Healthc Inform Res.
2015 Jan;21(1):3-9. 10.4258/hir.2015.21.1.3.
Big Data Analysis Framework for Healthcare and Social Sectors in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Statistics and Information Research Department, Korea Institute for Health and Social Affairs, Sejong, Korea.
- 2Department of Health Policy and Healthcare Management, Inje Institute of Advanced Studies, Seoul, Korea. seewon@inje.ac.kr
- KMID: 2284592
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4258/hir.2015.21.1.3
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
We reviewed applications of big data analysis of healthcare and social services in developed countries, and subsequently devised a framework for such an analysis in Korea.
METHODS
We reviewed the status of implementing big data analysis of health care and social services in developed countries, and strategies used by the Ministry of Health and Welfare of Korea (Government 3.0). We formulated a conceptual framework of big data in the healthcare and social service sectors at the national level. As a specific case, we designed a process and method of social big data analysis on suicide buzz.
RESULTS
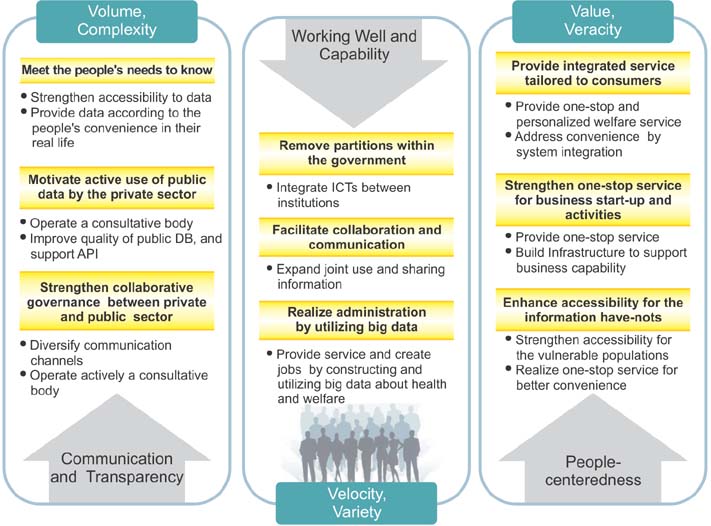
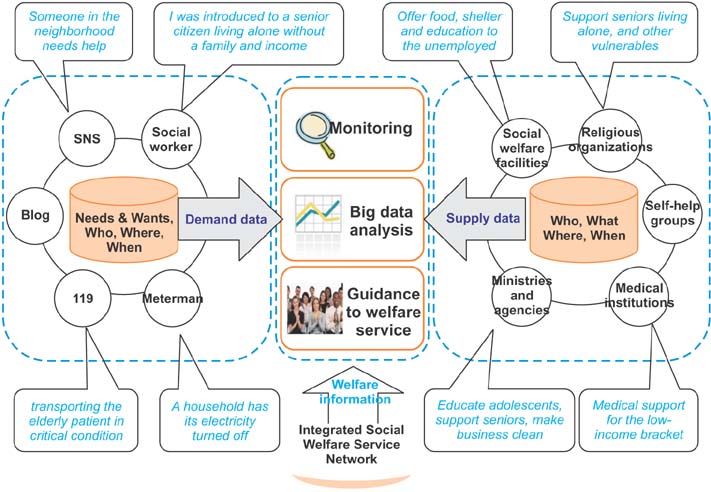
Developed countries (e.g., the United States, the UK, Singapore, Australia, and even OECD and EU) are emphasizing the potential of big data, and using it as a tool to solve their long-standing problems. Big data strategies for the healthcare and social service sectors were formulated based on an ICT-based policy of current government and the strategic goals of the Ministry of Health and Welfare. We suggest a framework of big data analysis in the healthcare and welfare service sectors separately and assigned them tentative names: 'health risk analysis center' and 'integrated social welfare service network'. A framework of social big data analysis is presented by applying it to the prevention and proactive detection of suicide in Korea.
CONCLUSIONS
There are some concerns with the utilization of big data in the healthcare and social welfare sectors. Thus, research on these issues must be conducted so that sophisticated and practical solutions can be reached.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Big Data and Healthcare: Building an Augmented World
Hyejung Chang, Mona Choi
Healthc Inform Res. 2016;22(3):153-155. doi: 10.4258/hir.2016.22.3.153.Development and Evaluation of an Obesity Ontology for Social Big Data Analysis
Ae Ran Kim, Hyeoun-Ae Park, Tae-Min Song
Healthc Inform Res. 2017;23(3):159-168. doi: 10.4258/hir.2017.23.3.159.National Healthcare Service and Its Big Data Analytics
Da Jeong Nam, Hyuk Won Kwon, Haeyeon Lee, Eun Kyung Ahn
Healthc Inform Res. 2018;24(3):247-249. doi: 10.4258/hir.2018.24.3.247.
Reference
-
1. Chen H, Chiang RH, Storey VC. Business intelligence and analytics: from big data to big impact. MIS Q. 2012; 36(4):1165–1188.
Article2. Song TM. Efficient utilization of big data on health and welfare. Health Welf Policy Forum. 2012; (193):68–76.3. Lee BH. Big data generation and new business opportunities [Internet]. Seoul: Hyundai Research Institute;2012. cited at 2015 Jan 5. Available from: http://www.hri.co.kr/board/reportView.asp?firstDepth=1&secondDepth=6%20&numIdx=18609.4. Pillbox [Internet]. Washington (DC): National Library of Medicine;c2013. cited at 2014 Dec 2. Available from: http://pillbox.nlm.nih.gov/.5. The Horizon Scanning Programme Team [Internet]. London: The UK Government;2014. cited at 2014 Aug 2. Available from: https://www.gov.uk/government/groups/horizon-scanning-centre.6. Risk Assessment and Horizon Scanning (RAHS) [Internet]. Singapore: National Security Coordination Secretariat;c2014. cited at 2014 Dec 2. Available from: http://app.nscs.gov.sg/public/home.aspx.7. National Information Strategy Committee of Korea. Implementation of smart government using big data [Internet]. Seoul: National Information Strategy Committee;2012. cited at 2015 Jan 5. Available from: http://mmlab.snu.ac.kr/courses/2011_information-universe/presentation/1121.pdf.8. OECD. Exploring data-driven innovation as a new source of growth: mapping the policy issues raised by 'big data' [Internet]. Paris: OECD Publishing;2013. cited at 2014 Dec 2. Available from: http://www.oecd-ilibrary.org/science-and-technology/exploring-data-driven-innovation-as-a-new-source-of-growth_5k47zw3fcp43-en.9. Song YJ. Data based on national future strategy and implications of the developed countries. IT Future Strategy. 2013; (2):1–18.10. The Economist. Data, data everywhere [Internet]. London: The Economist;c2010. cited at 2014 Dec 2. Available from: http://www.economist.com/node/15557443/.11. Gartner's 2012 hype cycle for emerging technologies identifies "tipping point" technologies that will unlock long-awaited technology scenarios [Internet]. Stamford (CT): Gartner Inc.;c2012. cited at 2014 Dec 2. Available from: http://www.gartner.com/newsroom/id/2124315.12. Manyika J, Chui M, Brown B, Bughin J, Dobbs R, Roxburgh C, et al. Big data: the next frontier for innovation, competition, and productivity. Washington (DC): McKinsey Global Institute;2011.13. Koch S. Achieving holistic health for the individual through person-centered collaborative care supported by informatics. Healthc Inform Res. 2013; 19(1):3–8.
Article14. Song YJ. Big data world! Evolution of SNS and the public policy. IT Future Strategy. 2012; (13):1–26.15. Go SJ, Jeoung YH. Health risk prediction using big health data. Health Welf Policy Forum. 2012; (193):43–52.16. Open data portal [Internet]. Seoul: National Information Society Agency;c2014. cited at 2014 Dec 2. Available from: https://www.data.go.kr.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Pediatric Cancer Research using Healthcare Big Data
- Potentiality of Big Data in the Medical Sector: Focus on How to Reshape the Healthcare System
- Making Sense of the Big Picture: Data Linkage and Integration in the Era of Big Data
- Current status and challenges on the big data of public sector in Korea
- Real World Data and Artificial Intelligence in Diabetology