Infect Chemother.
2011 Oct;43(5):416-420. 10.3947/ic.2011.43.5.416.
A Case of Libman-Sacks Endocarditis that Developed after Infective Endocarditis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Infectious Diseases, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Seoul, Korea. imfell@yuhs.ac
- 2Division of Cardiology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2285015
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3947/ic.2011.43.5.416
Abstract
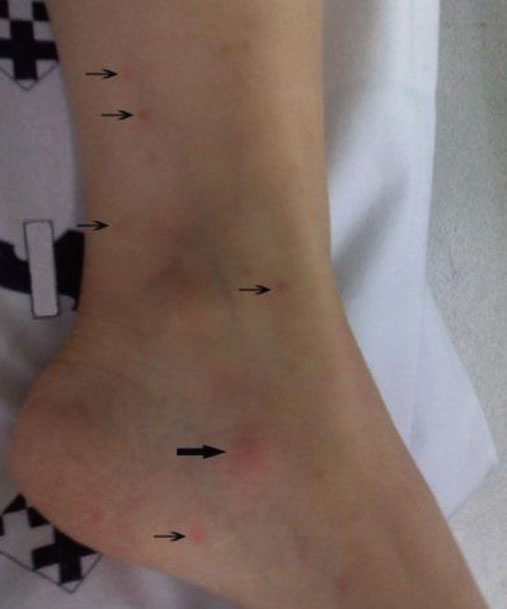
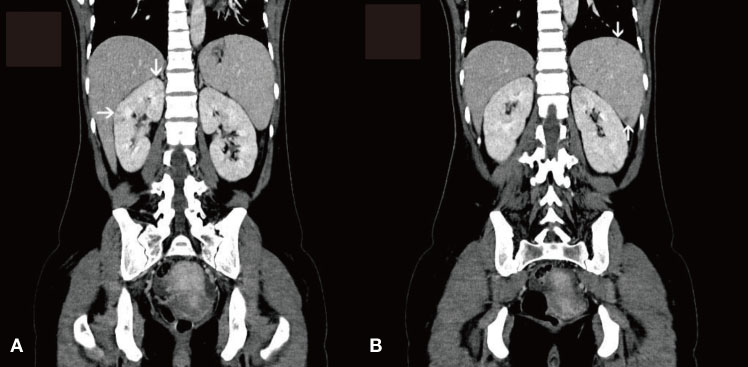
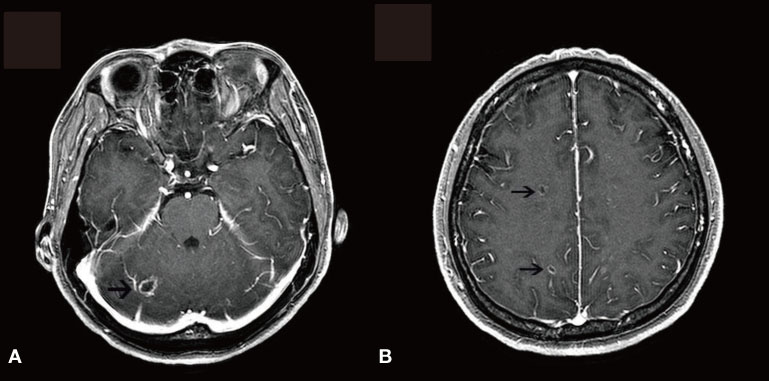
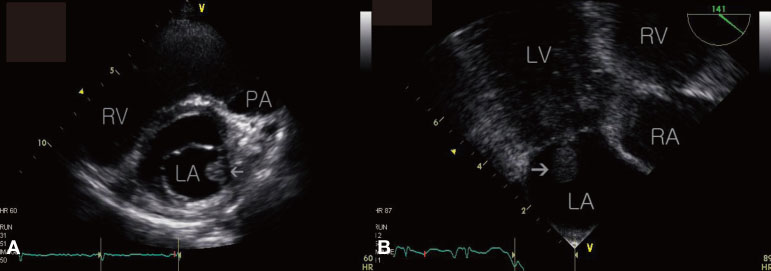
- Libman-Sacks endocarditis (LSE) is a valvular heart disease that is associated with autoimmune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus and antiphospholipid syndrome (APS). Cases of LSE and APS associated with infection have been reported during the last several years. Herein, we present a patient who was suspected to have developed LSE and catastrophic APS during the treatment of her definite infective endocarditis, which was caused by Staphylococcus aureus, and the patient's condition was complicated with cerebral abscess, sensorineural hearing loss, endophthalmitis, renal infarction, splenic abscess, and septic arthritis.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hojnik M, George J, Ziporen L, Shoenfeld Y. Heart valve involvement (Libman-Sacks endocarditis) in the antiphospholipid syndrome. Circulation. 1996. 93:1579–1587.
Article2. Cervera R, Asherson RA, Acevedo ML, Gómez-Puerta JA, Espinosa G, De La Red G, Gil V, Ramos-Casals M, García-Carrasco M, Ingelmo M, Font J. Antiphospholipid syndrome associated with infections: clinical and microbiological characteristics of 100 patients. Ann Rheum Dis. 2004. 63:1312–1317.
Article3. Hsu RB, Lin FY. Methicillin resistance and risk factors for embolism in Staphylococcus aureus infective endocarditis. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2007. 28:860–866.
Article4. Kupferwasser LI, Hafner G, Mohr-Kahaly S, Erbel R, Meyer J, Darius H. The presence of infection-related antiphospholipid antibodies in infective endocarditis determines a major risk factor for embolic events. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1999. 33:1365–1371.
Article5. Bouma W, Klinkenberg TJ, van der Horst IC, Wijdh-den Hamer IJ, Erasmus ME, Bijl M, Suurmeijer AJ, Zijlstra F, Mariani MA. Mitral valve surgery for mitral regurgitation caused by Libman-Sacks endocarditis: a report of four cases and a systematic review of the literature. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2010. 5:13.
Article6. Libman E, Sacks B. A hitherto undescribed form of valvular and mural endocarditis. Arch Intern Med. 1924. 33:701–737.
Article7. Miyakis S, Lockshin MD, Atsumi T, Branch DW, Brey RL, Cervera R, Derksen RH, DE Groot PG, Koike T, Meroni PL, Reber G, Shoenfeld Y, Tincani A, Vlachoyiannopoulos PG, Krilis SA. International consensus statement on an update of the classification criteria for definite antiphospholipid syndrome (APS). J Thromb Haemost. 2006. 4:295–306.
Article8. D'Alton JG, Preston DN, Bormanis J, Green MS, Kraag GR. Multiple transient ischemic attacks, lupus anticoagulant and verrucous endocarditis. Stroke. 1985. 16:512–514.9. Asherson RA, Hughes GR. The expanding spectrum of Libman Sacks endocarditis: the role of antiphospholipid antibodies. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1989. 7:225–228.10. Khamashta MA, Gil A, Asherson RA, Vazquez JJ, Hughes GR. Antiphospholipid antibodies, valvular heart disease and systemic lupus erythematosus. Am J Med. 1989. 86:633–634.11. Blank M, Shani A, Goldberg I, Kopolovic J, Amigo MC, Magrini L, Shoenfeld Y. Libman-Sacks endocarditis associated with antiphospholipid syndrome and infection. Thromb Res. 2004. 114:589–592.
Article12. Zinger H, Sherer Y, Goddard G, Berkun Y, Barzilai O, Agmon-Levin N, Ram M, Blank M, Tincani A, Rozman B, Cervera R, Shoenfeld Y. Common infectious agents prevalence in antiphospholipid syndrome. Lupus. 2009. 18:1149–1153.
Article13. Cervera R, Bucciarelli S, Plasín MA, Gómez-Puerta JA, Plaza J, Pons-Estel G, Shoenfeld Y, Ingelmo M, Espinos G. Catastrophic Antiphospholipid Syndrome (CAPS) Registry Project Group (European Forum On Antiphospholipid Antibodies). Catastrophic antiphospholipid syndrome (CAPS): descriptive analysis of a series of 280 patients from the "CAPS Registry". J Autoimmun. 2009. 32:240–245.
Article14. Kim JY, Choi SH, Hong GR, Kang SM, Park YB, Rim SJ, Chung N. A case of Libman-Sacks endocarditis with moderate mitral regurgitation. Korean Circ J. 2003. 33:715–718.
Article15. Rhee SY, Sohn IS, Kim SJ, Kang HS, Choue CW, Song JS, Bae JH. A case of Libman-Sacks endocarditis confused with infective endocarditis. Korean J Med. 2004. 67:89–93.16. Asherson RA, Cervera R, de Groot PG, Erkan D, Boffa MC, Piette JC, Khamashta MA, Shoenfeld Y. Catastrophic Antiphospholipid Syndrome Registry Project Group. Catastrophic antiphospholipid syndrome: international consensus statement on classification criteria and treatment guidelines. Lupus. 2003. 12:530–534.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A case of Libman-Sacks endocarditis confused with infective endocarditis
- A Case of Libman-Sacks Endocarditis with Moderate Mitral Regurgitation
- A Case of Hemophilus Paraphrophilus Endocarditis with Cerebral Embolism and Hemorrhage
- A Case of Infective Endocarditis caused by Abiotrophia defectiva in Korea
- A case of infective endocarditis presented as cervical spondylodiscitis