Korean Circ J.
2011 Oct;41(10):629-631. 10.4070/kcj.2011.41.10.629.
A Case of Postprandial Hypotension in the Intensive Care Unit Treated With Acarbose
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Medicine, Hanmaeum Hospital, Jeju, Korea. yumtong001@hanmail.net
- 2Department of Medicine, Cardiovascular Center, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2297926
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4070/kcj.2011.41.10.629
Abstract
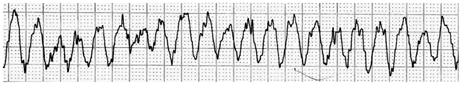
- Postprandial hypotension (PPH) has not been described as a cause of hypotension after the return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC) in the intensive care unit (ICU). A 74 year old man underwent cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) due to monomorphic ventricular tachycardia. After the ROSC, inotropic agents were not reduced but increased. PPH had occurred, according to the flow sheet, so a provocation test was performed. We noted hypotension but no serum hypoglycemia or tachycardia. The hypotension was diagnosed as PPH. We chose acarbose for treatment; thus, the inotropic agents were discontinued. This is the first case in which hypotension occurred in a patient recovering after CPR in the ICU and that the PPH was treated with acarbose. PPH should be considered and treated to manage hypotension in elderly patients in the ICU.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Neumar RW, Nolan JP, Adrie C, et al. Post-cardiac arrest syndrome: epidemiology, pathophysiology, treatment, and prognostication: a consensus statement from the International Liaison Committee on Resuscitation (American Heart Association, Australian and New Zealand Council on Resuscitation, European Resuscitation Council, Heart and Stroke Foundation of Canada, InterAmerican Heart Foundation, Resuscitation Council of Asia, and the Resuscitation Council of Southern Africa); the American Heart Association Emergency Cardiovascular Care Committee; the Council on Cardiovascular Surgery and Anesthesia; the Council on Cardiopulmonary, Perioperative, and Critical Care; the Council on Clinical Cardiology; and the Stroke Council. Circulation. 2008. 118:2452–2483.2. Reynolds HR, Hochman JS. Cardiogenic shock: current concepts and improving outcomes. Circulation. 2008. 117:686–697.3. Trzeciak S, Jones AE, Kilgannon JH, et al. Significance of arterial hypotension after resuscitation from cardiac arrest. Crit Care Med. 2009. 37:2895–2903. quiz 2904.4. Luciano GL, Brennan MJ, Rothberg MB. Postprandial hypotension. Am J Med. 2010. 123:281.5. O'Mara G, Lyons D. Postprandial hypotension. Clin Geriatr Med. 2002. 18:307–321.6. Shibao C, Gamboa A, Diedrich A, et al. Acarbose, an alpha-glucosidase inhibitor, attenuates postprandial hypotension in autonomic failure. Hypertension. 2007. 50:54–61.7. Jian ZJ, Zhou BY. Efficacy and safety of acarbose in the treatment of elderly patients with postprandial hypotension. Chin Med J (Engl). 2008. 121:2054–2059.8. Choi YR. Evaluation of in-hospital cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Korean Circ J. 1998. 28:1084–1090.9. Tack J, Arts J, Caenepeel P, De Wulf D, Bisschops R. Pathophysiology, diagnosis and management of postoperative dumping syndrome. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009. 6:583–590.10. Jansen RW, Lipsitz LA. Postprandial hypotension: epidemiology, pathophysiology, and clinical management. Ann Intern Med. 1995. 122:286–295.11. Yu SJ, Song MS, Kim HS. A Study on the prevalence and risk factors of postprandial hypotension among the community-dwelling aged. J Korean Acad Fundam Nurs. 2002. 9:434–446.12. Son JT, Lee E. Prevalence and risk factors of postprandial hypotension in Korean elderly people. J Korean Acad Nurs. 2009. 39:198–206.13. Fisher AA, Davis MW, Srikusalanukul W, Budge MM. Postprandial hypotension predicts all-cause mortality in older, low-level care residents. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2005. 53:1313–1320.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A case of postprandial hypotension presenting with postprandial dizziness
- The Effect of Acarbose as an Adjuvant Therapy in Sulfonylurea-Treated NIDDM Patients
- Postprandial Dizziness/Syncope Relieved by Alfa-Glucosidase Inhibitor: A Case Report
- Clinical applications of alpha2 adrenoceptor agonist
- Risk Factors for Cognitive Impairment in Intensive Care Unit Survivors