Korean J Urol.
2006 Aug;47(8):852-858. 10.4111/kju.2006.47.8.852.
A Randomised, Double-Blind, Parallel, Placebo-Controlled Study of the Efficacy and Safety of Tadalafil Administered On-Demand to Men with Erectile Dysfunction in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Yongdong Severance Hospital, Seoul, Korea. ssclinic@yumc.yonsei.ac.kr
- 2Department of Urology, Korea University Ansan Hospital, Ansan, Korea.
- 3Department of Urology, Chungang University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Urology, Inha University Hospital, Incheon, Korea.
- 5Department of Urology, Kyungpook University Hospital, Daegu, Korea.
- 6Department of Urology, Kosin University Hospital, Busan, Korea.
- 7Department of Urology, Dong Seoul Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 8Department of Urology, Yeungnam University Hospital, Daegu, Korea.
- 9Department of Urology, Hanyang University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 10Department of Urology, Chonbuk National University Hospital, Jeonju, Korea.
- 11Lilly Research Laboratories, Eli Lilly and Company, Indianapolis, Indiana, USA.
- 12Lilly Area Medical Center, Vienna, Austria.
- KMID: 2294114
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4111/kju.2006.47.8.852
Abstract
-
PURPOSE: Tadalafil is a phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitor that is used for the treatment of erectile dysfunction (ED). Previous clinical trials have assessed its efficacy and safety in Western populations, but this drug has not been investigated in a large clinical trial involving Korean men with ED. Thus, the aim of this study was to assess the efficacy and safety of 20 mg tadalafil in comparison to placebo when it is taken on demand by Korean men suffering with ED over a study period of 12 weeks.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
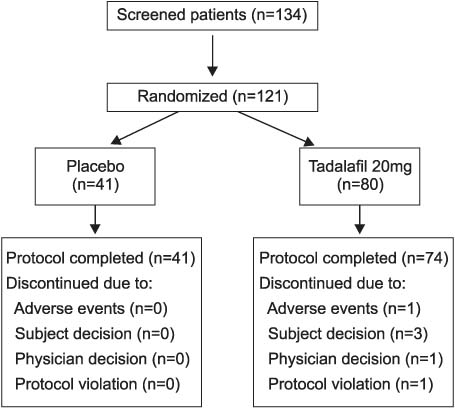
Men more than 18 years of age with mild to severe ED of various etiologies were randomized to receive placebo or tadalafil 20 mg that was taken as needed (maximum once daily). Efficacy assessments included the International Index of Erectile Function (IIEF), the Sexual Encounter Profile (SEP) diary and Global Assessment Questions (GAQ).
RESULTS
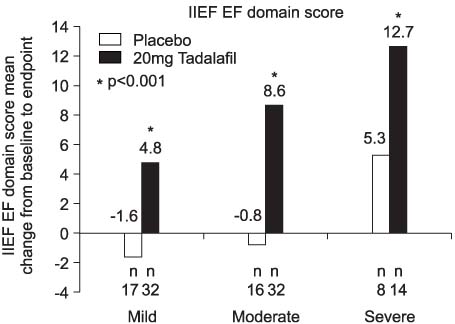
Tadalafil significantly improved erectile function, as measured by the erectile function domain of the IIEF, compared to placebo (p<0.001). At the endpoint, the patients receiving tadalafil 20mg reported a greater mean per-patient percentage of successful intercourse attempts (SEP3: 71% compared to 31% for placebo) and a greater proportion of improved erections (GAQ: 80% compared to 44%). The most common treatment emergent adverse events were headache (16.3%), flushing (5%) and eye pain (5%), and most of the adverse events were mild or moderate in severity.
CONCLUSIONS
Tadalafil was an effective, well-tolerated therapy for Korean men suffering with ED of broad-spectrum severity and etiology.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Korean Society for Sexual Medicine and Andrology (KSSMA) Guideline on Erectile Dysfunction
Ji Kan Ryu, Kang Su Cho, Su Jin Kim, Kyung Jin Oh, Sung Chul Kam, Kyung Keun Seo, Hong Seok Shin, Soo Woong Kim
World J Mens Health. 2013;31(2):83-102. doi: 10.5534/wjmh.2013.31.2.83.
Reference
-
1. Mc Kinlay JB. The worldwide prevalence and epidemiology of erectile dysfunction. Int J Impot Res. 2000. 12:S6–S11.2. Feldman HA, Goldstein I, Hatzichristou DG, Krane RJ, McKinlay JB. Impotence and its medical and psychosocial correlates: results of the Massachusetts Male Aging Study. J Urol. 1994. 151:54–61.3. Benet AE, Melman A. The epidemiology of erectile dysfunction. Urol Clin North Am. 1995. 22:699–709.4. NIH Consensus Conference. NIH consensus development panel on impotence. JAMA. 1993. 270:83–90.5. Rosen RC. Quality of life assessment in sexual dysfunction trials. Int J Impot Res. 1998. 10:Suppl 2. S21–S23.6. Meuleman EJ, Lycklama A, Nijeholt G, Slob K, Roeleveld X, Damen L, deBrazao GC, et al. Effects of IC351 on erectile response to visual stimulation. J Urol. 1999. 161:Suppl. 212.7. Juilfs DM, Soderling S, Burns F, Beavo JA. Cyclic GMP as substrate and regulator of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases (PDEs). Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1999. 135:67–104.8. Porst H, Padma-Nathan H, Giuliano F, Anglin G, Varanese L, Rosen R. Efficacy of tadalafil for the treatment of erectile dysfunction at 24 and 36 hours after dosing: a randomized controlled trial. Urology. 2003. 62:121–126.9. Carson CC, Rajfer J, Eardley I, Carrier S, Dennes JS, Walkers DJ, et al. The efficacy and safety of tadalafil: an update. BJU Int. 2004. 93:1276–1281.10. Rosen RC, Riley A, Wagner G, Osterloh IH, Kirkpatrick J, Mishra A. The International Index of Erectile Function (IIEF): a multidimensional scale for assessment of erectile dysfunction. Urology. 1997. 49:822–830.11. Cappelleri JC, Siegel RL, Osterloh IH, Rosen RC. Relationship between patient self-assessment of erectile function and the erectile function domain of the international index of erectile function. Urology. 2000. 56:477–481.12. Leung KF, Giroudet C. Cross-cultural adaptation of the International Index of Erectile Function (IIEF). Int J Impot Res. 1997. 9:Suppl 1. S47.13. Brock GB, McMahon CG, Chen KK, Costigan T, Shen W, Watkins V, et al. Efficacy and safety of tadalafil for the treatment of erectile dysfunction: results of integrated analysis. J Urol. 2002. 168:1332–1336.14. Chen KK, Jiann BP, Lin JS, Lee SS, Huang ST, Wang CJ, et al. Efficacy and safety of on-demand oral tadalafil in the treatment of men with erectile dysfunction in Taiwan: A randomized, double-blind, parallel, placebo-controlled clinical study. J Sex Med. 2004. 1:197–204.15. Chen KK, Hsieh JT, Huang ST, Jiaan DB, Lin JS, Wang CJ. ASSESS 3: a randomized, double-blind, flexible dose clinical trial of the efficacy and safety of oral sildenafil in the treatment of men with erectile dysfunction in Taiwan. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 2001. 13:221–229.16. Goldstein I, Lue TF, Padma-Nathan H, Rosen RC, Steers WD, Wicker PA. Oral sildenafil in the treatment of erectile dysfunction. N Engl J Med. 1998. 338:1397–1404.17. Choi HK, Ahn TY, Kim JJ, Kim SC, Paick JS, Suh JK, et al. A double-blind, randomised-placebo, controlled, parallel group, multicentre, flexible-dose escalation study to assess the efficacy and safety of sildenafil administered as required to male outpatients with erectile dysfunction in Korea. Int J Impot Res. 2003. 15:80–86.18. Sunwoo S, Kim YS, Cho BL, Cheon KS, Seo HG, Rho MK, et al. Post-marketing surveillance study of the safety and efficacy of sildenafil prescribed in primary care to erectile dysfunction patients. Int J Impot Res. 2005. 17:71–75.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Efficacy and Safety of Tadalafil 5 mg Once Daily in the Treatment of Erectile Dysfunction After Robot-Assisted Laparoscopic Radical Prostatectomy: 1-Year Follow-up
- Chronic Low Dosing of Phosphodiesterase Type 5 Inhibitor for Erectile Dysfunction
- Efficacy and Safety of Tadalafil 5 mg Administered Once Daily in Korean Men with Erectile Dysfunction: A Prospective, Multicenter Study
- Efficacy and Safety of a Herbal Formula that Mainly Consists of Cornus Officinalis for Erectile Dysfunction: A Double-blind, Placebo-controlled Study
- A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Double-Blind, Multi-Center Therapeutic Confirmatory Study to Evaluate the Safety and Efficacy of Avanafil in Korean Patients with Erectile Dysfunction