Diabetes Metab J.
2014 Jun;38(3):187-193. 10.4093/dmj.2014.38.3.187.
Journal Metrics-Based Position of Diabetes & Metabolism Journal after the Change of Its Text Language to English
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Parasitology and Institute of Medical Education, Hallym University College of Medicine, Chuncheon, Korea. shuh@hallym.ac.kr
- KMID: 2280688
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2014.38.3.187
Abstract
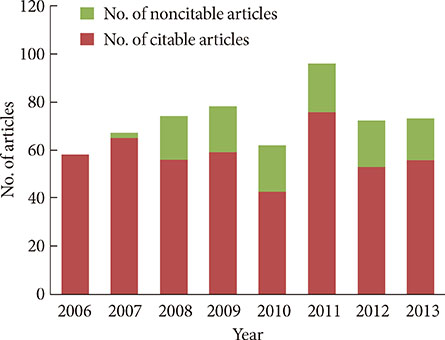
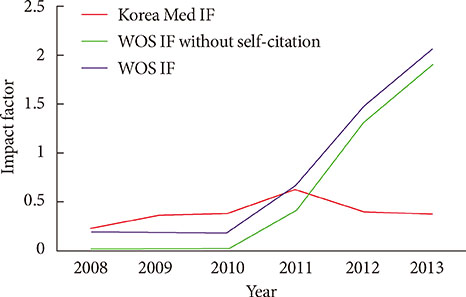
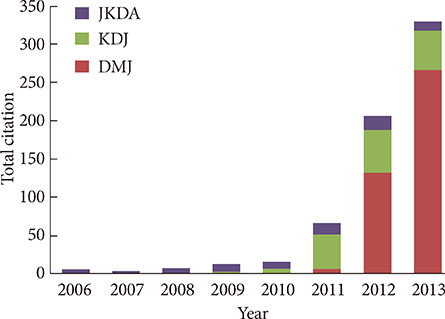
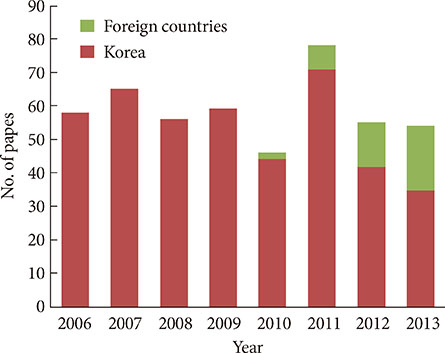
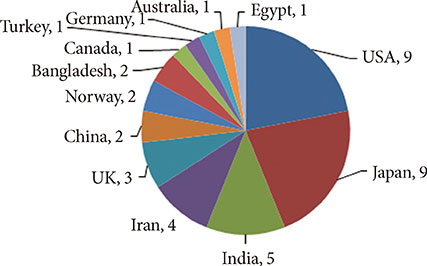
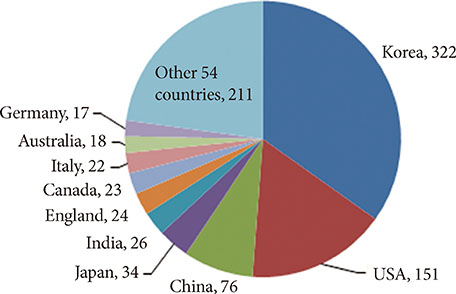
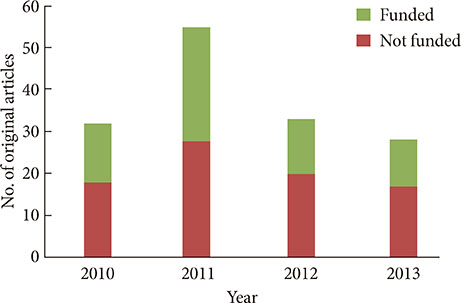
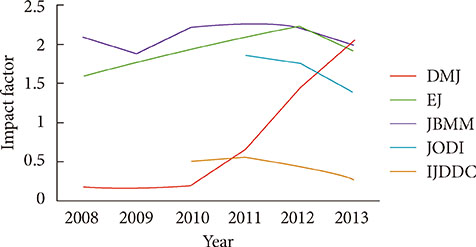
- After changing its language from Korean or English to English only in 2010, the journal metrics of Diabetes & Metabolism Journal (DMJ) were analyzed to assess whether this change in the journal policy was successful. The journal metric items that were analyzed were the following: impact factor; total citations; countries of authors; proportion of the articles funded out of the total number of original articles; and Hirsch-index (H-index). A retrospective, descriptive analysis was carried out using various databases, such as KoreaMed, Korean Medical Citation Index (KoMCI), KoreaMed Synapse, Web of Science, and Journal Citation Ranking. The journal's impact factor was 2.054, which corresponds to 83/122 (68.0%) out of the 2012 JCR endocrinology and metabolism category. The number of the journal's total citations was 330 in 2013. In addition to Korean authors, authors from 13 other countries published papers in the journal from 2010 to 2013. The number of funded papers from 2010 to 2013 was 65 out of 148 original articles (43.9%). The journal's H-index from KoreaMed Synapse was 7, and that from Web of Science was 9. It can be concluded that changing the journal's language to English was successful based on journal metrics. DMJ is currently positioned as an international journal based on the international diversity of authors and editors, its sufficiently high proportion of funded articles, its relatively high impact factor, and the number of total citations.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery's Evolution into an International Journal Based on Journal Metrics
Sun Huh
Clin Orthop Surg. 2016;8(2):127-132. doi: 10.4055/cios.2016.8.2.127.
Reference
-
1. U.S. National Library of Medicine. PubMed Central. Available from: http://pubmedcentral.org/. cited 2014 Apr 23.2. U.S. National Library of Medicine. PubMed. Available from: http://pubmed.org/. cited 2014 Apr 23.3. Korean Association of Medical Journal Editiors. KoreaMed. Available from: http://koreamed.org/. cited 2014 Apr 23.4. Korean Association of Medical Journal Editors. KoreaMed Synapse. Available from: http://synapse.koreamed.org/. cited 2014 Apr 23.5. Korean Association of Medical Journal Editors. KoMCI. Available from: http://komci.org/. cited 2014 Apr 23.6. Thomson Reuters. Web of Science. Available from: http://www.webofknowledge.com/wos/. cited 2014 Apr 23.7. Thomson Reuters. JCR Web. Available from: http://webofknowledge.com/jcr/. cited 2014 Apr 23.8. Hirsch JE. An index to quantify an individual's scientific research output. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005; 102:16569–16572.9. Huh S. Citation analysis of the Korean Journal of Urology from Web of Science, Scopus, Korean Medical Citation Index, KoreaMed Synapse, and Google Scholar. Korean J Urol. 2013; 54:220–228.10. Jeong GH, Huh S. Increase in frequency of citation by SCIE journals of non-Medline journals after listing in an open access full-text database. Sci Ed. 2014; 1:24–26.11. Huh S, Choi TJ, Kim SH. Using journal article tag suite extensible markup language for scholarly journal articles written in Korean. Sci Ed. 2014; 1:19–23.12. Huh S. Citation analysis of The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine from KoMCI, Web of Science, and Scopus. Korean J Intern Med. 2011; 26:1–7.13. Huh S. How far has The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine advanced in terms of journal metrics? Korean J Intern Med. 2013; 28:635–638.14. Huh S. How far has the international neurourology journal progressed since its transformation into an english language journal? Int Neurourol J. 2014; 18:3–9.15. Huh S. Why should Neurointervention be indexed in International Databases? Neurointervention. 2011; 6:49–50.16. Lammey R. CrossRef developments and initiatives: an update on services for the scholarly publishing community from CrossRef. Sci Ed. 2014; 1:13–18.17. Huh S. Revision of the instructions to authors to require a structured abstract, digital object identifier of each reference, and author's voice recording may increase journal access. J Educ Eval Health Prof. 2013; 10:3.18. Kim N. Past, present, and future of Journal of Neurogastroenterology and Motility. Sci Ed. 2014; 1:43–45.19. Huh S. The new era of journal of neurogastroenterology and motility: what should be prepared to be a top journal in the category of gastroenterology and hepatology. J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2013; 19:419–421.20. Hames I. The changing face of peer review. Sci Ed. 2014; 1:9–12.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- What is the position of Clinical and Experimental Reproductive Medicine in its scholarly journal network based on journal metrics?
- The rapid internationalization of Annals of Pediatric Endocrinology & Metabolism as evidenced by journal metrics
- Journal metrics of Clinical and Molecular Hepatology based on the Web of Science Core Collection
- Corrigendum: Table and Text Correction. Recent Updates on Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Management for Clinicians
- An Implementation of Natural Language Processing and Text Mining in Stroke Research