Korean J Adult Nurs.
2014 Dec;26(6):703-711. 10.7475/kjan.2014.26.6.703.
Rearranging Everyday Lives among People with Type 2 Diabetes in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1College of Nursing, The Research Institute of Nursing Science, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Nursing, Chodang University, Muan, Korea.
- 3Department of Nursing, University of Ulsan, Ulsan, Korea. sonhm@mail.ulsan.ac.kr
- KMID: 2298160
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7475/kjan.2014.26.6.703
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The purpose of the study was to understand what are the experiences and management of type 2 diabetes in everyday lives among Korean people.
METHODS
A grounded theory method was utilized to explore how people with type 2 diabetes to experience and manage their disease under the Korean socio-cultural context. The data were collected via narrative in-depth interviews with 21 people with type 2 diabetes during 2010-2011 and all interviews were transcribed for verbatim analysis.
RESULTS
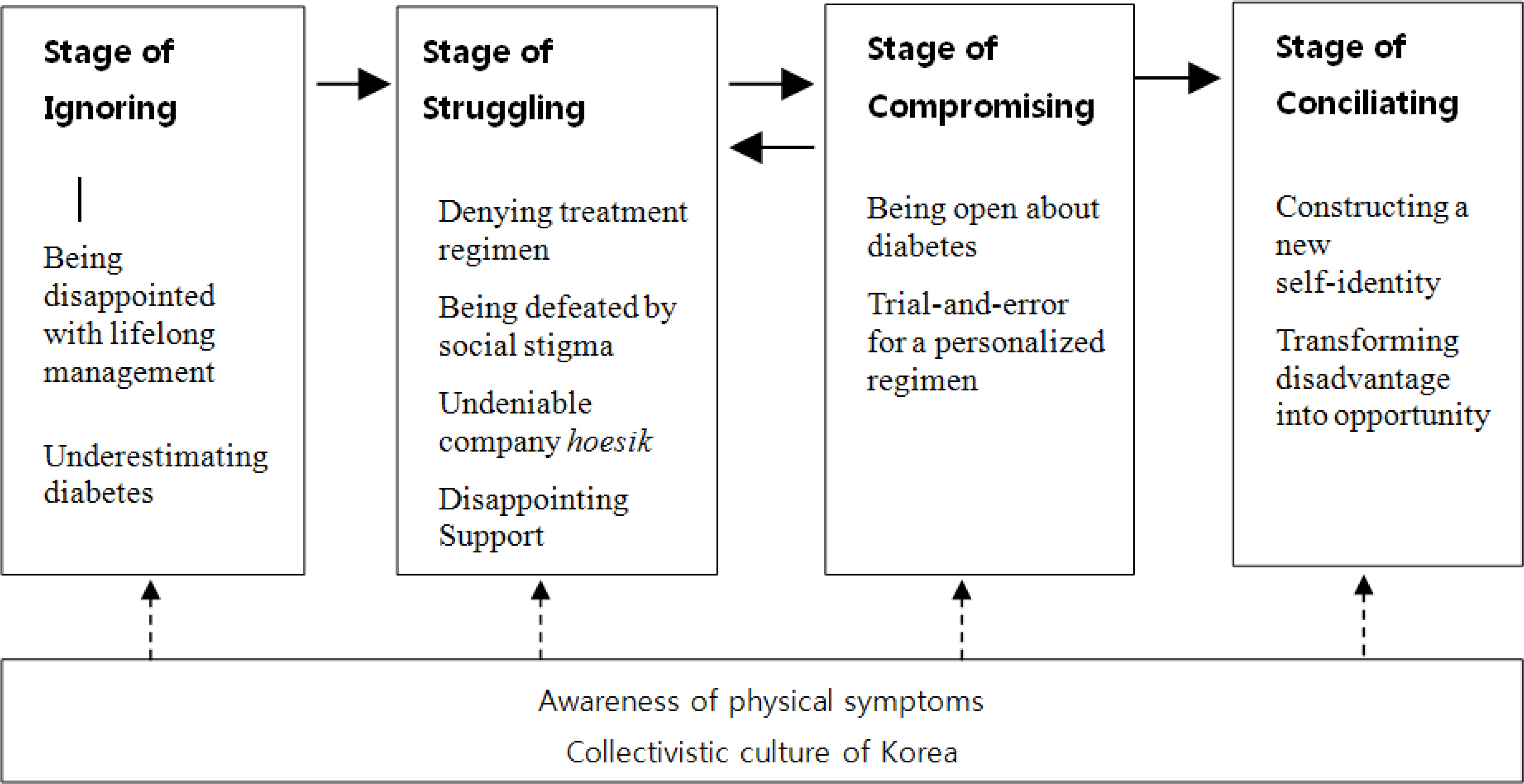
The core category was 'Rearranging everyday lives by accepting diabetes as lifelong annoying companion.' Four stages were identified: ignoring; struggling compromising and conciliating. Each stage illustrates major problems and/or strategies that the participants face in dealing with diabetes. The process illustrates the transference from their ordinary life, in which diabetes or health was ignored, to the health-oriented life, within which diabetes is integrated into their lives. The most difficult barriers they faced in everyday lives include social stigma of diabetes and collectivistic culture in Korea. Within the culture, the group goals are concerned over individual ones, making it harder for the participants to take care of their own health.
CONCLUSION
The findings of the study imply that health care professionals may consider the influence of social stigma in caring diabetic patients. Also, the intervention study is warranted to educate Korean people with diabetes to get aware of the sociocultural context and stigma as well as personal difficulties in self-caring diabetes.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
A Review of Qualitative Research in Korea: The Life Experiences of Diabetes Patients
Been Yoo
J Korean Diabetes. 2017;18(4):270-274. doi: 10.4093/jkd.2017.18.4.270.
Reference
-
1.World Health Organization. Media centre: diabetes fact sheet [Internet]. U.S.A: Author;2012. [cited 2014 April 10]. Available from:. http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs312/en/.2.Korean Diabetes Association/Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Diabetes fact sheet in Korea 2012 [Internet]. Seoul: Author;2013. [cited 2014 April 10]. Available from:. http://www.diabetes.or.kr/temp/Diabetes_Fact_sheet2012.pdf.3.Guidelines for diabetes mellitus. Lifestyle guidelines for type 2 diabetes. Seoul: Gold Agency;2008.4.Nelson KM., McFarland L., Reiber G. Factors influencing disease self-management among veterans with diabetes and poor glycemic control. Journal of General Internal Medicine. 2007. 22(4):442–7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11606-006-0053-8.
Article5.Egede LE., Ellis C. Diabetes and depression: global perspectives. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice. 2010. 87(3):302–12. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2010.01.024.
Article6.Brown JB., Harris SB., Webster-Bogaert S., Wetmore S., Faulds C., Stewart M. The role of patient, physician and systemic factors in the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Family Practice. 2002. 19(4):344–9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/fampra/19.4.344.
Article7.Norris SL., Lau J., Smith SJ., Schmid CH., Engelgau MM. Self-management education for adults with type 2 diabetes: ameta-analysis of the effect on glycemic control. Diabetes Care. 2002. 25(7):1159–71. http://dx.doi.org/10.2337/diacare.25.7.1159.8.Lujan J., Ostwald SK., Ortiz M. Promotora diabetes intervention for Mexican Americans. The Diabetes Educator. 2007. 33(4):660–70. http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/0145721707304080.
Article9.Vincent D., Pasvogel A., Barrera L. A feasibility study of a culturally tailored diabetes intervention for Mexican Americans. Biological Research for Nursing. 2007. 9(2):130–41. http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/1099800407304980.
Article10.Cherrington A., Ayala GX., Amick H., Allison J., Corbie-Smith G., Scarinci I. Implementing the community health worker model within diabetes management challenges and lessons learned from programs across the United States. The Diabetes Educator. 2008. 34(5):824–33. http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/0145721708323643.11.Russell S., Daly J., Hughes E. Nurses and ‘difficult'patients: negotiating non-compliance. Journal of Advanced Nursing. 2003. 43(3):281–7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2648.2003.02711.x.12.Abdoli S., Ashktorab T., Ahmadi F., Parvizi S., Dunning T. The empowerment process in people with diabetes: an Iranian perspective. International Nursing Review. 2008. 55(4):447–53. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1466-7657.2008.00664.x.
Article13.Ingadottir B., Halldorsdottir S. To discipline a "dog": the essential structure of mastering diabetes. Qualitative Health Research. 2008. 18(5):606–19. http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/1049732308316346.
Article14.Oyserman D., Coon HM., Kemmelmeier M. Rethinking individualism and collectivism: evaluation of theoretical assumptions and meta-analyses. Psychological Bulletin. 2002. 128(1):3–72. http://dx.doi.org/10.1037//0033-2909.128.1.3.
Article15.Yi M., Jezewski MA. Korean nurses'adjustment to hospitals in the United States of America. Journal of Advanced Nursing. 2000. 32(3):721–9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2648.2000.01533.x.16.Strauss A., Corbin J. Basics of qualitative research: techniques and procedures for developing grounded theory. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage;1998.17.Guba EG., Lincoln YS. Effective evaluation: improving the usefulness of evaluation results through responsive and naturalistic approaches. San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass;;1981.18.Mathison S. Why triangulate? Educational Researcher. 1988. 17(2):13–7.
Article19.de Alba Garcia JG., Rocha ALS., Lopez I., Baer RD., Dressler W., Weller SC. "Diabetes is my companion": lifestyle and self-management among good and poor control Mexican diabetic patients. Social Science & Medicine. 2007. 64(11):2223–35. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.socscimed.2007.02.001.
Article20.Moser A., Van Der Bruggen H., Spreeuwenberg C., Widdersho-ven G. Autonomy through identification: a qualitative study of the process of identification used by people with type 2 diabetes. Journal of Clinical Nursing. 2008. 17(7b):209–16. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2702.2007.01983.x.
Article21.Whittemore R., Chase SK., Mandle CL., Roy C. Lifestyle change in type 2 diabetes: a process model. Nursing Research. 2002. 51(1):18–25. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/00006199-200201000-00004.22.Whittemore R., Dixon J. Chronic illness: the process of integration. Journal of Clinical Nursing. 2008. 17(7b):177–87. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2702.2007.02244.x.
Article23.Kralik D. The quest for ordinariness: transition experienced by midlife women living with chronic illness. Journal of Advanced Nursing. 2002. 39(2):146–54. http://dx.doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2648.2000.02254.x.
Article24.Jarrett L. Living with chronic illness: a transitional model of coping. British Journal of Therapy and Rehabilitation. 2000. 7(1):40–4. http://dx.doi.org/10.12968/bjtr.2000.7.1.13913.
Article25.Manderson L., Kokanovic R. “Worried all the time”: distress and the circumstances of everyday life among immigrant Australians with type 2 diabetes. Chronic Illness. 2009. 5(1):21–32. http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/1742395309102243.
Article26.Lawton J., Peel E., Parry O., Araoz G., Douglas M. Lay perceptions of type 2 diabetes in Scotland: bringing health services back in. Social Science & Medicine. 2005. 60(7):1423–35. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.socscimed.2004.08.013.
Article27.Spenceley SM., Williams BA. Self-care from the perspective of people living with diabetes. Canadian Journal of Nursing Research. 2006. 38(3):124–45.28.Yamakawa M., Makimoto K. Positive experiences of type 2 diabetes in Japanese patients: an exploratory qualitative study. International Journal of Nursing Studies. 2008. 45(7):1032–41. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2007.05.003.
Article29.Davis R., Magilvy JK. Quiet pride: The experience of chronic illness by rural older adults. Journal of Nursing Scholarship. 2000. 32(4):385–90. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1547-5069.2000.00385.x.
Article30.Cagle CS., Appel S., Skelly AH., Carter-Edwards L. Mid-life African-American women with type 2 diabetes: influence on work and the multicaregiver role. Ethnicity and Disease. 2002. 12(4):555–66.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Reorganization of the Everyday Lives of Women with Lymphedema
- History of insulin treatment of pediatric patients with diabetes in Korea
- Dietary Habits of Diabetes Patients during the COVID-19 Pandemic
- Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Therapy: From Discovery to Type 2 Diabetes and Beyond
- Diabetes in People with Disabilities: a Call for Action