. S.., Choi S. H.., Hong M. S.2008. Validity and reliability of a clinical performance examination using standardized patients. The Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 38(1):83–91.
ArticleDreifuerst K. T.2009. The essentials of debriefing in simulation learning: A concept analysis. Nursing Education Perspectives. 30(2):109–114.Dreifuerst K. T.2012. Using debriefing for meaningful learning to foster development of clinical reasoning in simulation. The Journal of Nursing Education. 51(6):326–33. http://dx.doi.org/10.3928/01484834-20120409-02.
ArticleEom M. R.., Kim H. S.., Kim E. K.., Seong K.2010. Effects of teaching method using standardized patients on nursing competence in subcutaneous injection, self-directed learning readiness, and problem solving ability. The Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 40(2):151–160. http://dx.doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2010.40.2.151.
ArticleFeingold C. E.., Calaluce M.., Kallen M. A.2004. Computerized patient model and simulated clinical experiences: Evaluation with baccalaureate nursing students. The Journal of Nursing Education. 43(4):156–163.
ArticleHyun K. S.., Kang H. S.., Kim W. O.., Park S.., Lee J.., Sok S.2009. Development of a multimedia learning DM diet education program using standardized patients and analysis of its effects on clinical competency and learning satisfaction for nursing students. The Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 39(2):249–258. http://dx.doi.org/I:10.4040/jkan.2009.39.2.249.
ArticleJeffries P. R.2005. A framework for designing, implementing, and evaluating simulations used as teaching strategies in nursing. Nursing Education Perspectives. 26(2):96–103.Jeong Y. J.2005. Analysis of undergraduate clinical education based on a standard of clinical nursing education: Focusing on adult nursing. Unpublished doctoral dissertation, Inje University, Busan.Kaddoura M. A.2010. New graduate nurses' perceptions of the effects of clinical simulation on their critical thinking, learning, and confidence. Journal of Continuing Education in Nursing. 41(11):506–16. http://dx.doi.org/10.3928/00220124-20100701-02.Epub2010Jul6.
ArticleKaplan B. G.., Abraham C.., Gary R.2012. Effects of participation vs. observation of a simulation experience on testing outcomes: Implications for logistical planning for a school of nursing. International Journal of Nursing Education Scholarship. 9(1):article 14. http://dx.doi.org/0.1515/1548-923X.2398.
ArticleKim H. M.2009. The effect of the solution-focused communication training on the problem solving ability and interpersonal relationship of nursing students. Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing. 18(4):399–408.Kim J. H.., Lee Y. M.2006. A study on the educational conditions of medical simulation using the simulator manikin. The Journal of the Korean Society of Emergency Medical Technology. 10(2):15–23.Kim J. Y.., Choi E. Y.2008. Learning element recognition and academic achievement of nursing student receiving PBL with simulation education. The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Adult Nursing. 20(5):731–741.Kim M. J.2010. Symptom experience and health-related quality of life in adults with voiding dysfunction. Unpublished master's thesis, Yonsei University, Seoul.Kim U. H.., Kim J. M.., Kim Y. H.., Jeon Y. S.., Kim M. E.., Lee N. K., et al. 2003. The prevalence of overactive bladder syndrome and urinary incontinence in young and middle aged women. The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Wo-men's Health. 4(1):175–185.
ArticleKneebone R.., Bello F.., Nestel D.., Yadollahi F.., Darzi A.2007. Training and assessment of procedural skills in context using an Integrated Procedural Performance Instrument (IPPI). Studies in Health Technology and Informatics. 125:229–31.Lee S. E.2011. Evaluation of the Standardized Patients (SP) Managed instruction for a clinical maternity nursing course. The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education. 17(1):14–24.Lee S. J.., Roh Y. S.., Kim J. O.., Jang K. I.., Ryoo E. N.., Park Y. M.2010. Comparison of multi-mode simulation and simMan(R) simulation on evaluation of nursing care for patients with dyspnea. The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education. 16(1):51–60.McGaghie W. C.., Issenberg S. B.., Petrusa E. R.., Scalese R. J.2010. A critical review of simulation-based medical education research: 2003-2009. Medical Education. 44(1):50–63. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2923.2009.03547.x.
ArticleMelville J. L.., Walker E.., Katon W.., Lentz G.., Miller J.., Fen-ner D.2002. Prevalence of comorbid psychiatric illness and its impact on symptom perception, quality of life, and functional status in women with urinary incontinence. American Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology. 187(1):80–87. http://dx.doi.org/10.1067/mob.2002.124839.
ArticlePark H. K.2012. Medical education using standardized patients. Hanyang Medical Reviews. 32(1):35–44.
ArticleSchlegel C.., Woermann U.., Shaha M.., Rethans J. J.., van der Vleuten C.2012. Effects of a communication training on real practice performance: A role-play module versus a standardized patient module. The Journal of Nursing Education. 51(1):16–22. http://dx.doi.org/10.3928/01484834-20111116-02. Epub 2011 Nov 16.Seo Y. M.2012. Nursing students' needs for clinical nursing education. The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education. 18(1):25–33. http://dx.doi.org/10.5977/jkasne.2012.18.1.025.
ArticleShin K. A.., Lee E. S.2011. The effects of a communication training program on communication and interpersonal relationships of Nursing Students. The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education. 17(2):149–158.
ArticleWotton K.., Davis J.., Button D.., Kelton M.2010. Third-year undergraduate nursing students' perceptions of high-fidelity simulation. The Journal of Nursing Education. 49(11):632–639. http://dx.doi.org/10.3928/01484834-20100831-01. Epub 2010 Aug 31.
ArticleYoo M. S.., Yoo I. Y.2001. The effectiveness of standardized patient managed instruction for a fundamentals of nursing course. Journal of Nursing Query. 10(1):89–109.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Differences of Pre-Post Simulation Training on Problem solving, Performance confidence and Critical thinking Skill in Nursing Students according to Degree of Self-leadership
- The Effects of Team-based Simulation Education on Problem Solving Process, Communication Ability and Communication Confidence of Nursing Students
- Development and effect of hybrid simulation program for nursing students: focusing on a case of pediatric cardiac catheterization in Korea: quasi-experimental study
- Nursing Students' Experiences of Virtual and Hybrid Simulation in Gerontological Nursing: A Mixed-Methods Study
- Effects and Adequacy of High-Fidelity Simulation-Based Training for Obstetrical Nursing