A Multi-Classifier Based Guideline Sentence Classification System
- Affiliations
-
- 1U-Healthcare Institute, Gachon University of Medicine and Science, Incheon, Korea. leeyh@gachon.ac.kr
- 2LNISOFT, Incheon, Korea.
- 3U-Healthcare Center, Gachon University Gil Hospital, Incheon, Korea.
- KMID: 2284549
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4258/hir.2011.17.4.224
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
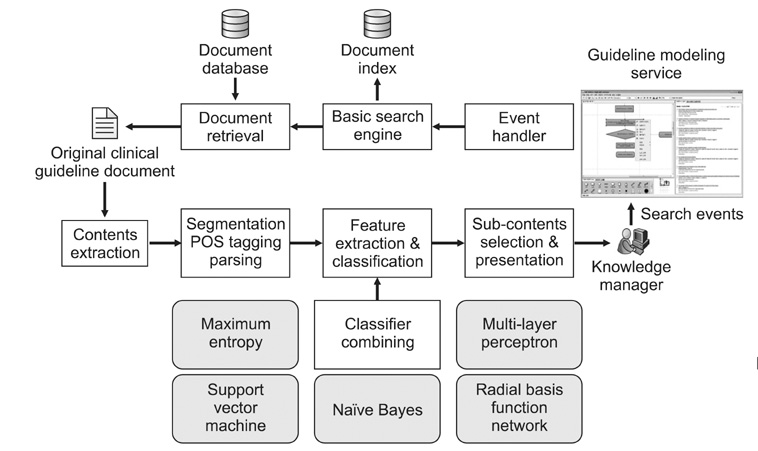
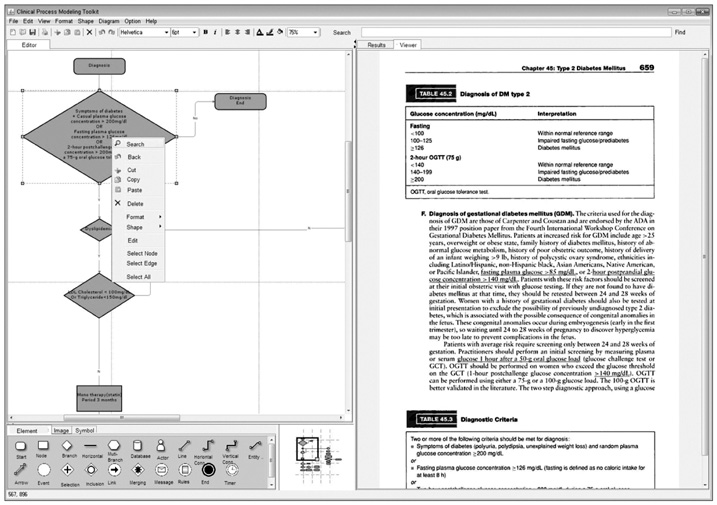
An efficient clinical process guideline (CPG) modeling service was designed that uses an enhanced intelligent search protocol. The need for a search system arises from the requirement for CPG models to be able to adapt to dynamic patient contexts, allowing them to be updated based on new evidence that arises from medical guidelines and papers.
METHODS
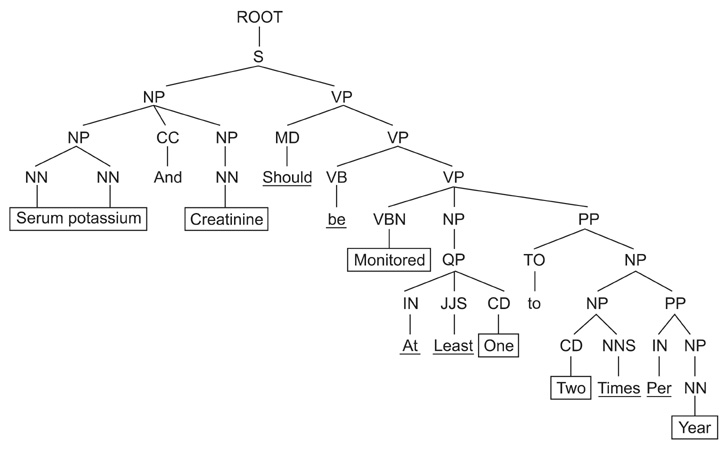
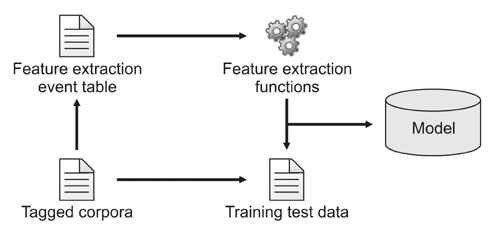
A sentence category classifier combined with the AdaBoost.M1 algorithm was used to evaluate the contribution of the CPG to the quality of the search mechanism. Three annotators each tagged 340 sentences hand-chosen from the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure (JNC7) clinical guideline. The three annotators then carried out cross-validations of the tagged corpus. A transformation function is also used that extracts a predefined set of structural feature vectors determined by analyzing the sentential instance in terms of the underlying syntactic structures and phrase-level co-occurrences that lie beneath the surface of the lexical generation event.
RESULTS
The additional sub-filtering using a combination of multi-classifiers was found to be more effective than a single conventional Term Frequency-Inverse Document Frequency (TF-IDF)-based search system in pinpointing the page containing or adjacent to the guideline information.
CONCLUSIONS
We found that transformation has the advantage of exploiting the structural and underlying features which go unseen by the bag-of-words (BOW) model. We also realized that integrating a sentential classifier with a TF-IDF-based search engine enhances the search process by maximizing the probability of the automatically presented relevant information required in the context generated by the guideline authoring environment.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 5 articles
-
Comparison of Machine Learning Algorithms for Classification of the Sentences in Three Clinical Practice Guidelines
Mi Hwa Song, Young Ho Lee, Un Gu Kang
Healthc Inform Res. 2013;19(1):16-24. doi: 10.4258/hir.2013.19.1.16.Korean Anaphora Recognition System to Develop Healthcare Dialogue-Type Agent
Junggi Yang, Youngho Lee
Healthc Inform Res. 2014;20(4):272-279. doi: 10.4258/hir.2014.20.4.272.Data-Mining-Based Coronary Heart Disease Risk Prediction Model Using Fuzzy Logic and Decision Tree
Jaekwon Kim, Jongsik Lee, Youngho Lee
Healthc Inform Res. 2015;21(3):167-174. doi: 10.4258/hir.2015.21.3.167.Statistics and Deep Belief Network-Based Cardiovascular Risk Prediction
Jaekwon Kim, Ungu Kang, Youngho Lee
Healthc Inform Res. 2017;23(3):169-175. doi: 10.4258/hir.2017.23.3.169.Medical informatics methods for the clinical evidence extraction
Mi Hwa Song, Dong Kyun Park, Young Ho Lee
J Korean Med Assoc. 2012;55(8):741-747. doi: 10.5124/jkma.2012.55.8.741.
Reference
-
1. Woolf SH, Grol R, Hutchinson A, Eccles M, Grimshaw J. Potential benefits, limitations, and harms of clinical guidelines. BMJ. 1999. 318:527–530.
Article2. Buchanan B, Shortliffe EH. Rule-based expert systems: the MYCIN experiments of the Stanford Heuristic Programming Project. 1984. Reading, MA: Addison-Wesley.3. Pan F. Multi-dimensional fragment classification in biomedical text. 2006. Kingston, OT: Queen's University.4. Xin L, Xuan-Jing H, Li-de W. Question classification by ensemble learning. Int J Comput Sci Netw Secur. 2006. 6:146–153.5. Freund Y, Schapire RE. Saitta L, editor. European Coordinating Committee for Artificial Intelligence. Associazione italiana per l'intelligenza artificiale. Experiments with a new boosting algorithm. Thirteenth International Conference on Machine Learning. 1996. San Mateo, CA: Morgan Kaufmann Publishersn;148–156.6. Marsland S. Machine learning: an algorithmic perspective. 2009. Boca Raton, FL: Chapman & Hall/CRC.7. Duda RO, Hart PE, Stork DG. Pattern classification. 2000. 2nd ed. New York: Wiley.8. Salton G, McGill MJ. Introduction to modern information retrieval. 1983. New York: McGraw-Hill.9. Domingos P, Pazzani M. On the optimality of the simple Bayesian classifier under zero-one loss. Mach Learn. 1997. 29:103–130.10. Cristianini N, Shawe-Taylor J. An introduction to support vector machines and other kernel-based learning methods. 2000. Cambridge, NY: Cambridge University Press.11. Berger AL, Della Pietra SA, Della Pietra VJ. A maximum entropy approach to natural language processing. Comput Linguist. 1996. 22:39–71.12. Darroch JN, Ratcliff D. Generalized iterative scaling for log-linear models. Ann Math Statist. 1972. 43:1470–1480.
Article13. Vapnik VN. Statistical learning theory. 1998. New York: Wiley Interscienc.14. Ethem A. Introduction to machine learning. 2004. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.15. Cardoso-Cachopo A, Oliveira AL. An empirical comparison of text categorization methods. Lect Notes Comput Sci. 2003. 2857:183–196.
Article16. Guyon I, Elisseeff A. An introduction to variable and feature selection. J Mach Learn Res. 2003. 3:1157–1182.17. Yang Y, Pedersen JO. A comparative study on feature selection in text categorization. Proceedings of ICML-97, 14th International Conference on Machine Learning. 1997 Jul 8-12; Nashville, TN, USA. 412–420.18. Feldman R, Sanger J. The text mining handbook: advanced approaches in analyzing unstructured data. 2007. Cambridge, NY: Cambridge University Press.19. Welcome to Apache Nutch [Internet]. The Apache Software Foundation. c2011. cited at 2011 Sep 14. The Apache Software Foundation;Available from: http://nutch.apache.org/.20. Apache Tika: a content analysis toolkit [Internet]. The Apache Software Foundation. c2011. cited at 2011 Sep 14. The Apache Software Foundation;Available from: http://tika.apache.org/.21. Welcome to Apache OpenNLP [Internet]. OpenNLP. c2010. cited at 2011 Sep 14. The Apache Software Foundation;Available from: http://incubator.apache.org/opennlp/.22. The Stanford parser: a statistical parser [Internet]. The Stanford Natural Language Processing Group (SNLP). cited at 2011 Sep 14. The Stanford Natural Language Processing Group;Available from: http://nlp.stanford.edu/software/lex-parser.shtml.23. Shatkay H, Pan F, Rzhetsky A, Wilbur WJ. Multi-dimensional classification of biomedical text: toward automated, practical provision of high-utility text to diverse users. Bioinformatics. 2008. 24:2086–2093.
Article24. Chobanian AV, Bakris GL, Black HR, Cushman WC, Green LA, Izzo JL Jr, Jones DW, Materson BJ, Oparil S, Wright JT Jr, Roccella EJ. National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure. National High Blood Pressure Education Program Coordinating Committee. The Seventh Report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure: the JNC 7 report. JAMA. 2003. 289:2560–2572.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Implementation of Pattern Classifier for Karyotype Classification
- Context-Dependent Classification of Multi-Echo MRI Using Bayes Compound Decision Model
- Classification of a volumetric MRI using gibbs distributions and a line model
- Comparison of Machine Learning Algorithms for Classification of the Sentences in Three Clinical Practice Guidelines
- Feasibility of fully automated classification of whole slide images based on deep learning