Korean J Physiol Pharmacol.
2014 Apr;18(2):169-175. 10.4196/kjpp.2014.18.2.169.
Identification and Functional Characterization of Novel Genetic Variations in the OCTN1 Promoter
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pharmacology, Tissue Injury Defense Research Center, School of Medicine, Ewha Womans University, Seoul 158-710, Korea. jihachoi@ewha.ac.kr
- KMID: 2285507
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4196/kjpp.2014.18.2.169
Abstract
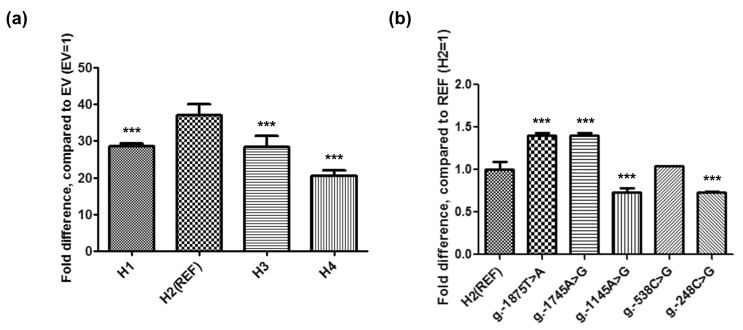
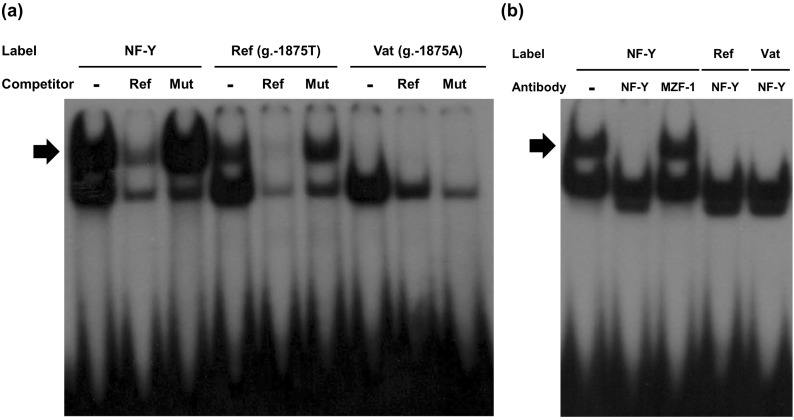
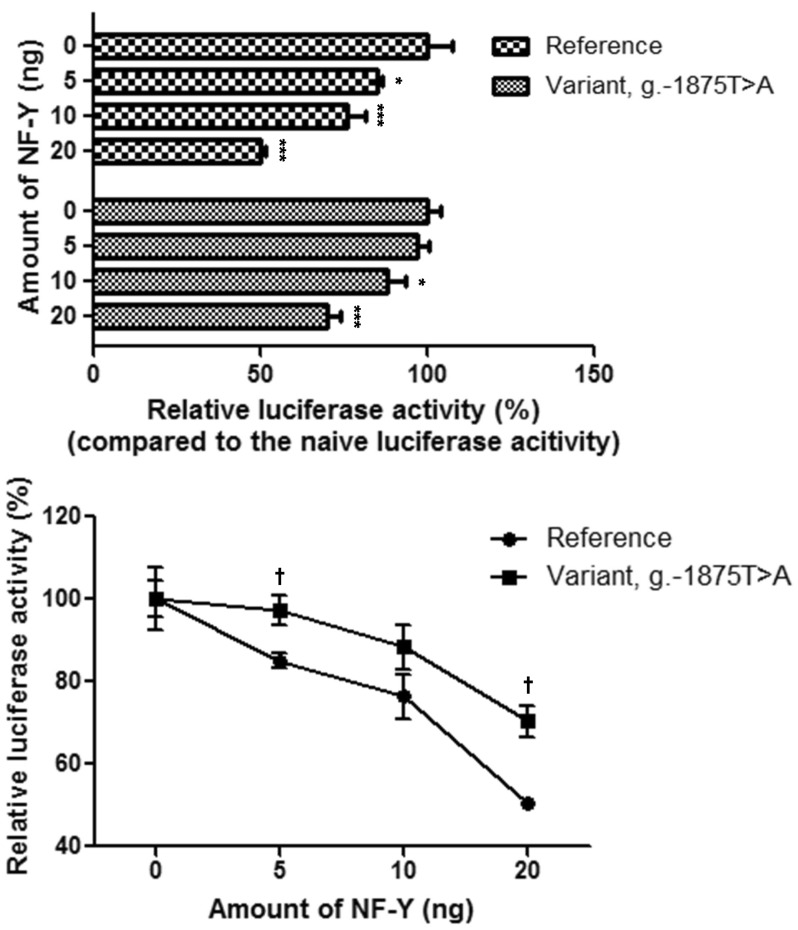
- Human organic cation/carnitine transporter 1 (OCTN1) plays an important role in the transport of drugs and endogenous substances. It is known that a missense variant of OCTN1 is significantly associated with Crohn's disease susceptibility. This study was performed to identify genetic variants of the OCTN1 promoter in Korean individuals and to determine their functional effects. First, the promoter region of OCTN1 was directly sequenced using genomic DNA samples from 48 healthy Koreans. OCTN1 promoter activity was then measured using a luciferase reporter assay in HCT-116 cells. Seven variants of the OCTN1 promoter were identified, two of which were novel. There were also four major OCTN1 promoter haplotypes. Three haplotypes (H1, H3, and H4) showed decreased transcriptional activity, which was reduced by 22.9%, 23.0%, and 44.6%, respectively (p<0.001), compared with the reference haplotype (H2). Transcription factor binding site analyses and gel shift assays revealed that NF-Y could bind to the region containing g.-1875T>A, a variant present in H3, and that the binding affinity of NF-Y was higher for the g.-1875T allele than for the g.-1875A allele. NF-Y could also repress OCTN1 transcription. These data suggest that three OCTN1 promoter haplotypes could regulate OCTN1 transcription. To our knowledge, this is the first study to identify functional variants of the OCTN1 promoter.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Tamai I, Yabuuchi H, Nezu J, Sai Y, Oku A, Shimane M, Tsuji A. Cloning and characterization of a novel human pH-dependent organic cation transporter, OCTN1. FEBS Lett. 1997; 419:107–111. PMID: 9426230.2. Yabuuchi H, Tamai I, Nezu J, Sakamoto K, Oku A, Shimane M, Sai Y, Tsuji A. Novel membrane transporter OCTN1 mediates multispecific, bidirectional, and pH-dependent transport of organic cations. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1999; 289:768–773. PMID: 10215651.3. Tokuhiro S, Yamada R, Chang X, Suzuki A, Kochi Y, Sawada T, Suzuki M, Nagasaki M, Ohtsuki M, Ono M, Furukawa H, Nagashima M, Yoshino S, Mabuchi A, Sekine A, Saito S, Takahashi A, Tsunoda T, Nakamura Y, Yamamoto K. An intronic SNP in a RUNX1 binding site of SLC22A4, encoding an organic cation transporter, is associated with rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Genet. 2003; 35:341–348. PMID: 14608356.
Article4. Nakamichi N, Taguchi T, Hosotani H, Wakayama T, Shimizu T, Sugiura T, Iseki S, Kato Y. Functional expression of carnitine/organic cation transporter OCTN1 in mouse brain neurons: possible involvement in neuronal differentiation. Neurochem Int. 2012; 61:1121–1132. PMID: 22944603.
Article5. Sugiura T, Kato S, Shimizu T, Wakayama T, Nakamichi N, Kubo Y, Iwata D, Suzuki K, Soga T, Asano M, Iseki S, Tamai I, Tsuji A, Kato Y. Functional expression of carnitine/organic cation transporter OCTN1/SLC22A4 in mouse small intestine and liver. Drug Metab Dispos. 2010; 38:1665–1672. PMID: 20601551.
Article6. Kawasaki Y, Kato Y, Sai Y, Tsuji A. Functional characterization of human organic cation transporter OCTN1 single nucleotide polymorphisms in the Japanese population. J Pharm Sci. 2004; 93:2920–2926. PMID: 15459889.
Article7. Gründemann D, Harlfinger S, Golz S, Geerts A, Lazar A, Berkels R, Jung N, Rubbert A, Schömig E. Discovery of the ergothioneine transporter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005; 102:5256–5261. PMID: 15795384.8. Peltekova VD, Wintle RF, Rubin LA, Amos CI, Huang Q, Gu X, Newman B, Van Oene M, Cescon D, Greenberg G, Griffiths AM, St George-Hyslop PH, Siminovitch KA. Functional variants of OCTN cation transporter genes are associated with Crohn disease. Nat Genet. 2004; 36:471–475. PMID: 15107849.
Article9. Noble CL, Nimmo ER, Drummond H, Ho GT, Tenesa A, Smith L, Anderson N, Arnott ID, Satsangi J. The contribution of OCTN1/2 variants within the IBD5 locus to disease susceptibility and severity in Crohn's disease. Gastroenterology. 2005; 129:1854–1864. PMID: 16344054.
Article10. Russell RK, Drummond HE, Nimmo ER, Anderson NH, Noble CL, Wilson DC, Gillett PM, McGrogan P, Hassan K, Weaver LT, Bisset WM, Mahdi G, Satsangi J. Analysis of the influence of OCTN1/2 variants within the IBD5 locus on disease susceptibility and growth indices in early onset inflammatory bowel disease. Gut. 2006; 55:1114–1123. PMID: 16469794.
Article11. Martínez A, Martín MC, Mendoza JL, Taxonera C, Díaz-Rubio M, de la Concha EG, Urcelay E. Association of the organic cation transporter OCTN genes with Crohn's disease in the Spanish population. Eur J Hum Genet. 2006; 14:222–226. PMID: 16333318.
Article12. Leung E, Hong J, Fraser AG, Merriman TR, Vishnu P, Krissansen GW. Polymorphisms in the organic cation transporter genes SLC22A4 and SLC22A5 and Crohn's disease in a New Zealand Caucasian cohort. Immunol Cell Biol. 2006; 84:233–236. PMID: 16519742.13. Lin Z, Nelson L, Franke A, Poritz L, Li TY, Wu R, Wang Y, MacNeill C, Thomas NJ, Schreiber S, Koltun WA. OCTN1 variant L503F is associated with familial and sporadic inflammatory bowel disease. J Crohns Colitis. 2010; 4:132–138. PMID: 21122496.
Article14. Xuan C, Zhang BB, Yang T, Deng KF, Li M, Tian RJ. Association between OCTN1/2 gene polymorphisms (1672C-T, 207G-C) and susceptibility of Crohn's disease: a meta-analysis. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2012; 27:11–19. PMID: 21706137.
Article15. Angelini S, Pantaleo MA, Ravegnini G, Zenesini C, Cavrini G, Nannini M, Fumagalli E, Palassini E, Saponara M, Di Battista M, Casali PG, Hrelia P, Cantelli-Forti G, Biasco G. Polymorphisms in OCTN1 and OCTN2 transporters genes are associated with prolonged time to progression in unresectable gastrointestinal stromal tumours treated with imatinib therapy. Pharmacol Res. 2013; 68:1–6. PMID: 23127916.
Article16. Urban TJ, Brown C, Castro RA, Shah N, Mercer R, Huang Y, Brett CM, Burchard EG, Giacomini KM. Effects of genetic variation in the novel organic cation transporter, OCTN1, on the renal clearance of gabapentin. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2008; 83:416–421. PMID: 17609685.
Article17. Nakamichi N, Shima H, Asano S, Ishimoto T, Sugiura T, Matsubara K, Kusuhara H, Sugiyama Y, Sai Y, Miyamoto K, Tsuji A, Kato Y. Involvement of carnitine/organic cation transporter OCTN1/SLC22A4 in gastrointestinal absorption of metformin. J Pharm Sci. 2013; 102:3407–3417. PMID: 23666872.
Article18. Tahara H, Yee SW, Urban TJ, Hesselson S, Castro RA, Kawamoto M, Stryke D, Johns SJ, Ferrin TE, Kwok PY, Giacomini KM. Functional genetic variation in the basal promoter of the organic cation/carnitine transporters OCTN1 (SLC22A4) and OCTN2 (SLC22A5). J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2009; 329:262–271. PMID: 19141711.
Article19. Maeda T, Hirayama M, Kobayashi D, Miyazawa K, Tamai I. Mechanism of the regulation of organic cation/carnitine transporter 1 (SLC22A4) by rheumatoid arthritis-associated transcriptional factor RUNX1 and inflammatory cytokines. Drug Metab Dispos. 2007; 35:394–401. PMID: 17142562.
Article20. Jang GH, Kim TH, Choe Y, Ham A, Choi JH. Functional characterization of genetic variations in the MDR3 promoter. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013; 430:1312–1318. PMID: 23261441.
Article21. Yoo YK, Ke X, Hong S, Jang HY, Park K, Kim S, Ahn T, Lee YD, Song O, Rho NY, Lee MS, Lee YS, Kim J, Kim YJ, Yang JM, Song K, Kimm K, Weir B, Cardon LR, Lee JE, Hwang JJ. Fine-scale map of encyclopedia of DNA elements regions in the Korean population. Genetics. 2006; 174:491–497. PMID: 16702437.
Article22. Inoue T, Kamiyama J, Sakai T. Sp1 and NF-Y synergistically mediate the effect of vitamin D(3) in the p27(Kip1) gene promoter that lacks vitamin D response elements. J Biol Chem. 1999; 274:32309–32317. PMID: 10542271.
Article23. Lützner N, De-Castro Arce J, Rösl F. Gene expression of the tumour suppressor LKB1 is mediated by Sp1, NF-Y and FOXO transcription factors. PLoS One. 2012; 7:e32590. PMID: 22412893.
Article24. Bungartz G, Land H, Scadden DT, Emerson SG. NF-Y is necessary for hematopoietic stem cell proliferation and survival. Blood. 2012; 119:1380–1389. PMID: 22072554.
Article25. Bernadt CT, Nowling T, Wiebe MS, Rizzino A. NF-Y behaves as a bifunctional transcription factor that can stimulate or repress the FGF-4 promoter in an enhancer-dependent manner. Gene Expr. 2005; 12:193–212. PMID: 16128003.26. Ceribelli M, Dolfini D, Merico D, Gatta R, Viganò AM, Pavesi G, Mantovani R. The histone-like NF-Y is a bifunctional transcription factor. Mol Cell Biol. 2008; 28:2047–2058. PMID: 18212061.
Article27. Newman B, Wintle RF, van Oene M, Yazdanpanah M, Owen J, Johnson B, Gu X, Amos CI, Keystone E, Rubin LA, Siminovitch KA. SLC22A4 polymorphisms implicated in rheumatoid arthritis and Crohn's disease are not associated with rheumatoid arthritis in a Canadian Caucasian population. Arthritis Rheum. 2005; 52:425–429. PMID: 15693005.
Article28. Barton A, Eyre S, Bowes J, Ho P, John S, Worthington J. Investigation of the SLC22A4 gene (associated with rheumatoid arthritis in a Japanese population) in a United Kingdom population of rheumatoid arthritis patients. Arthritis Rheum. 2005; 52:752–758. PMID: 15751072.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Association study between OCTN1 functional haplotypes and Crohn's disease in a Korean population
- Identification of Novel Genetic Variations in the Proximal Promoter of the Human Transporter, OCT2
- Identification and Functional Characterization of ST3GAL5 and ST8SIA1 Variants in Patients with Thyroid-Associated Ophthalmopathy
- Early growth response protein 1 acts as an activator of SOX18 promoter
- Functional Haplotype Frequencies of the Interleukin-1B Promoter in the Korean Population