Intest Res.
2014 Apr;12(2):157-161. 10.5217/ir.2014.12.2.157.
Superior Mesenteric Vein Thrombosis as an Early Presentation of Myelodysplastic Syndrome: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Jeju National University School of Medicine, Jeju, Korea.
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Jeju National University School of Medicine, Jeju, Korea. songhj@jejunu.ac.kr
- 3Department of Laboratory Medicine, Jeju National University School of Medicine, Jeju, Korea.
- KMID: 2284902
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5217/ir.2014.12.2.157
Abstract
- Mesenteric venous thrombosis (MVT) is a serious condition due to its potential association with mesenteric ischemia and infarction of the small bowel. Symptoms of MVT are often vague, making accurate diagnosis and sufficient treatment difficult. However, increased awareness and new imaging modalities for this condition have improved outcomes for patients with MVT. Treatment includes anticoagulation, transcatheter therapy, and surgery. In the present report, we describe the case study of a 62-year-old woman with a presenting diagnosis of superior MVT, who was finally diagnosed with myelodysplastic syndrome. The superior MVT spontaneously dissolved after the patient underwent 6 months of systemic anticoagulation therapy. Invasive surgery or bowel resection was not required.
MeSH Terms
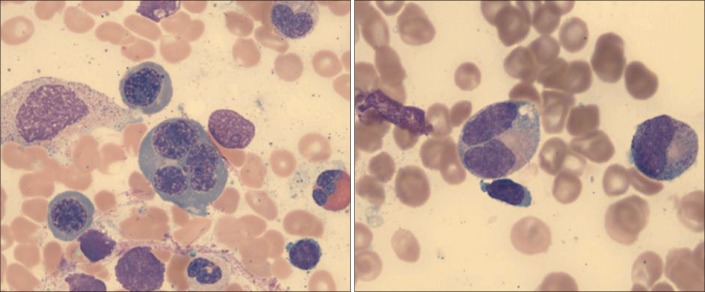
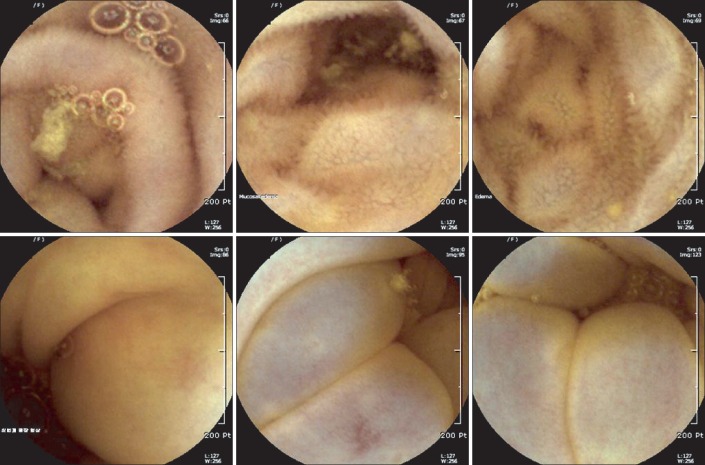
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kumar S, Sarr MG, Kamath PS. Mesenteric venous thrombosis. N Engl J Med. 2001; 345:1683–1688. PMID: 11759648.
Article2. Singal AK, Kamath PS, Tefferi A. Mesenteric venous thrombosis. Mayo Clin Proc. 2013; 88:285–294. PMID: 23489453.
Article3. Kaminsky M, Hochman D. Superior mesenteric venous thrombosis. CMAJ. 2011; 183:693. PMID: 21324855.
Article4. Abu-Daff NS, Abu-Daff SN, Rubayaan A, Abu-Shaaban A. Laparoscopy in the treatment of a giant true epiphrenic diverticulum with migration of the gastrointestinal anastomosis staples. Saudi Med J. 2009; 30:295–298. PMID: 19198724.5. Schoots IG, Levi M, van Vliet AK, Declerck PJ, Maas AM, van Gulik TM. Enhancement of endogenous fibrinolysis does not reduce local fibrin deposition, but modulates inflammation upon intestinal ischemia and reperfusion. Thromb Haemost. 2004; 91:497–505. PMID: 14983225.
Article6. Kang JH, Keller JJ, Lin YK, Lin HC. A population-based case-control study on the association between rheumatoid arthritis and deep vein thrombosis. J Vasc Surg. 2012; 56:1642–1648. PMID: 23085092.
Article7. Kim SC, Schneeweiss S, Liu J, Solomon DH. Risk of venous thromboembolism in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2013; 65:1600–1607. PMID: 23666917.8. Cenedese A, Monneuse O, Gruner L, Tissot E, Mennesson N, Barth X. Initial management of extensive mesenteric venous thrombosis: retrospective study of nine cases. World J Surg. 2009; 33:2203–2208. PMID: 19672653.
Article9. Zhang J, Duan ZQ, Song QB, Luo YW, Xin SJ, Zhang Q. Acute mesenteric venous thrombosis: a better outcome achieved through improved imaging techniques and a changed policy of clinical management. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2004; 28:329–334. PMID: 15288639.
Article10. Landolfi R, Di Gennaro L. Thrombosis in myeloproliferative and myelodysplastic syndromes. Hematology. 2012; 17(Suppl 1):S174–S176. PMID: 22507813.
Article11. Chen HC, Chiu YM. Large-vessel thrombosis in intestinal Behcet's disease complicated with myelodysplastic syndrome and trisomy 8. World J Gastroenterol. 2012; 18:1137–1140. PMID: 22416191.
Article12. Kimura S, Kuroda J, Akaogi T, Hayashi H, Kobayashi Y, Kondo M. Trisomy 8 involved in myelodysplastic syndromes as a risk factor for intestinal ulcers and thrombosis--Behcet's syndrome. Leuk Lymphoma. 2001; 42:115–121. PMID: 11699198.
Article13. Hsu HC, Lee YM, Tsai WH, et al. Circulating levels of thrombopoietic and inflammatory cytokines in patients with acute myeloblastic leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome. Oncology. 2002; 63:64–69. PMID: 12187073.
Article14. Martin S, Baldock SC, Ghoneim AT, Child JA. Defective neutrophil function and microbicidal mechanisms in the myelodysplastic disorders. J Clin Pathol. 1983; 36:1120–1128. PMID: 6311878.
Article15. Tada Y, Koarada S, Haruta Y, Mitamura M, Ohta A, Nagasawa K. The association of Behcet's disease with myelodysplastic syndrome in Japan: a review of the literature. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2006; 24:S115–S119. PMID: 17067441.16. Kawabata H, Sawaki T, Kawanami T, et al. Myelodysplastic syndrome complicated with inflammatory intestinal ulcers: significance of trisomy 8. Intern Med. 2006; 45:1309–1314. PMID: 17170506.
Article17. Kumar S, Kamath PS. Acute superior mesenteric venous thrombosis: one disease or two? Am J Gastroenterol. 2003; 98:1299–1304. PMID: 12818273.
Article18. Brunaud L, Antunes L, Collinet-Adler S, et al. Acute mesenteric venous thrombosis: case for nonoperative management. J Vasc Surg. 2001; 34:673–679. PMID: 11668323.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Acute Appendicitis with Superior Mesenteric Vein Thrombosis and Portal Vein Thrombosis
- Spontaneous Dissolution of Isolated Superior Mesenteric Vein Thrombosis in Acute Pancreatitis
- A Case of Ulcerative Colitis Associated with Portal Vein and Superior Mesenteric Vein Terombosis
- Portal Vein and Superior Mesenteric Vein Thrombosis following Cholecystectomy and Choledochostomy
- A Case of Isolated Superior Mesenteric Vein Thrombosis in Acute Pancreatitis