Korean J Physiol Pharmacol.
2010 Jun;14(3):191-198. 10.4196/kjpp.2010.14.3.191.
The Effects of Tramadol on Electroencephalographic Spectral Parameters and Analgesia in Rats
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pharmacology, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu 700-422, Korea. mglee@knu.ac.kr
- 2Brain Science and Engineering Institute, Kyungpook National University, Daegu 700-422, Korea.
- 3Department of Pharmacology, School of Dentistry, Kyungpook National University, Daegu 700-422, Korea.
- KMID: 2285402
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4196/kjpp.2010.14.3.191
Abstract
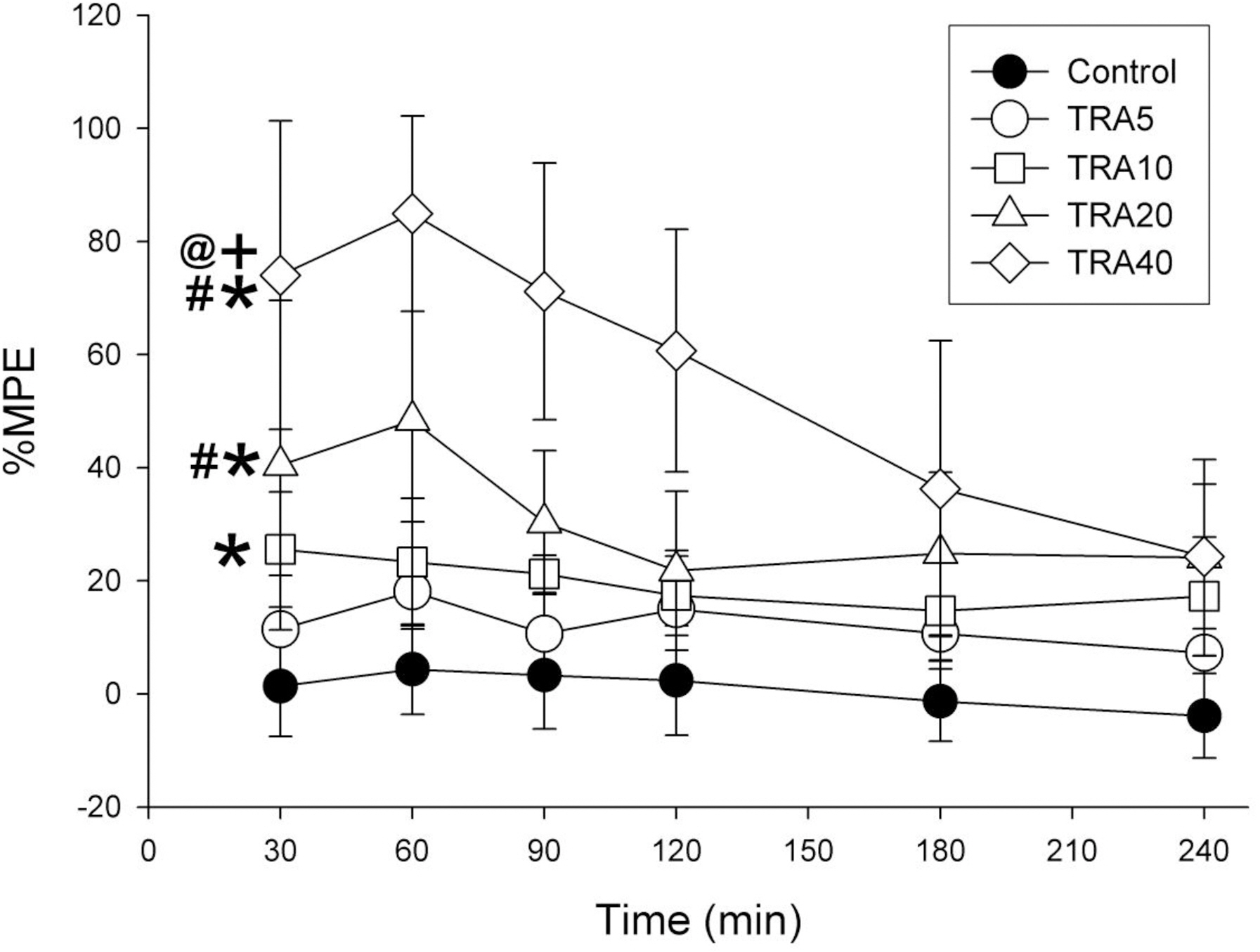
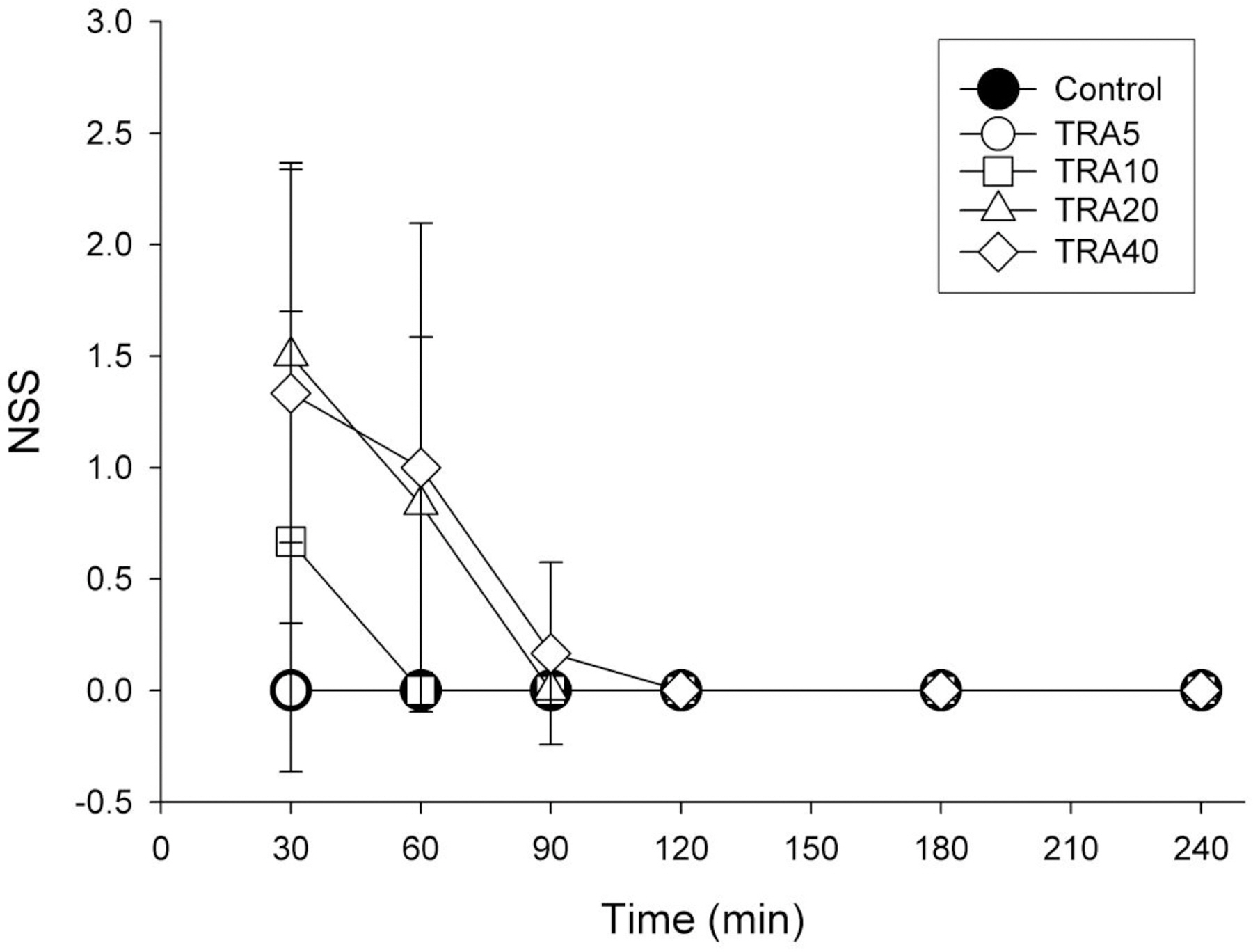
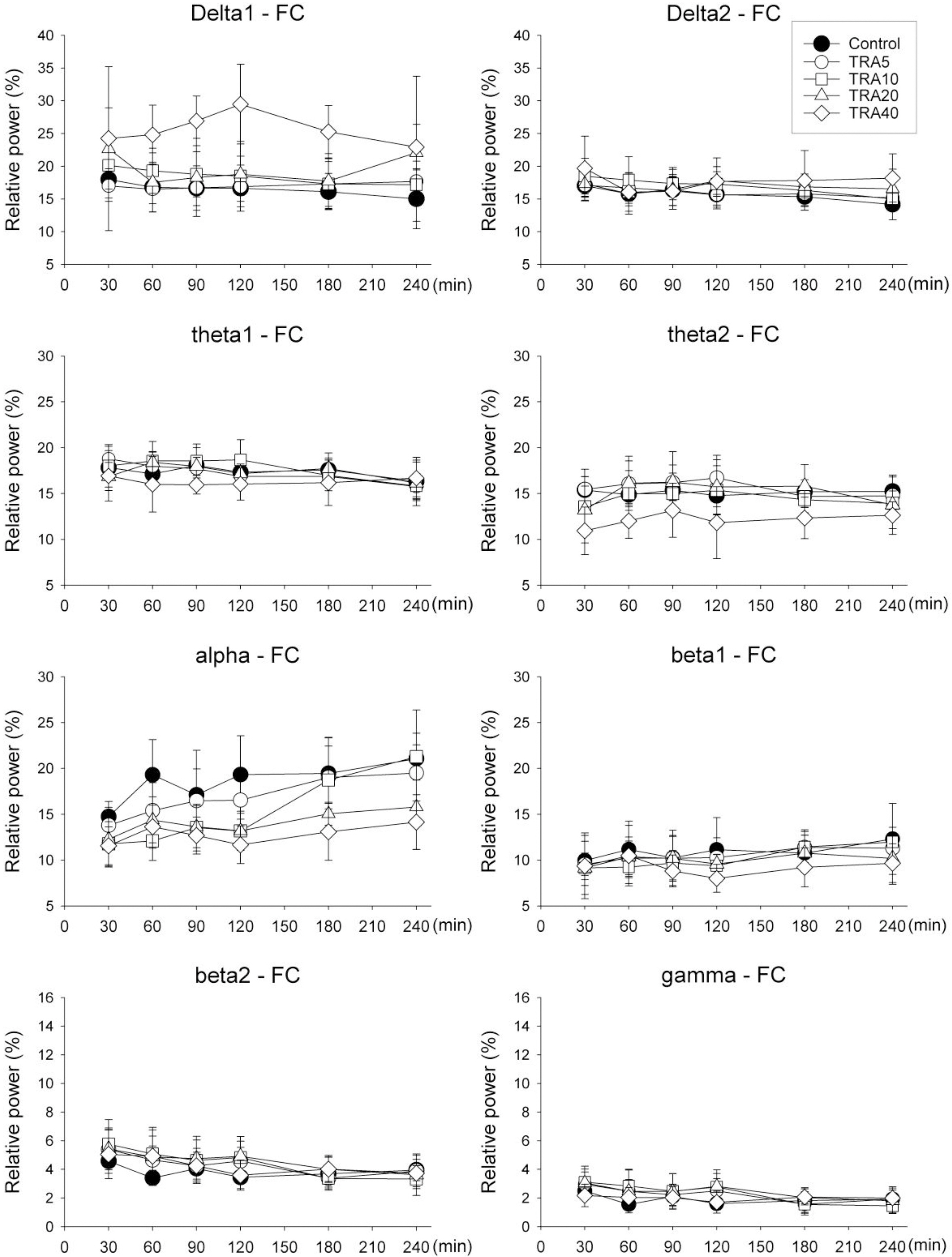
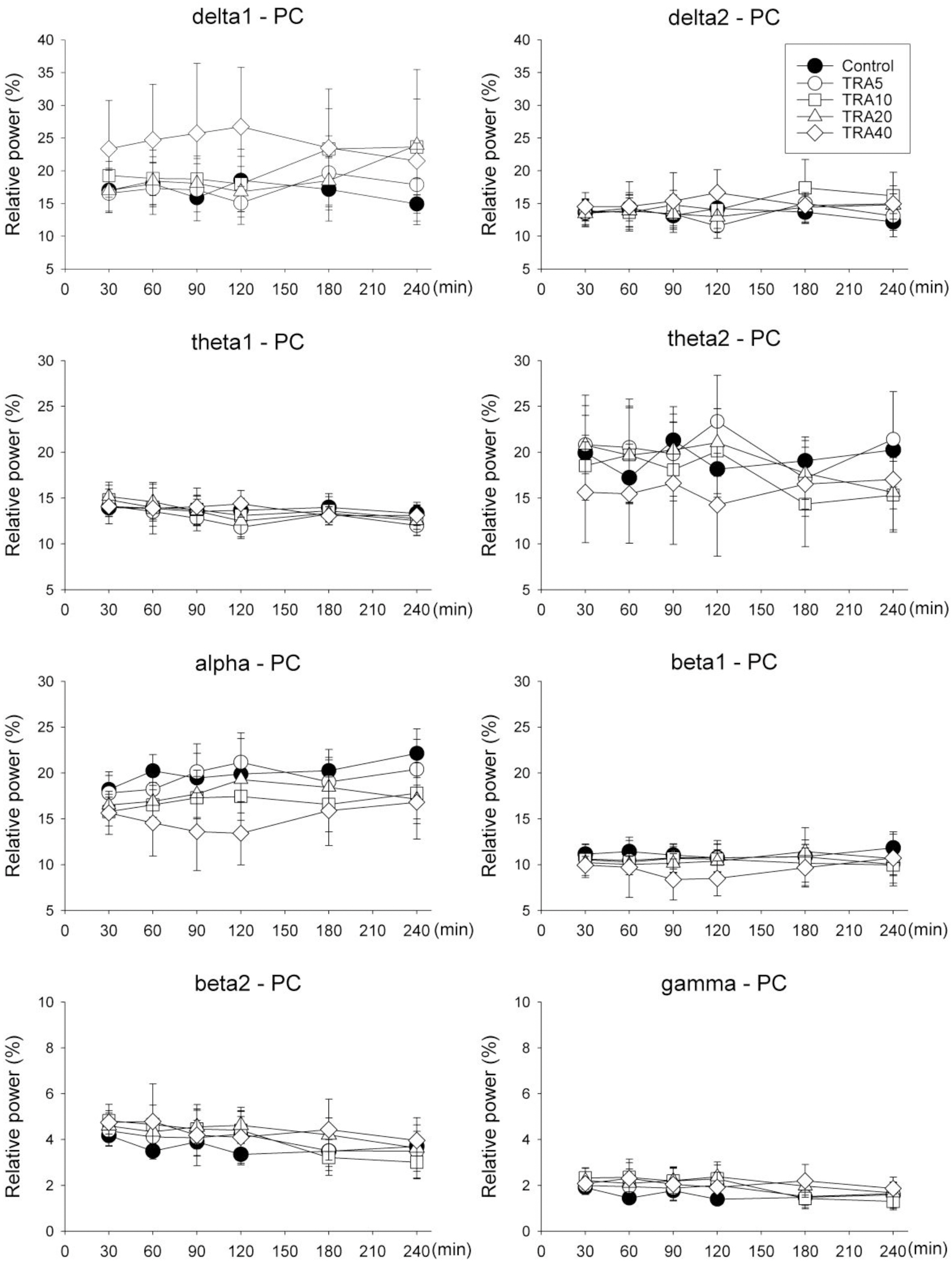
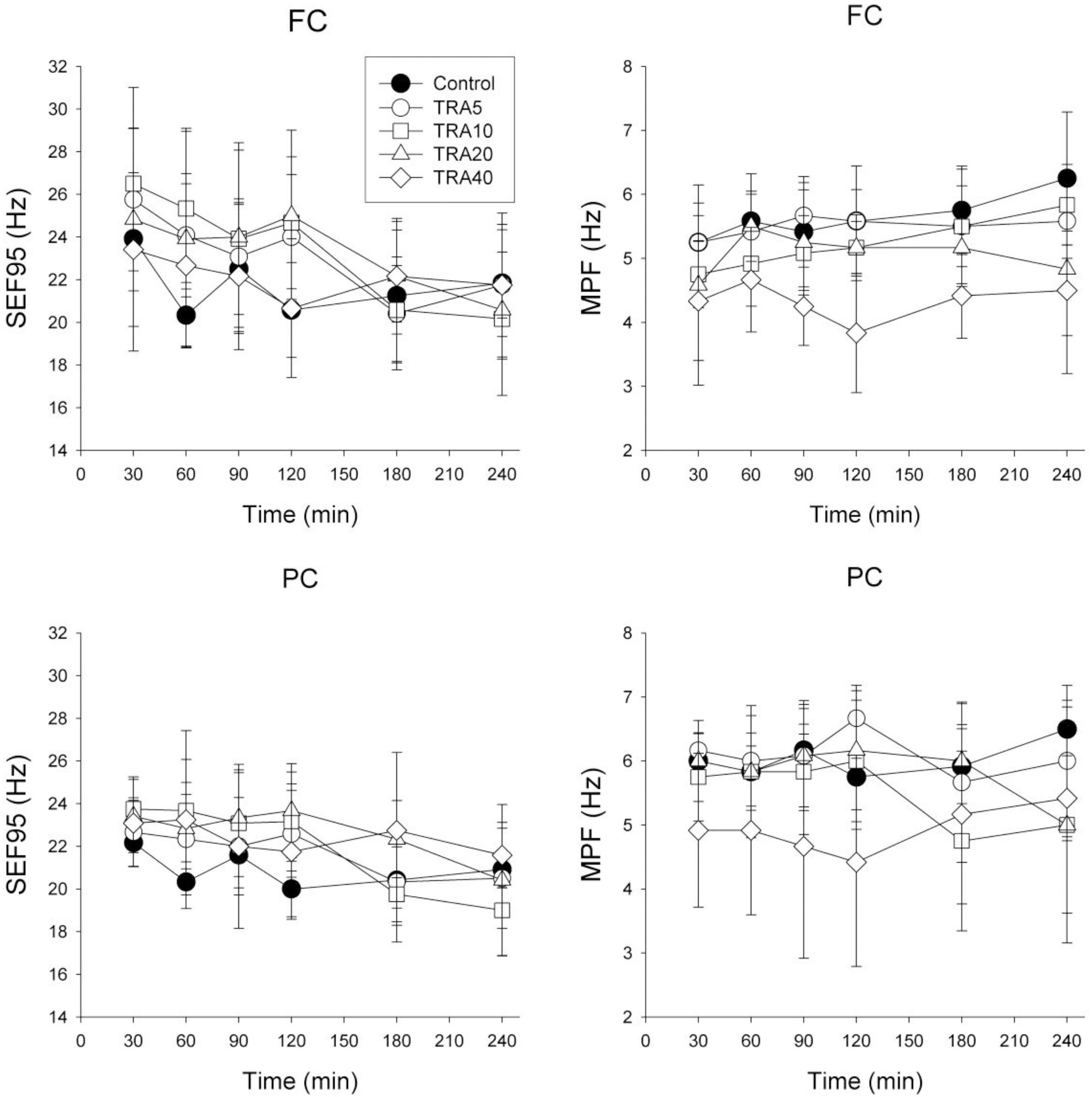
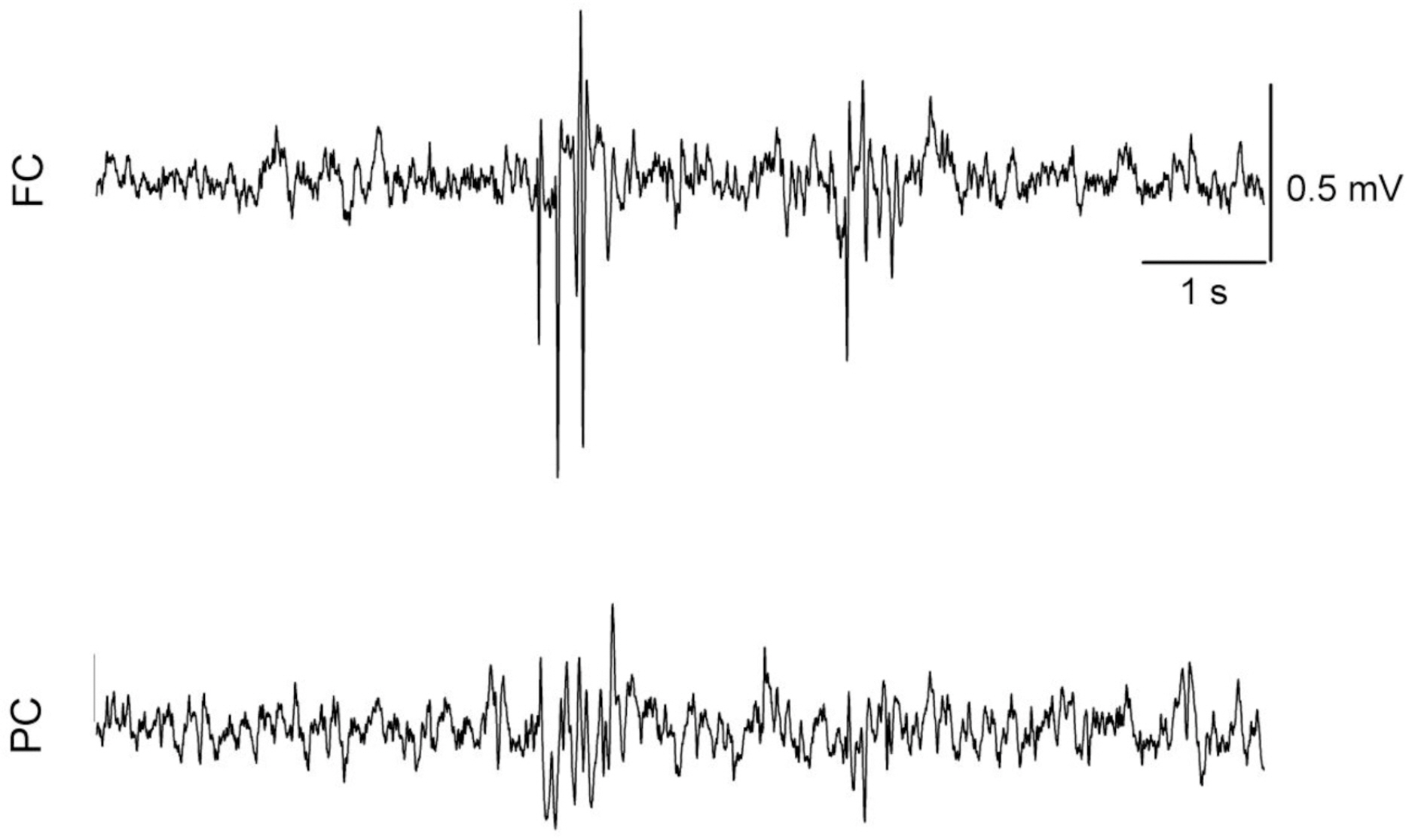
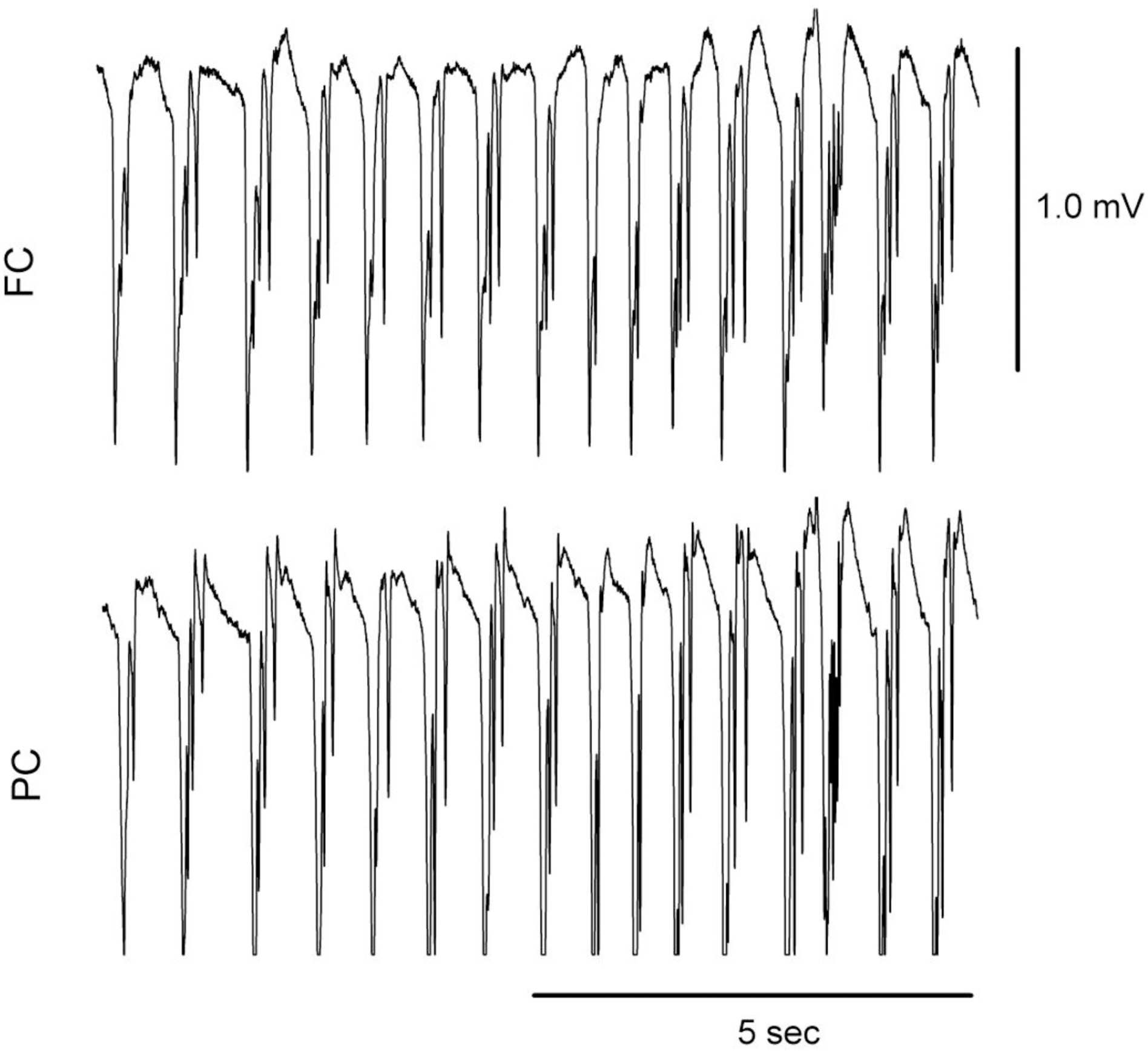
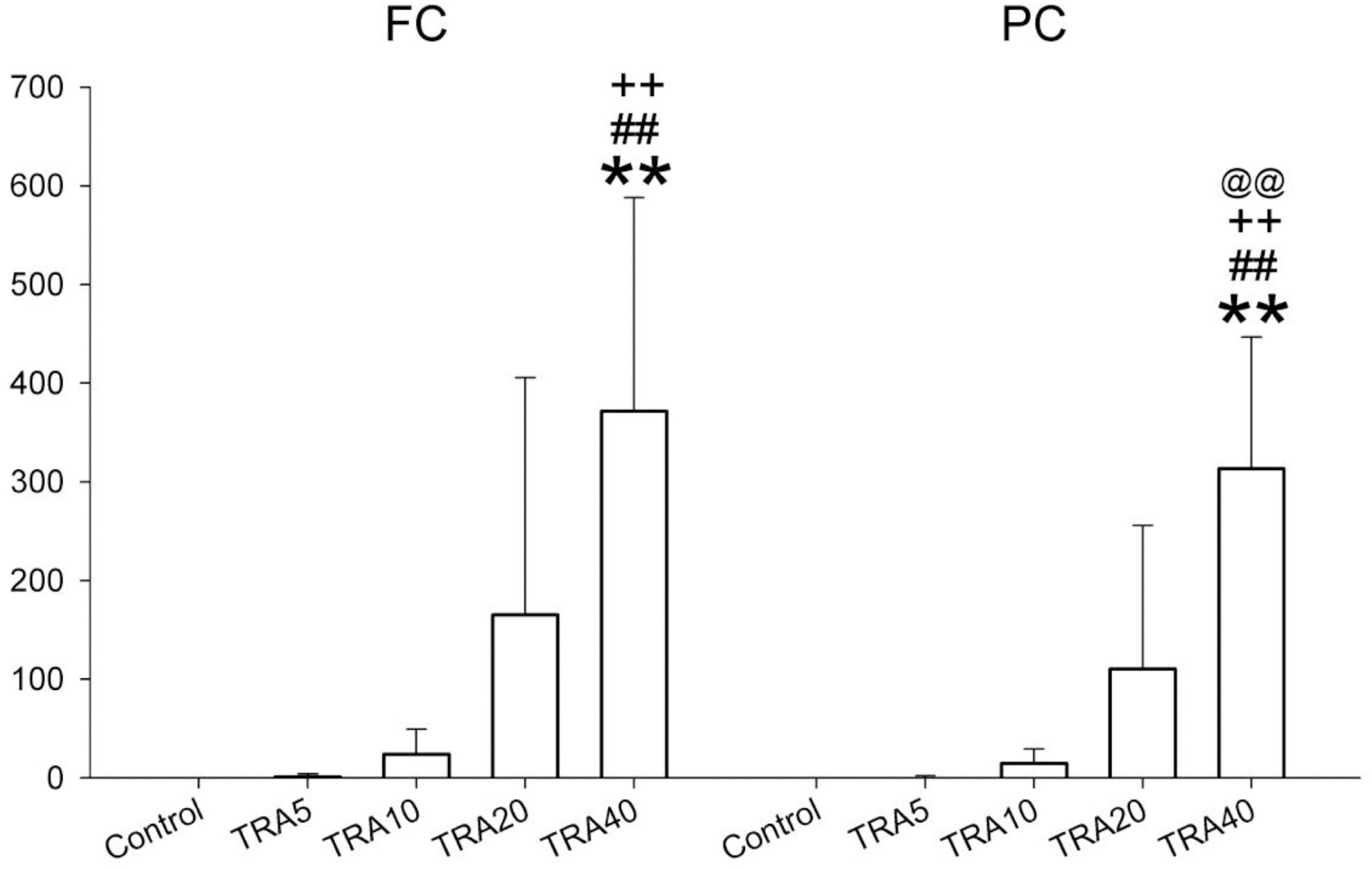
- The effects of different doses of tramadol on analgesia and electroencephalographic (EEG) spectral parameters were compared in rats. Saline or tramadol 5, 10, 20 or 40 mg/kg was administered. The degree of analgesia was evaluated by tail-flick latency, and the degree of seizure was measured using numerical seizure score (NSS). Additionally, band powers, median power frequency and spectral edge frequency 95 were measured to quantify the EEG response. All doses of tramadol produced spike-wave discharge. Tramadol significantly and dose-dependently increased the analgesia, but these effects did not correspond with the changes in the EEG spectral parameters. NSS significantly increased in the Tramadol 20 and 40 mg/kg treatment groups compared to the Control and TRA5 groups, and two rats given 40 mg/kg had convulsions. In conclusion, tramadol dose-dependently increased the analgesic effect, and the 10 mg/kg dose appears to be a reliable clinical dose for analgesia in rats, but dose-dependent increases in analgesia and seizure severity did not correlate with EEG spectral parameters.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Xie H, Dong ZQ, Ma F, Bauer WR, Wang X, Wu GC. Involvement of serotonin 2A receptors in the analgesic effect of tramadol in mono-arthritic rats. Brain Res. 2008; 1210:76–83.
Article2. Giorgi M, Del Carlo S, Saccomanni G, Lebkowska-Wieruszewska B, Turini V, Kowalski C. Biopharmaceutical profile of tramadol in the dog. Vet Res Commun. 2009; 33 Suppl. 1:189–192.
Article3. Poulsen L, Arendt-Nielsen L, Brosen K, Sindrup SH. The hypoalgesic effect of tramadol in relation to CYP2D6. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1996; 60:636–644.
Article4. Ide S, Minami M, Ishihara K, Uhl GR, Sora I, Ikeda K. Mu opioid receptor-dependent and independent components in effects of tramadol. Neuropharmacology. 2006; 51:651–658.
Article5. Sansone RA, Sansone LA. Tramadol: seizures, serotonin syndrome, and coadministered antidepressants. Psychiatry (Edgmont). 2009; 6:17–21.6. Pypendop BH, Ilkiw JE. Pharmacokinetics of tramadol, and its metabolite O-desmethyl-tramadol, in cats. J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 2008; 31:52–59.
Article7. Shilo Y, Britzi M, Eytan B, Lifschitz T, Soback S, Steinman A. Pharmacokinetics of tramadol in horses after intravenous, intramuscular and oral administration. J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 2008; 31:60–65.
Article8. Kongara K, Chambers P, Johnson CB. Glomerular filtration rate after tramadol, parecoxib and pindolol following anaesthesia and analgesia in comparison with morphine in dogs. Vet Anaesth Analg. 2009; 36:86–94.
Article9. Seddighi MR, Egger CM, Rohrbach BW, Cox SK, Doherty TJ. Effects of tramadol on the minimum alveolar concentration of sevoflurane in dogs. Vet Anaesth Analg. 2009; 36:334–340.
Article10. de Wolff MH, Leather HA, Wouters PF. Effects of tramadol on minimum alveolar concentration (MAC) of isoflurane in rats. Br J Anaesth. 1999; 83:780–783.
Article11. KuKanich B, Papich MG. Pharmacokinetics of tramadol and the metabolite O-desmethyltramadol in dogs. J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 2004; 27:239–246.
Article12. McMillan CJ, Livingston A, Clark CR, Dowling PM, Taylor SM, Duke T, Terlinden R. Pharmacokinetics of intravenous tramadol in dogs. Can J Vet Res. 2008; 72:325–331.13. Potschka H, Friderichs E, Loscher W. Anticonvulsant and proconvulsant effects of tramadol, its enantiomers and its M1 metabolite in the rat kindling model of epilepsy. Br J Pharmacol. 2000; 131:203–212.
Article14. Kahn LH, Alderfer RJ, Graham DJ. Seizures reported with tramadol. Jama. 1997; 278:1661.
Article15. Sen H, Ozkan S, Dagli G. Epileptic seizure during patient-controlled analgesia with tramadol. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2009; 26:447.16. Spiller HA, Gorman SE, Villalobos D, Benon BE, Ruskosky DR, Stancavage MM, Anderson DL. Prospective multicenter evaluation of tramadol exposure. J Toxicol Clin Toxicol. 1997; 35:361–364.
Article17. Kongara K, Chambers JP, Johnson CB. Electroencephalographic responses of tramadol, parecoxib and morphine to acute noxious electrical stimulation in anaesthetised dogs. Res Vet Sci. 2010; 88:127–133.
Article18. Fodale V, Tescione M, Roscitano C, Pino G, Amato A, Santamaria LB. Effect of tramadol on Bispectral Index during intravenous anaesthesia with propofol and remifentanil. Anaesth Intensive Care. 2006; 34:36–39.
Article19. Terrier G, Gottesmann CL. Study of cortical spindles during sleep in the rat. Brain Res Bull. 1978; 3:701–706.
Article20. Midzianovskaia IS, Kuznetsova GD, Coenen AM, Spiridonov AM, van Luijtelaar EL. Electrophysiological and pharmacological characteristics of two types of spike-wave discharges in WAG/Rij rats. Brain Res. 2001; 911:62–70.
Article21. Coenen AM, Van Luijtelaar EL. Genetic animal models for absence epilepsy: a review of the WAG/Rij strain of rats. Behav Genet. 2003; 33:635–655.22. Back SK, Won SY, Hong SK, Na HS. Gabapentin relieves mechanical, warm and cold allodynia in a rat model of peripheral neuropathy. Neurosci Lett. 2004; 368:341–344.
Article23. Park JH, Kim SK, Kim HN, Sun B, Koo S, Choi SM, Bae H, Min BI. Spinal cholinergic mechanism of the relieving effects of electroacupuncture on cold and warm allodynia in a rat model of neuropathic pain. J Physiol Sci. 2009; 59:291–298.
Article24. Jang HS, Choi HS, Lee SH, Jang KH, Lee MG. Evaluation of the anaesthetic effects of medetomidine and ketamine in rats and their reversal with atipamezole. Vet Anaesth Analg. 2009; 36:319–327.
Article25. Jang HS, Lee MG. Atipamezole changes the antinociceptive effects of butorphanol after medetomidine-ketamine anaesthesia in rats. Vet Anaesth Analg. 2009; 36:591–596.
Article26. Koh S, Tibayan FD, Simpson JN, Jensen FE. NBQX or topiramate treatment after perinatal hypoxia-induced seizures prevents later increases in seizure-induced neuronal injury. Epilepsia. 2004; 45:569–575.
Article27. Osterloh G, Friderichs E, Felgenhauer F, Gunzler WA, Henmi Z, Kitano T, Nakamura M, Hayashi H, Ishii I. General pharmacological studies on tramadol, a potent analgetic agent (author's transl). Arzneimittelforschung. 1978; 28:135–151.28. Short CE, Raiha JE, Raiha MP, Otto K. Comparison of neurologic responses to the use of medetomidine as a sole agent or preanesthetic in laboratory beagles. Acta Vet Scand. 1992; 33:77–88.
Article29. Otto KA, Voight S, Piepenbrock S, Deegen E, Short CE. Differences in quantitated electroencephalographic variables during surgical stimulation of horses anesthetized with isoflurane. Vet Surg. 1996; 25:249–255.
Article30. Murrell JC, Johnson CB, White KL, Taylor PM, Haberham ZL, Waterman-Pearson AE. Changes in the EEG during castration in horses and ponies anaesthetized with halothane. Vet Anaesth Analg. 2003; 30:138–146.
Article31. Murrell JC, Mitchinson SL, Waters D, Johnson CB. Comparative effect of thermal, mechanical, and electrical noxious stimuli on the electroencephalogram of the rat. Br J Anaesth. 2007; 98:366–371.
Article32. Gibson TJ, Johnson CB, Stafford KJ, Mitchinson SL, Mellor DJ. Validation of the acute electroencephalographic responses of calves to noxious stimulus with scoop dehorning. N Z Vet J. 2007; 55:152–157.
Article33. Itamoto K, Taura Y, Wada N, Takuma T, Une S, Nakaichi M, Hikasa Y. Quantitative electroencephalography of medetomidine, medetomidine-midazolam and medetomidine-midazolam-butorphanol in dogs. J Vet Med A Physiol Pathol Clin Med. 2002; 49:169–172.
Article34. Haga HA, Dolvik NI. Electroencephalographic and cardiovascular variables as nociceptive indicators in isofluraneanaesthetized horses. Vet Anaesth Analg. 2005; 32:128–135.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Intravenous Regional Anesthesia Using Mepivacaine and Tramadol
- Antinociceptive Effects of Tramadol on the Neuropathic Pain in Rats
- Electroencephalographic correlation dimension changes with depth of halothane
- The Combined Effect of Epidural Tramadol and Clonidine for Postoperative Analgesia
- Continuous Epidural Infusion of Bupivacaine with Tramadol for Post - Cesarean Analgesia