Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol.
2012 Mar;5(1):28-33.
Open-Label Observational Study for Evaluating the Short-term Benefits of Rabeprazole Medication on Laryngopharyngeal Reflux
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Social & Preventive Medicine, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea.
- 2Department of Otolaryngology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Otolaryngology-Head & Neck Surgery, The Catholic University of Korea School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head & Neck Surgery, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. yison@skku.edu
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
The aims of this study were to determine the benefits of short-term empirical proton pump inhibitor (PPI) medication on laryngopharyngeal reflux (LPR) and to determine whether scores on the reflux symptom index (RSI) and the reflux finding score (RFS) could be combined to identify subgroups of patients that will more likely to improve with this medication.
METHODS
Fifty-one Korean Otolaryngology Board-certified specialists joined this prospective, multi-center, and open-label observational study. A total of 1,142 adult patients with LPR was enrolled for 12 weeks of rabeprazol medication. According to pre-treatment scores on RSI and RFS, patients were divided into 4 subgroups. RFS and RSI were measured repeatedly with a month interval along the treatment period. Changes of RSI and RFS were analyzed in an overall study cohort as well as in each subgroup.
RESULTS
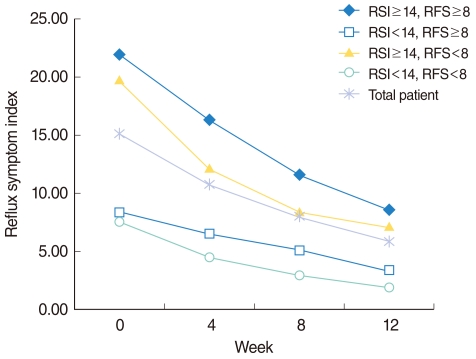
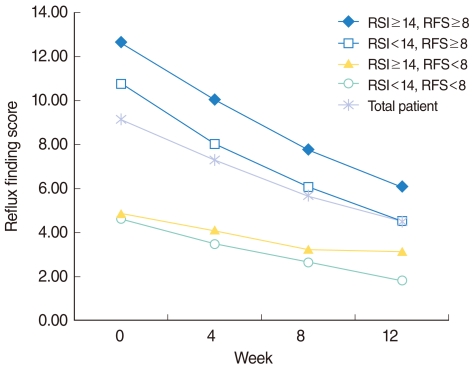
Approximately 40% (n=455) of enrolled patients were followed up until 12 weeks of PPI treatment. Significant improvement in RSI was obtained in 29%, 58%, and 75% of patients after 4, 8, and 12 weeks of PPI medication. RFS was improved in 16%, 42%, and 57% of the patients with 4, 8, and 12 weeks of PPI medication. All subgroups showed improvement regardless of their pre-treatment scores on the RSI and RFS.
CONCLUSION
Even though RSI and RFS may be used as a general guideline for LPR management, pre-treatment RSI and RFS are not useful in predicting the patients' response to short-term PPI medication in the usual pattern of practice for LPR, which is mostly based on the physical evaluation and history taking.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Koufman JA. The otolaryngologic manifestations of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD): a clinical investigation of 225 patients using ambulatory 24-hour pH monitoring and an experimental investigation of the role of acid and pepsin in the development of laryngeal injury. Laryngoscope. 1991; 4. 101(4 Pt 2 Suppl 53):1–78. PMID: 1895864.2. Book DT, Rhee JS, Toohill RJ, Smith TL. Perspectives in laryngopharyngeal reflux: an international survey. Laryngoscope. 2002; 8. 112(8 Pt 1):1399–1406. PMID: 12172252.
Article3. Fraser AG. Review article: gastro-oesophageal reflux and laryngeal symptoms. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 1994; 6. 8(3):265–272. PMID: 7918920.
Article4. Bove MJ, Rosen C. Diagnosis and management of laryngopharyngeal reflux disease. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2006; 6. 14(3):116–123. PMID: 16728885.5. Tutuian R, Castell DO. Diagnosis of laryngopharyngeal reflux. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2004; 6. 12(3):174–179. PMID: 15167025.6. Belafsky PC, Postma GN, Koufman JA. Laryngopharyngeal reflux symptoms improve before changes in physical findings. Laryngoscope. 2001; 6. 111(6):979–981. PMID: 11404607.
Article7. Qadeer MA, Swoger J, Milstein C, Hicks DM, Ponsky J, Richter JE, et al. Correlation between symptoms and laryngeal signs in laryngopharyngeal reflux. Laryngoscope. 2005; 11. 115(11):1947–1952. PMID: 16319603.
Article8. Ford CN. Evaluation and management of laryngopharyngeal reflux. JAMA. 2005; 9. 28. 294(12):1534–1540. PMID: 16189367.
Article9. Belafsky PC, Postma GN, Koufman JA. Validity and reliability of the reflux symptom index (RSI). J Voice. 2002; 6. 16(2):274–277. PMID: 12150380.
Article10. Belafsky PC, Postma GN, Koufman JA. The validity and reliability of the reflux finding score (RFS). Laryngoscope. 2001; 8. 111(8):1313–1317. PMID: 11568561.
Article11. Mesallam TA, Stemple JC, Sobeih TM, Elluru RG. Reflux symptom index versus reflux finding score. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2007; 6. 116(6):436–440. PMID: 17672246.
Article12. Kelchner LN, Horne J, Lee L, Klaben B, Stemple JC, Adam S, et al. Reliability of speech-language pathologist and otolaryngologist ratings of laryngeal signs of reflux in an asymptomatic population using the reflux finding score. J Voice. 2007; 1. 21(1):92–100. PMID: 16546351.
Article13. Branski RC, Bhattacharyya N, Shapiro J. The reliability of the assessment of endoscopic laryngeal findings associated with laryngopharyngeal reflux disease. Laryngoscope. 2002; 6. 112(6):1019–1024. PMID: 12160267.
Article14. Karkos PD, Benton J, Leong SC, Karkanevatos A, Badran K, Srinivasan VR, et al. Trends in laryngopharyngeal reflux: a British ENT survey. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2007; 5. 264(5):513–517. PMID: 17404773.
Article15. Gupta R, Sataloff RT. Laryngopharyngeal reflux: current concepts and questions. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2009; 6. 17(3):143–148. PMID: 19395970.
Article16. Fass R. Empirical trials in treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Dig Dis. 2000; 18(1):20–26. PMID: 10729734.
Article17. Reichel O, Dressel H, Wiederanders K, Issing WJ. Double-blind, placebo-controlled trial with esomeprazole for symptoms and signs associated with laryngopharyngeal reflux. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2008; 9. 139(3):414–420. PMID: 18722223.
Article18. Siupsinskiene N, Adamonis K, Toohill RJ, Sereika R. Predictors of response to short-term proton pump inhibitor treatment in laryngopharyngeal reflux patients. J Laryngol Otol. 2008; 11. 122(11):1206–1212. PMID: 18331659.
Article19. Park W, Hicks DM, Khandwala F, Richter JE, Abelson TI, Milstein C, et al. Laryngopharyngeal reflux: prospective cohort study evaluating optimal dose of proton-pump inhibitor therapy and pretherapy predictors of response. Laryngoscope. 2005; 7. 115(7):1230–1238. PMID: 15995512.
Article20. Williams RB, Szczesniak MM, Maclean JC, Brake HM, Cole IE, Cook IJ. Predictors of outcome in an open label, therapeutic trial of high-dose omeprazole in laryngitis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2004; 5. 99(5):777–785. PMID: 15128336.
Article21. Fraser AG, Morton RP, Gillibrand J. Presumed laryngo-pharyngeal reflux: investigate or treat? J Laryngol Otol. 2000; 6. 114(6):441–447. PMID: 10962677.
Article22. Lam PK, Ng ML, Cheung TK, Wong BY, Tan VP, Fong DY, et al. Rabeprazole is effective in treating laryngopharyngeal reflux in a randomized placebo-controlled trial. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010; 9. 8(9):770–776. PMID: 20303417.
Article23. Friedman M, Maley A, Kelley K, Pulver T, Foster M, Fisher M, et al. Impact of pH monitoring on laryngopharyngeal reflux treatment: improved compliance and symptom resolution. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2011; 4. 144(4):558–562. PMID: 21493235.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Efficacy of 4-week Short-term Therapy with Proton Pump Inhibitor as an Initial Treatment Regimen for the Patients with Laryngopharyngeal Reflux
- Change of Voice Quality before and after Treatment of Short-Term Therapy with Proton Pump Inhibitor in Laryngopharyngeal Reflux
- Electrical Stimulation Therapy for Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
- The Usefulness of Esophagography as a Screening Test for Laryngopharyngeal Reflux
- Mapping Regional Laryngopharyngeal Mechanoreceptor Response