J Rhinol.
2015 May;22(1):44-46. 10.18787/jr.2015.22.1.44.
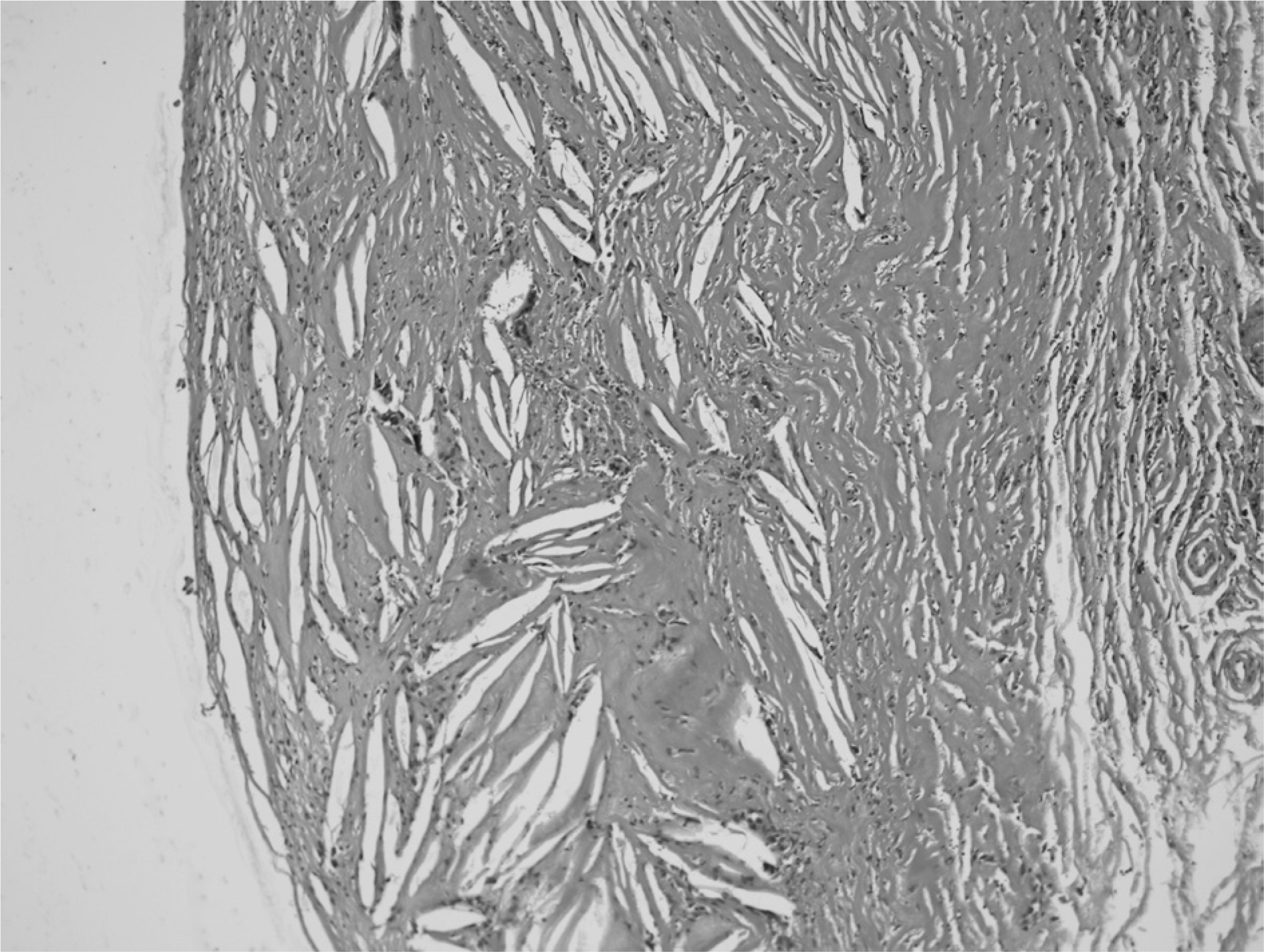
Cholesterol Granuloma of Nasal Septum
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Busan Saint Mary's Medical Center, Busan, Korea. koosookweon@naver.com
- 2Department of Pathology, Busan Saint Mary's Medical Center, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 2297554
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.18787/jr.2015.22.1.44
Abstract
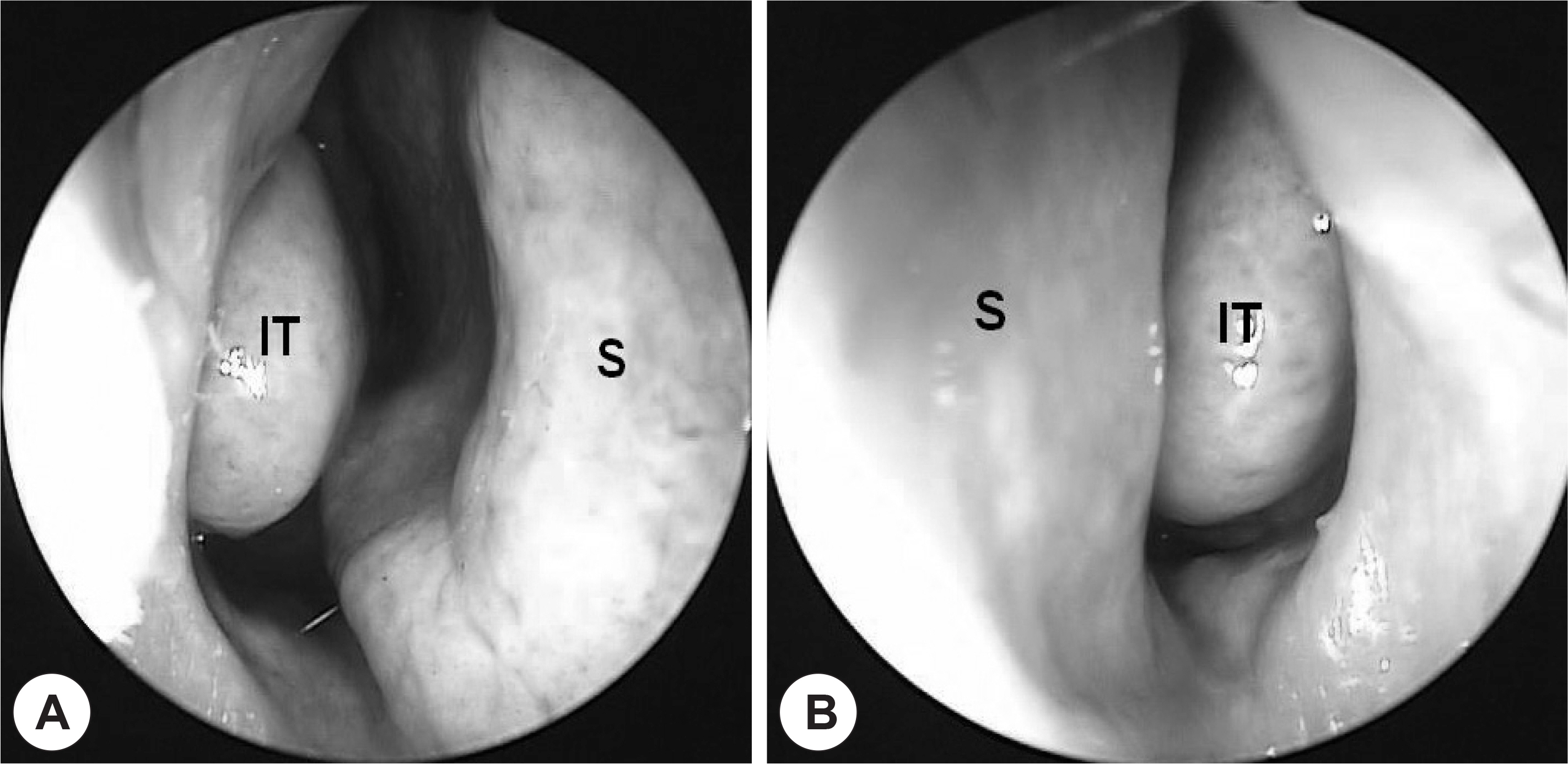
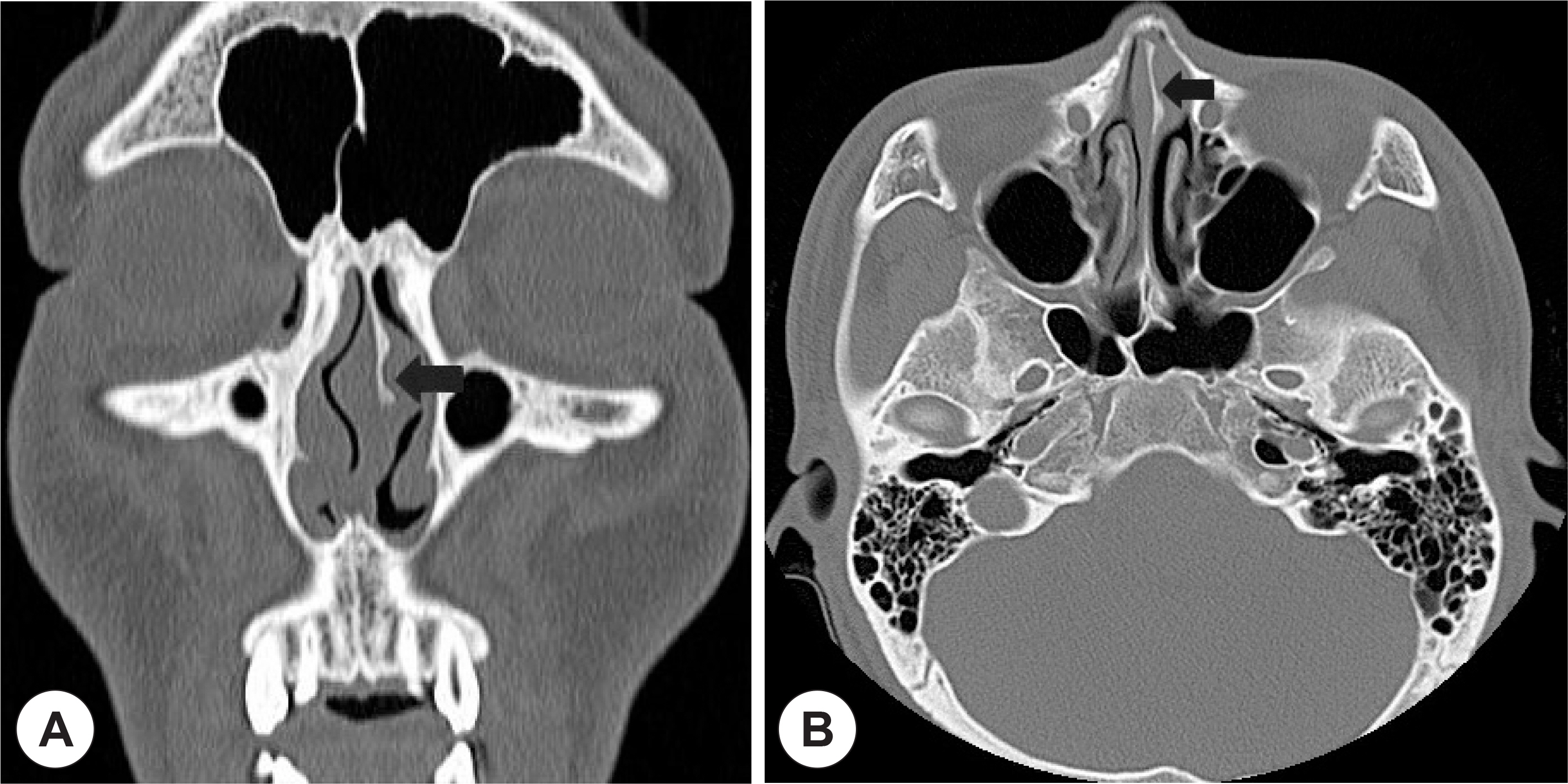
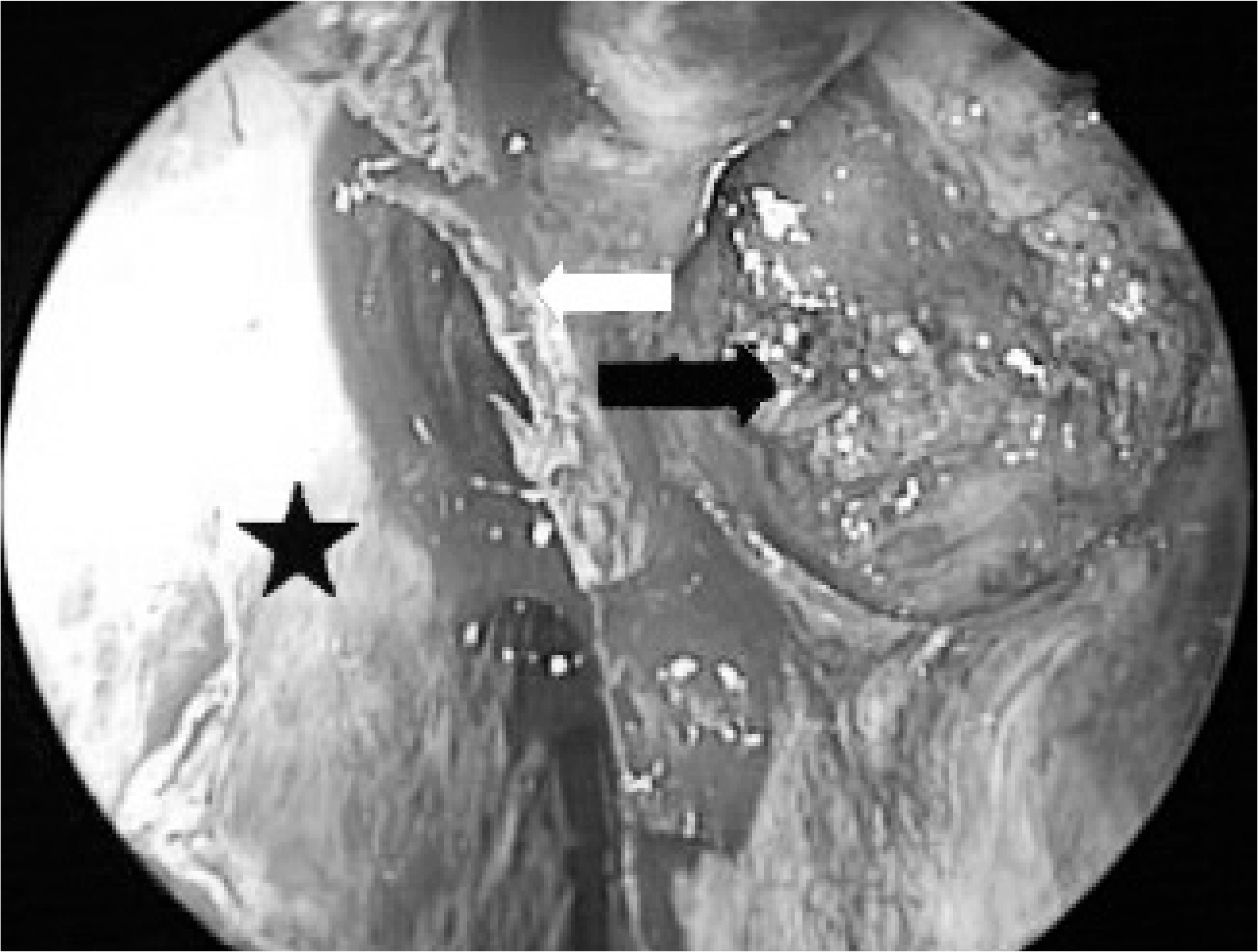
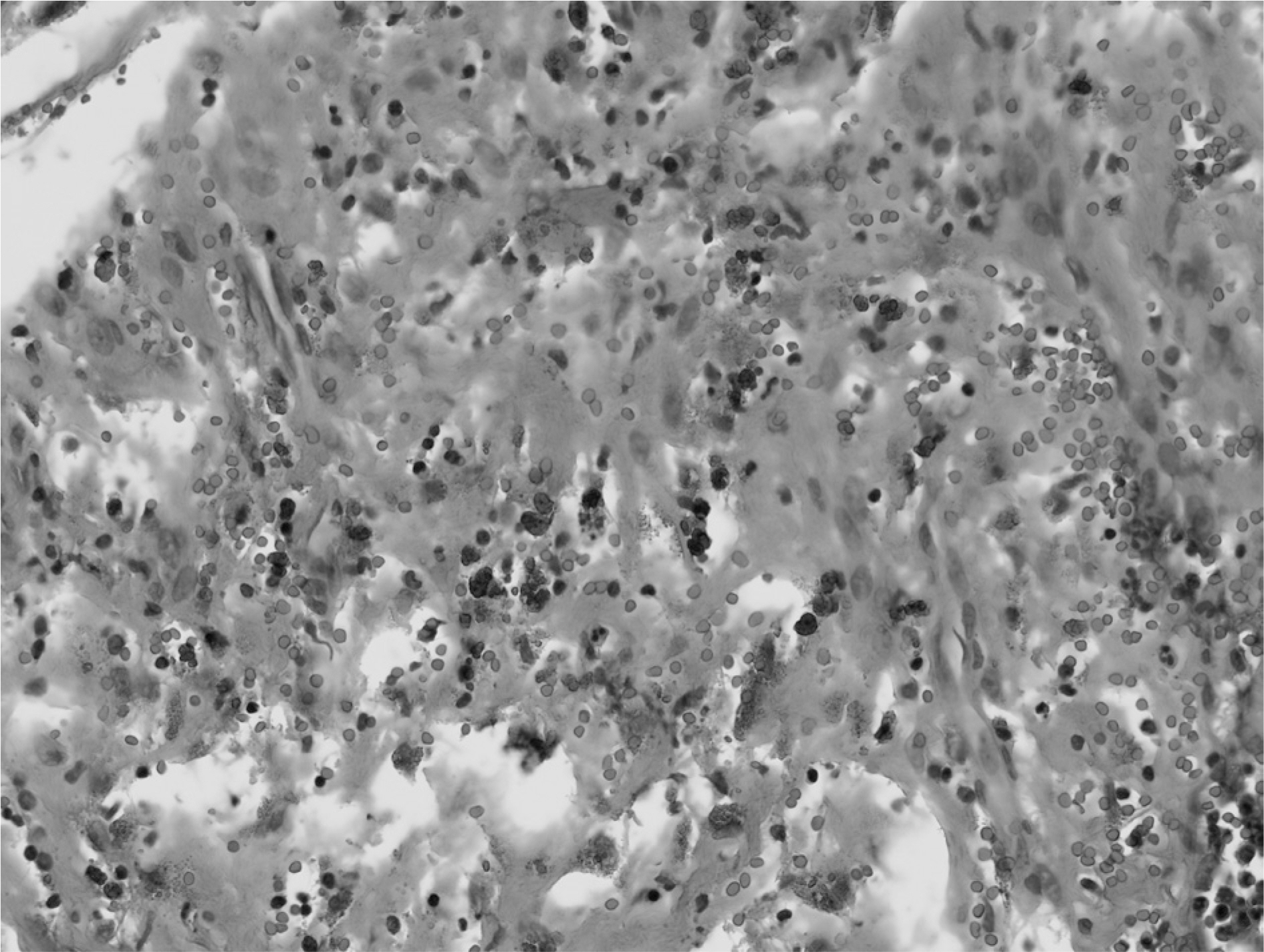
- Cholesterol granulomas are inflammatory deposits commonly found in the mastoid antrum and air cells of temporal bone. They rarely occur in the nose. Here, we report an extremely rare case of cholesterol granuloma in the nasal septum, and include a short literature review. The clinical characteristics, pathology, and surgical treatment are also discussed.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
A Case of Cholesterol Granuloma of Maxillary Sinus Misdiagnosed as Odontogenic Cyst
Byung Hyun Han, Ick Soo Choi
J Rhinol. 2018;25(2):108-113. doi: 10.18787/jr.2018.25.2.108.
Reference
-
References
1). Graham J, Michaels L. Cholesterol granuloma of the maxillary antrum. Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci. 1978; 3(2):155–60.
Article2). Kuperan AB, Gaffey MM, Langer PD, Mirani NM, Liu JK, Eloy JA. Nasoseptal cholesterol granuloma: a case report and review of pathogenesis. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2012; 138(1):83–6.3). 3) Jackler Rk1. Cho M. A new theory to explain the genesis of petrous apex cholesterol granuloma. Otol Neurotol. 2003; 24(1):96–106.4). Bella Z1. Torkos A, Tiszlavicz L, Iván L, Jóri J. Cholesterol granuloma of the maxillary sinus resembling an invasive, destructive tumor. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2005; 262(7):531–3.
Article5). Bütler S, Grossenbacher R. Cholesterol granuloma of the paranasal sinuses. J Laryngol Otol. 1989; 103(8):776–9.
Article6). Dilek FH, Kiriş M, Uğraş S. Cholesterol granuloma of the maxillary sinus. A case report. Rhinology. 1997; 35(3):140–1.7). Marks SC, Smith DM. Endoscopic treatment of maxillary sinus cholesterol granuloma. Laryngoscope. 1995; 105(5 Pt 1):551–2.
Article8). Milton CM, Bickerton RC. A review of maxillary sinus cholesterol granuloma. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1986; 24(4):293–9.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Cholesterol Granuloma in the Nasal Septum
- A Case of Cholesterol Granuloma in the Nasal Septum
- A Case of Inflammatory Pseudotumor Cerebri and Nasal Septum
- A Case of Giant Nasal Lobular Capillary Hemangioma During Pregnancy
- A Case of Cholesterol Granuloma of Maxillary Sinus Misdiagnosed as Odontogenic Cyst