Infect Chemother.
2013 Jun;45(2):230-233. 10.3947/ic.2013.45.2.230.
Detection of an Infected N-butyl-2-cyanoacrylate Plug by F-18 FDG PET/CT Scan in a Patient Who Received Endoscopic Intervention for Gastric Variceal Bleeding
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Inha University Hospital, Incheon, Korea. ljinsoo@inha.ac.kr
- 2Department of Nuclear Medicine, Inha University Hospital, Incheon, Korea.
- KMID: 2285005
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3947/ic.2013.45.2.230
Abstract
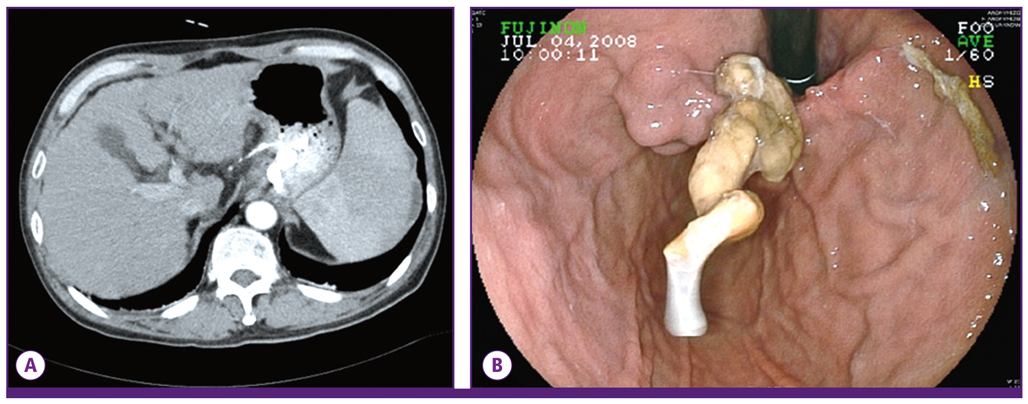
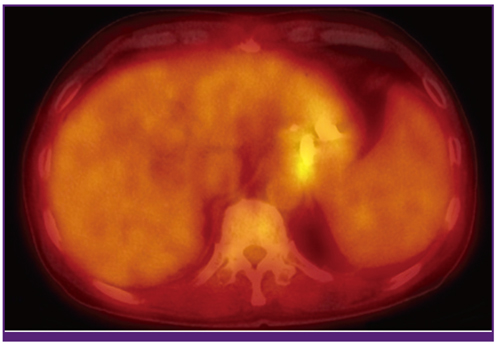
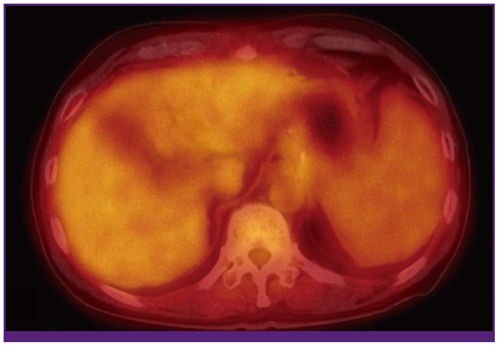
- Injection of N-butyl-2-cyanoacrylate has been used successfully for treatment of gastric variceal bleeding. Bacteremia after injection of N-butyl-2-cyanoacrylate is well known, however, the method for diagnosis of infected endovascular injected material has remained uncertain. This is the first case reporting use of F-18 FDG PET/CT in detection of the source of infection after control of endoscopic bleeding with N-butyl-2-cyanoacrylate.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Sarin SK. Long-term follow-up of gastric variceal sclerotherapy: an eleven-year experience. Gastrointest Endosc. 1997. 46:8–14.
Article2. Ho H, Zuckerman MJ, Wassem C. A prospective controlled study of the risk of bacteremia in emergency sclerotherapy of esophageal varices. Gastroenterology. 1991. 101:1642–1648.
Article3. Camara DS, Gruber M, Barde CJ, Montes M, Caruana JA Jr, Chung RS. Transient bacteremia following endoscopic injection sclerotherapy of esophageal varices. Arch Intern Med. 1983. 143:1350–1352.
Article4. Cohen LB, Korsten MA, Scherl EJ, Velez ME, Fisse RD, Arons EJ. Bacteremia after endoscopic injection sclerosis. Gastrointest Endosc. 1983. 29:198–200.
Article5. Quinn J, Wells G, Sutcliffe T, Jarmuske M, Maw J, Stiell I, Johns P. Tissue Tissue adhesive versus suture wound repair at 1 year: randomized clinical trial correlating early, 3-month, and 1-year cosmetic outcome. Ann Emerg Med. 1998. 32:645–649.
Article6. Brayko CM, Kozarek RA, Sanowski RA, Testa AW. Bacteremia during esophageal variceal sclerotherapy: its cause and prevention. Gastrointest Endosc. 1985. 31:10–12.
Article7. Liao SC, Ko CW, Yeh HZ, Chang CS, Yang SS, Chen GH. Successful treatment of persistent bacteremia after endoscopic injection of N-butyl-2-cyanoacrylate for gastric varices bleeding. Endoscopy. 2007. 39:Suppl 1. E176–E177.
Article8. Wahl P, Lammer F, Conen D, Schlumpf R, Rock A. Septic complications after injection of N-butyl-2-cyanoacrylate: report of two cases and review. Gastrointest Endosc. 2004. 59:911–916.
Article9. Blockmans D, Knockaert D, Maes A, De Caestecker J, Stroobants S, Bobbaers H, Mortelmans L. Clinical value of [(18)F]fluoro-deoxyglucose positron emission tomography for patients with fever of unknown origin. Clin Infect Dis. 2001. 32:191–196.
Article10. Stumpe KD, Dazzi H, Schaffner A, von Schulthess GK. Infection imaging using whole-body FDG-PET. Eur J Nucl Med. 2000. 27:822–832.
Article11. Güngör T, Engel-Bicik I, Eich G, Willi UV, Nadal D, Hossle JP, Seger RA, Steinert HC. Diagnostic and therapeutic impact of whole body positron emission tomography using fluorine-18-fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose in children with chronic granulomatous disease. Arch Dis Child. 2001. 85:341–345.
Article12. Basu S, Chryssikos T, Moghadam-Kia S, Zhuang H, Torigian DA, Alavi A. Positron emission tomography as a diagnostic tool in infection: present role and future possibilities. Semin Nucl Med. 2009. 39:36–51.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Multiple Cerebral Infarction after Injection of N-Butyl-2-Cyanoacrylate for Gastric Variceal Bleeding
- Spinal, Cerebral and Cerebellar Embolism after Injection of N-Butyl-2-Cyanoacrylate in Esophageal Variceal Bleeding
- Effect of Endoscopic Sclerotherapy Using N-butyl-2-cyanoacrylate in Patients with Gastric Variceal Bleeding
- A Case of Portal Vein and Splenic Vein Occlusion after Endoscopic Variceal Occlusion Therapy in Gastric Variceal Bleeding
- The Effect of Histoacryl(R) for Gastric Variceal Bleeding Which Failed by Ethanolamine Oleate Injection Sclerotherapy