Korean J Pediatr Infect Dis.
2014 Dec;21(3):214-218. 10.14776/kjpid.2014.21.3.214.
Unilateral Parotitis and Kawasaki Disease in a Child
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Pusan National University Children's Hospital, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Yangsan, Korea. psepse@naver.com
- KMID: 2279096
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14776/kjpid.2014.21.3.214
Abstract
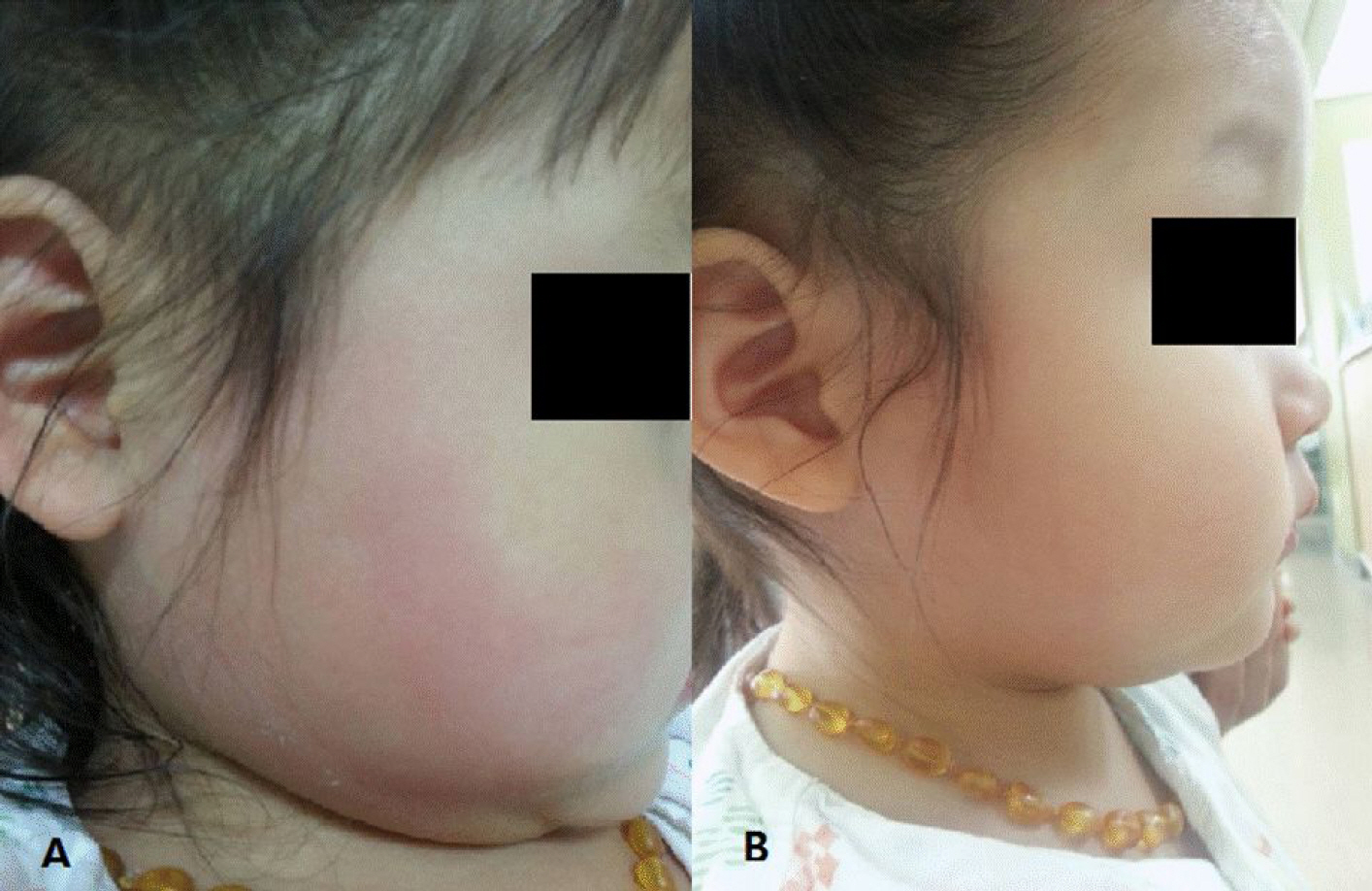
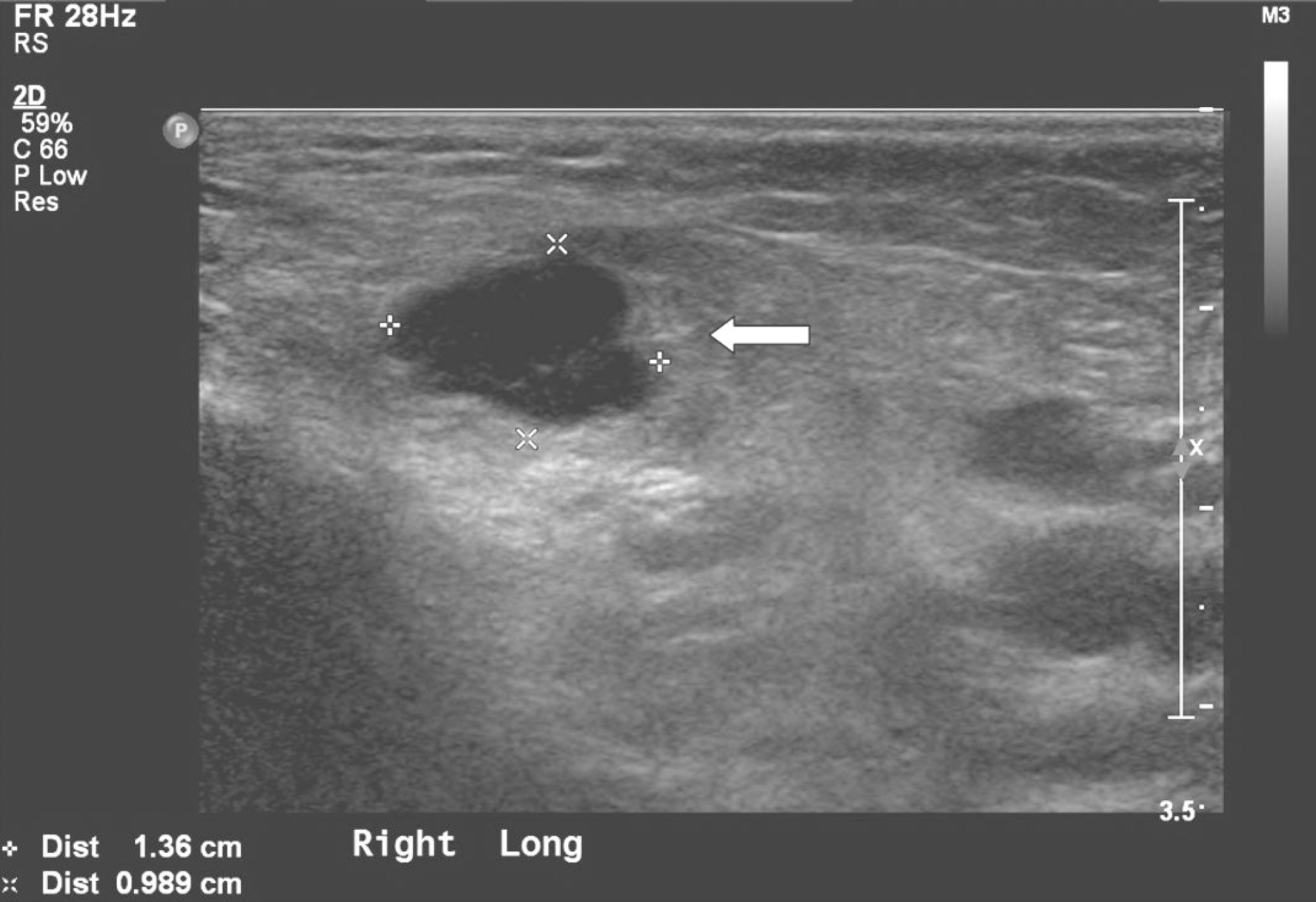
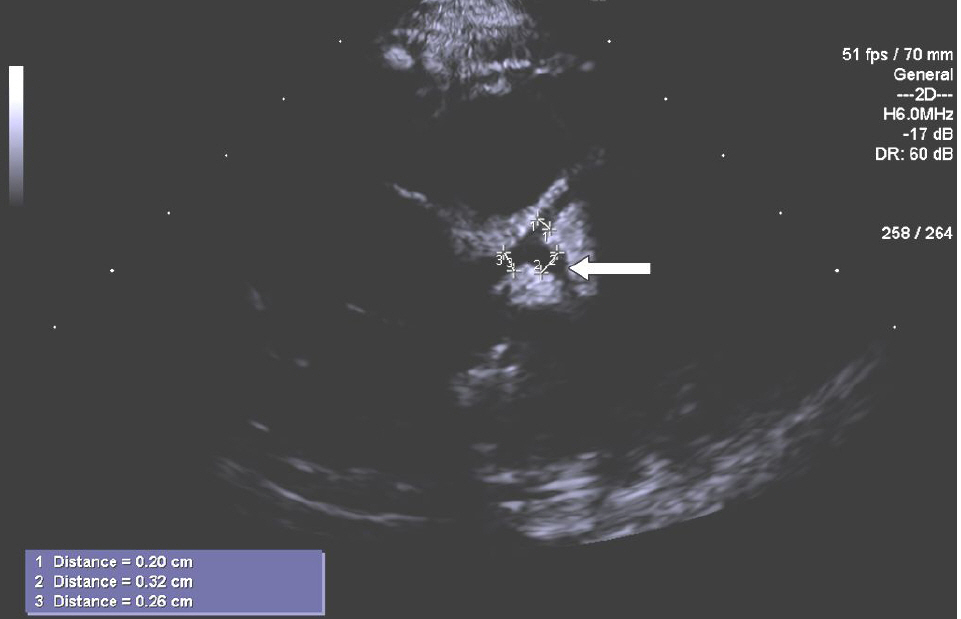
- Kawasaki disease is generally diagnosed base on its clinical features. Sometimes unusual or atypical presentations make the diagnosis of Kawasaki disease difficult. We experienced an unusual case of Kawasaki disease presented with unilateral parotitis in a 23-month old girl. Despite of intravenous antibiotics treatment, fever and unilateral parotid swelling persisted. Skin rashes, conjunctival injections, and coronary abnormalities showed up on the 8th day of fever. After the intravenous immunoglobulin and salicylates treatment, all symptoms disappeared. Although unilateral parotitis is very unusual presentation of Kawasaki disease, in case of no response to antibiotics, Kawasaki disease should be included in the differential diagnosis.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Cho SY, Cho HK, Cho KY, Kim HS, Sohn S. Kawasaki disease presenting as retropharyngeal abscess. Korean J Pediatr. 2008; 51:1023–7.
Article2. Ganesh R, Srividhya VS, Vasanthi T, Shivbalan S. Kawasaki disease mimicking retropharyngeal abscess. Yonsei Med J. 2010; 51:784–6.
Article3. Cavicchiolo ME, Berlese P, Bressan S, Trincia E, Inches I, Strafella MS, et al. Retropharyngeal abscess: An unusual presentation of Kawasaki disease. case report and review of the literature. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol Extra. 2012; 7:179–82.
Article4. Homicz MR, Carvalho D, Kearns DB, Edmonds J. An atypical presentation of Kawasaki disease resembling a retropharyngeal abscess. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2000; 54:45–9.
Article6. Do HJ, Baek JG, Kim HJ, Yeom JS, Park JS, Park ES, et al. Kawasaki disease presenting as parotitis in a 3-month-old infant. Korean Circ J. 2009; 39:502–4.
Article7. Seyedabadi KS, Howes RF, Yazdi M. Parotitis associated with Kawasaki syndrome. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1987; 6:223.
Article8. Douvoyiannis M, Belamarich PF, Litman N. Parotitis and Kawasaki disease in a child with Noonan syndrome. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2008; 27:89–90.
Article9. Amano S, Hazama F, Kubagawa H, Tasaka K, Haebara H, Hamashima Y. General pathology of Kawasaki disease. Acta Pathol Jpn. 1980; 30:681–94.
Article10. Kanegaye JT, Van Cott E, Tremoulet AH, Salgado A, Shimizu C, Kruk P, et al. Lymph-node-first presentation of Kawasaki disease compared with bacterial cervical adenitis and typical Kawasaki disease. J Pediatr. 2013; 162:1259–63.e2.
Article11. Choi SH, Kim HJ. A case of Kawasaki disease with coexistence of a parapharyngeal abscess requiring incision and drainage. Korean J Pediatr. 2010; 53:855–8.
Article