J Clin Neurol.
2008 Sep;4(3):107-110. 10.3988/jcn.2008.4.3.107.
Residual Dizziness after Successful Repositioning Treatment in Patients with Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, School of Medicine, Catholic University of Daegu, Daegu, Korea. jihelpgod@cu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2287673
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3988/jcn.2008.4.3.107
Abstract
-
BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV) is the most common form of vertigo. Although the repositioning maneuver dramatically improves the vertigo, some patients complain of residual dizziness. We evaluated the incidence and characteristics of persistent dizziness after successful particle repositioning and the clinical factors associated with the residual dizziness.
METHODS
We performed a prospective investigation in 49 consecutive patients with confirmed BPPV. The patients were treated with a repositioning maneuver appropriate for the type of BPPV. Success was defined by the resolution of nystagmus and positional vertigo. All patients were followed up until complete resolution of all dizziness, for a maximum of 3 months. We collected data on the characteristics and duration of any residual dizziness and analyzed the clinical factors associated with the residual dizziness.
RESULTS
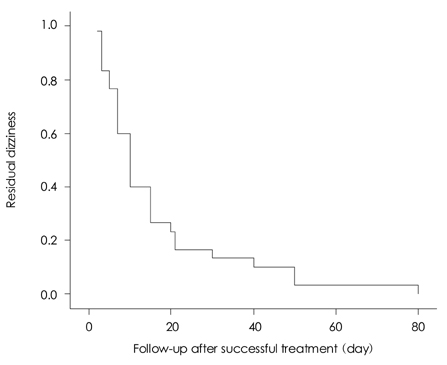
Of the 49 patients, 11 were men and 38 were women aged 60.4+/-13.0 years (mean +/-SD), and 30 (61%) of them complained of residual dizziness after successful repositioning treatment. There were two types of residual dizziness: continuous lightheadedness and short-lasting unsteadiness occurring during head movement, standing, or walking. The dizziness lasted for 16.4+/-17.6 days (range=2-80 days, median=10 days). A longer duration of BPPV before treatment was significantly associated with residual dizziness (p=0.04).
CONCLUSIONS
Residual dizziness after successful repositioning was observed in two-thirds of the patients with BPPV and disappeared within 3 months without specific treatment in all cases. The results indicate that early successful repositioning can reduce the incidence of residual dizziness.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo
Seung-Han Lee, Ji Soo Kim
J Clin Neurol. 2010;6(2):51-63. doi: 10.3988/jcn.2010.6.2.51.Vestibular Rehabilitation Therapy: Review of Indications, Mechanisms, and Key Exercises
Byung In Han, Hyun Seok Song, Ji Soo Kim
J Clin Neurol. 2011;7(4):184-196. doi: 10.3988/jcn.2011.7.4.184.Residual Dizziness after Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo
Munyoung Chang, Seog-Kyun Mun
Korean J Otorhinolaryngol-Head Neck Surg. 2020;63(10):443-447. doi: 10.3342/kjorl-hns.2020.00794.
Reference
-
1. Baloh RW, Honrubia V, Jacobson K. Benign positional vertigo: clinical and oculographic features in 240 cases. Neurology. 1987. 37:371–378.
Article2. Nedzelski JM, Barber HO, McIlmoyl L. Diagnoses in a dizziness unit. J Otolaryngol. 1986. 15:101–104.3. Dix MR, Hallpike CS. The pathology, symptomatology and diagnosis of certain common disorders of the vestibular system. Proc R Soc Med. 1952. 45:341–354.
Article4. Herdman SJ, Tusa RJ, Clendaniel RA. Fuchs AF, Brandt T, Buttner U, Zee D, editors. Eye movement signs in vertical canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Contemporary Ocular Motor and Vestibular Research: a Tribute to David A Robinson Stuttgart. 1994. Germany: Georg Thieme;385–387.5. Baloh RW, Jacobson K, Honrubia V. Horizontal semicircular canal variant of benign positional vertigo. Neurology. 1993. 43:2542–2549.
Article6. Lempert T, Tiel-Wilck K. A positional maneuver for treatment of horizontal-canal benign positional vertigo. Laryngoscope. 1996. 106:476–478.
Article7. Nuti D, Agus G, Barbieri MT, Passali D. The management of horizontal-canal paroxysmal positional vertigo. Acta Otolaryngol. 1998. 118:455–460.
Article8. Epley J. The canalith repositioning procedure for treatment of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1992. 107:399–404.
Article9. Herdman SJ. Advances in the treatment of vestibular disorders. Phys Ther. 1997. 77:602–618.
Article10. Di Girolamo S, Ottaviani F, Scarano E, Picciotti P, Di Nardo W. Postural control in horizontal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2000. 257:372–375.
Article11. von Brevern M, Schmidt T, Schönfeld U, Lempert T, Clarke AH. Utricular dysfuction in patients with benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Otol Neurotol. 2006. 27:92–96.
Article12. Gall RM, Ireland DJ, Robertson DD. Subjective visual vertical in patients with benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. J Otolaryngol. 1999. 28:162–165.13. Pollak L, Davies RA, Luxon LL. Effectiveness of the particle repositioning maneuver in benign paroxysmal positional vertigo with and without additional vestibular pathology. Otol Neurotol. 2002. 23:79–83.
Article14. Stambolieva K, Angov G. Postural stability in patients with different durations of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2006. 263:118–122.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Residual Dizziness after Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo
- Positional Dizziness and Vertigo without Nystagmus and Orthostatic Hypotension
- Clinical Study of Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo
- Conservative Management of Horizontal Canal Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo Resistant to Treatment
- Canal Conversion and Reentry of Otolith in Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo