Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol.
2009 Sep;2(3):155-158.
Adenomatous Hyperplasia Arising from Dual Ectopic Thyroid
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Seoul, Korea. entlsh@hanmail.net
- 2Department of Pathology, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
Abstract
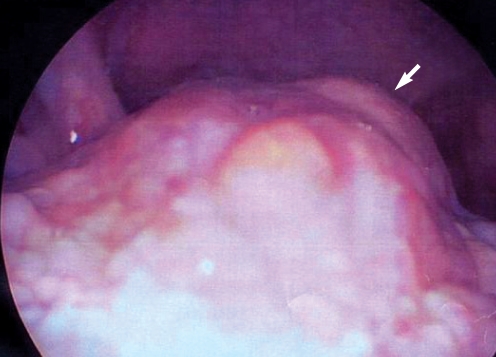
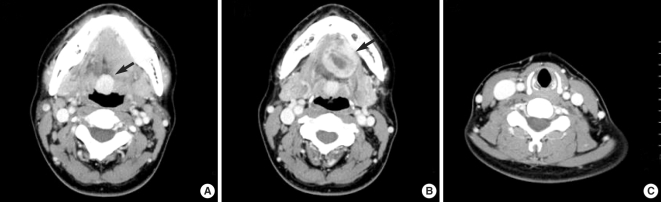
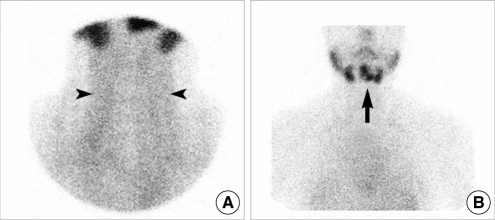
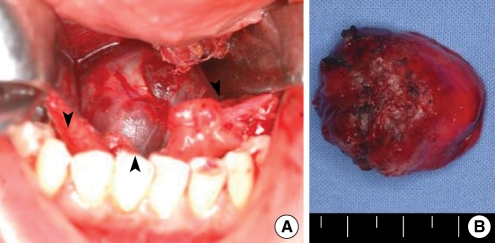
- Ectopic thyroid tissue is an uncommon embryologic aberration characterized by the presence of thyroid tissue in a site other than its usual pre-tracheal location. Single ectopic thyroid tissue is the most common variant, and the base of the tongue is the most frequent ectopic location. Dual ectopic thyroid is extremely rare, and only eleven cases have been reported in the English literature. Furthermore, adenomatous hyperplasia has never been reported to arise from dual ectopic thyroid. There has been only one reported case of adenomatous hyperplasia arising from a single intratracheal ectopic thyroid. We report a case of adenomatous hyperplasia arising from dual ectopic thyroid tissue that presented as a sublingual mass in a 37-yr-old woman. The diagnosis was made through pathologic examination after surgical resection. We also discuss the diagnosis and treatment of ectopic thyroid, along with a review of the literature.
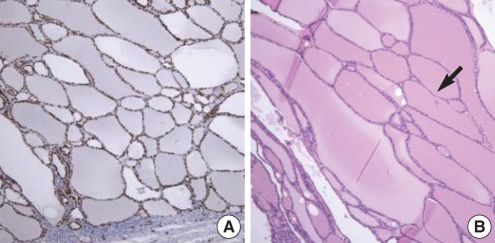
Figure
Reference
-
1. Leung AK, Wong AL, Robson WL. Ectopic thyroid gland simulating a thyroglossal duct cyst: a case report. Can J Surg. 1995; 2. 38(1):87–89. PMID: 7882219.2. Ulug T, Ulubil SA, Alagol F. Dual ectopic thyroid: report of a case. J Laryngol Otol. 2003; 7. 117(7):574–576. PMID: 12901819.
Article3. Sung YM, Lee KS, Han J, Cho EY. Intratracheal ectopic thyroid tissue with adenomatous hyperplasia in a pregnant woman. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2008; 2. 190(2):W161–W163. PMID: 18212201.
Article4. Bayat MR, Vawda F, Campbell H. Dual ectopic thyroid. Clin Radiol. 2005; 7. 60(7):821–825. PMID: 15978895.
Article5. Baik SH, Choi JH, Lee HM. Dual ectopic thyroid. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2002; 2. 259(2):105–107. PMID: 11954930.
Article6. Kumar R, Khullar S, Gupta R, Marwah A, Drm MA. Dual thyroid ectopy: case report and review of the literature. Clin Nucl Med. 2000; 4. 25(4):253–254. PMID: 10750961.7. Arancibia P, Veliz J, Barria M, Pineda G. Lingual thyroid: report of three cases. Thyroid. 1998; 11. 8(11):1055–1057. PMID: 9848723.
Article8. Mussak EN, Kacker A. Surgical and medical management of midline ectopic thyroid. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2007; 6. 136(6):870–872. PMID: 17547972.
Article9. Misaki T, Koh T, Shimbo S, Kasagi K, Konishi J. Dual-site thyroid ectopy in a mother and son. Thyroid. 1992; Winter. 2(4):325–327. PMID: 1493375.
Article10. Conklin WT, Davis RM, Dabb RW, Reilly CM. Hypothyroidism following removal of a "thyroglossal duct cyst". Plast Reconstr Surg. 1981; 12. 68(6):930–932. PMID: 7301988.
Article11. Helidonis E, Dokianakis G, Papazoglou G, Pantazopoulos P, Thomopoulou H. Ectopic thyroid gland in the submandibular region. J Laryngol Otol. 1980; 2. 94(2):219–224. PMID: 7373125.
Article12. Katz AD, Zager WJ. The lingual thyroid: its diagnosis and treatment. Arch Surg. 1971; 6. 102(6):582–585. PMID: 5577049.