Korean Diabetes J.
2008 Feb;32(1):38-43. 10.4093/kdj.2008.32.1.38.
Mutation Screening of HNF-1alpha Gene in Korean Women with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Medicine, Cheil General Hospital & Women's Healthcare Center, Kwandong University College of Medicine, Korea.
- 2Department of Medicine, Kyung Hee University College of Medicine, Korea.
- 3Center for Genome Science, National Genome Research Institute, NIH, Korea.
- KMID: 2298108
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/kdj.2008.32.1.38
Abstract
-
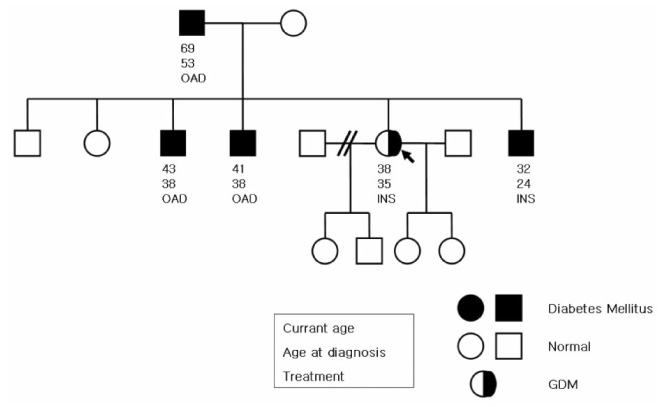
BACKGROUNDS: Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) is defined as glucose intolerance with onset or first detection during pregnancy and mostly caused by insulin resistance and beta-cell dysfunction like type 2 diabetes. However, autoimmune or monogenic diabetes can contribute to GDM. Maturity-onset diabetes of the young (MODY) is a monogenic form of diabetes characterized by an early age of onset and an autosomal dominant pattern of inheritance. Most MODY cases are attributable to mutations in HNF-1alpha gene, also known as MODY3. We investigated whether mutations in HNF-1alpha gene are present in Korean women with GDM.
METHODS
A total of 96 Korean women with GDM who have a family history of DM were screened for mutations in the HNF-1alpha gene. We evaluated the clinical characteristics of GDM women with HNF-1alpha gene mutations.
RESULTS
Five of 96 patients (5.2%) were found to have a mutation in HNF-1alpha gene. Four of those (-23C > G, 833G > A (Arg278Gln), 923C > T, IVS5 + 106A > G) were novel and one (-124G > C) in promoter region was reported in previous study. The mean age of GDM women with mutations of HNF-1alpha gene was 34 years. Four women with MODY3 gene mutations required insulin therapy during pregnancy. GDM women with MODY3 gene mutations appeared to be decreased insulin secretion (HOMA-%B) than those without mutations.
CONCLUSIONS
We have found the existence of MODY3 as well as novel HNF-1alpha gene mutations in Korean women with GDM.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. American Diabetes Association. Report of the expert committee on the diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 2002. 25:Suppl. 1. S5–S20.2. Damm P, Kuhl C, Buschard K, Jakobsen BK, Svejgaard A, Sodoyez-Goffaux F, Shattock M, Bottazzo GF, Mlsted-Pedersen L. Prevalence and predictive value of islet cell antibodies and insulin autoantibodies in women with gestational diabetes. Diabet Med. 1994. 11:558–563.3. Buchanan TA, Xiang AH. Gestational diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest. 2005. 115:485–491.4. Tattersall RB, Fajans SS. A difference between the inheritance of classical juvenile-onset and maturity-onset type diabetes of young people. Diabetes. 1975. 24:44–53.5. Yamagata K, Oda N, Kaisaki PJ, Menzel S, Furuta H, Vaxillaire M, Southam L, Cox RD, Lathrop GM, Boriraj VV, Chen X, Cox NJ, Oda Y, Yano H, Le Beau MM, Yamada S, Nishigori H, Takeda J, Fajans SS, Hattersley AT, Iwasaki N, Hansen T, Pedersen O, Polonsky KS, Bell GI, et al. Mutations in the hepatocyte nuclear factor-1alpha gene in maturity-onset diabetes of the young (MODY3). Nature. 1996. 384:455–458.6. Horikawa Y, Iwasaki N, Hara M, Furuta H, Hinokio Y, Cockburn BN, Lindner T, Yamagata K, Ogata M, Tomonaga O, Kuroki H, Kasahara T, Iwamoto Y, Bell GI. Mutation in hepatocyte nuclear factor-1β gene (TCF2) associated with MODY. Nat Genet. 1997. 17:384–385.7. Fajans SS, Bell GI, Polonsky KS. Molecular mechanisms and clinical pathophysiology of maturity-onset diabetes of the young. N Engl J Med. 2001. 345:971–980.8. Frayling TM, Evans JC, Bulman MP, Pearson E, Allen L, Owen K, Bingham C, Hannemann M, Shepherd M, Ellard S, Hattersley AT. Beta-cell genes and diabetes: molecular and clinical characterization of mutations in transcription factors. Diabetes. 2001. 50:Suppl. 1. S94–S100.9. Iwasaki N, Oda N, Ogata M, Hara M, Hinokio Y, Oda Y, Yamagata K, Kanematsu S, Ohgawara H, Omori Y, Bell GI. Mutations in the hepatocyte nuclear factor-1alpha/MODY3 gene in Japanese subjects with early- and late-onset NIDDM. Diabetes. 1997. 46:1504–1508.10. Weng J, Ekelund M, Lehto M, Li H, Ekberg G, Frid A, berg A, Groop LC, Berntrop K. Screening for MODY mutations, GAD antibodies, and type 1 diabetes-associated HLA genotypes in women with gestational diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 2002. 25:68–71.13. Lee HJ, Ahn CW, Kim SJ, Song YD, Lim SK, Kim KR, Lee HC, Huh KB. Mutation in hepatocyte nuclear factor-1α is not a common cause of MODY and early-onset type 2 diabetes in Korea. Acta Diabetol. 2001. 38:123–127.14. Yoshiuchi I, Yamagata K, Yang Q, Iwahashi H, Okita K, Yamamoto K, Oue T, Imagawa A, Hamaguchi T, Yamasaki T, Horikawa Y, Satoh T, Nakajima H, Miyazaki J, Higashiyama S, Miyagawa J, Namba M, Hanafusa T, Matsuzawa Y. Three new mutations in the hepatocyte nuclear factor-1 alpha gene in Japanese subjects with diabetes mellitus: clinical features and functional characterization. Diabetologia. 1999. 42:621–626.15. Stride A, Ellard S, Clark P, Shakespeare L, Salzmann M, Shepherd M, Hattersley AT. β-cell dysfunction, insulin sensitivity, and glycosuria precede diabetes in hepatocyte nuclear factor-1 mutation carriers. Diabetes Care. 2005. 28:1751–1756.16. Zouali H, Vaxillaire M, Lesage S, Sun F, Velho G, Vionnet N, Chiu K, Passa P, Permutt A, Demenais F, Cohen D, Beckman JS, Froguel P. Linkage analysis and molecular scanning of glucokinase gene in NIDDM families. Diabetes. 1993. 42:1238–1245.17. Saker PJ, Hattersley AT, Barrow B, Hammersley MS, McLellan JA, Lo Olds RJ, Gillmer MD, Holman RR, Turner RC. High prevalence of a missense mutation of the glucokinase gene gestational diabetic patients due to a founder-effect in a local population. Diabetologia. 1996. 39:1325–1328.18. Lehto M, Tuomi T, Mahtani MM, Widen E, Forsblom C, Sarelin L, Gullstrom M, Isomaa B, Lehtovirta M, Hyrkko A, Kanninen T, Orho M, Manley S, Turner RC, Brettin T, Kirby A, Thomas J, Duyk G, Lander E, Taskinen MR, Groop LC. Characterization of the MODY3 phenotype: early-onset diabetes caused by an insulin secretion defect. J Clin Invest. 1997. 99:582–590.19. Pearson ER, Starkey BJ, Powell RJ, Gribble FM, Clark PM, Hattersley AT. Genetic cause of hyperglycaemia and response to treatment in diabetes. Lancet. 2003. 362:1275–1281.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Polymorphism of the Hepatocyte Nuclear Factor-1alpha Gene in the Early-onset of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus with a Strong Family History in Korea
- The Prevalence of Maturity Onset Diabetes of the Young(MODY) 3 in Children with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Mutations in Hepatocyte Nuclear Factor-la in Early-Onset Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Korea
- Nutrition Care in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
- Diabetes in pregnancy