Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol.
2014 Jun;7(2):102-105.
The Efficacy of Preemptive Analgesia With Pregabalin in Septoplasty
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rhinology, HANA ENT HOSPITAL, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. hjdhong@skku.ed
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
Pregabalin is used to treat neuropathic pain and has shown analgesic properties in postoperative pain. The aim of this study was to investigate the effectiveness and safety of pregabalin in reducing postoperative pain in patients after septoplasty.
METHODS
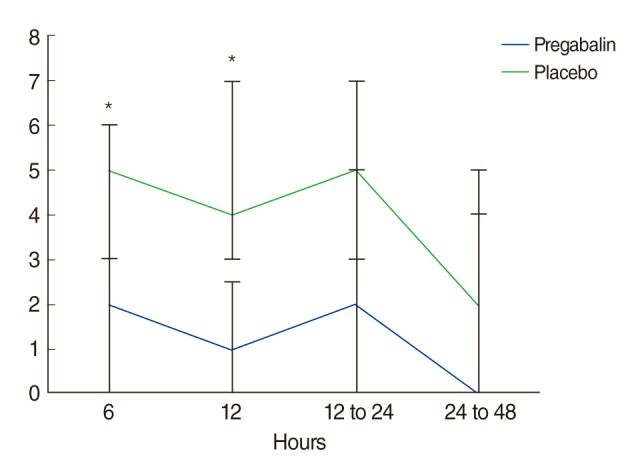
Forty-seven patients scheduled for elective septoplasty were randomly assigned to groups that received either pregabalin (150 mg) or placebo, both one hour before surgery and 12 hours after the initial dose. Pain (verbal numerical rating scale, VNRS) and side effect assessments were performed at 6, 12, 12 to 24, and 24 to 48 hours postoperatively.
RESULTS
From 1 to 12 hours postoperatively, VNRS scores for pain were lower in the pregabalin group (n=24) than in the placebo group (n=23; P<0.05). The number of patients who needed rescue analgesics was lower in the pregabalin group (P=0.042). The incidence of nausea and vomiting did not differ between groups (P=0.666), and the incidence of sedation was higher in the placebo groups (P=0.022).
CONCLUSION
The perioperative administration of oral pregabalin (150 mg twice) is an effective and safe way to reduce early postoperative pain in patients undergoing septoplasty.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Dubin MR, Pletcher SD. Postoperative packing after septoplasty: is it necessary. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 2009; 4. 42(2):279–285. PMID: 19328892.
Article2. Dahl JB, Mathiesen O, Moiniche S. 'Protective premedication': an option with gabapentin and related drugs? A review of gabapentin and pregabalin in in the treatment of post-operative pain. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2004; 10. 48(9):1130–1136. PMID: 15352959.3. Agarwal A, Gautam S, Gupta D, Agarwal S, Singh PK, Singh U. Evaluation of a single preoperative dose of pregabalin for attenuation of postoperative pain after laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Br J Anaesth. 2008; 11. 101(5):700–704. PMID: 18716003.
Article4. Jokela R, Ahonen J, Tallgren M, Haanpaa M, Korttila K. A randomized controlled trial of perioperative administration of pregabalin for pain after laparoscopic hysterectomy. Pain. 2008; 1. 134(1-2):106–112. PMID: 17507163.
Article5. Jokela R, Ahonen J, Tallgren M, Haanpaa M, Korttila K. Premedication with pregabalin 75 or 150 mg with ibuprofen to control pain after day-case gynaecological laparoscopic surgery. Br J Anaesth. 2008; 6. 100(6):834–840. PMID: 18448418.
Article6. Kim SY, Jeong JJ, Chung WY, Kim HJ, Nam KH, Shim YH. Perioperative administration of pregabalin for pain after robot-assisted endoscopic thyroidectomy: a randomized clinical trial. Surg Endosc. 2010; 11. 24(11):2776–2781. PMID: 20376496.
Article7. Kim SY, Song JW, Park B, Park S, An YJ, Shim YH. Pregabalin reduces post-operative pain after mastectomy: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2011; 3. 55(3):290–296. PMID: 21288209.
Article8. Mathiesen O, Jacobsen LS, Holm HE, Randall S, Adamiec-Malmstroem L, Graungaard BK, et al. Pregabalin and dexamethasone for postoperative pain control: a randomized controlled study in hip arthroplasty. Br J Anaesth. 2008; 10. 101(4):535–541. PMID: 18653493.
Article9. Woolf CJ. Evidence for a central component of post-injury pain hypersensitivity. Nature. 1983; 12. 306(5944):686–688. PMID: 6656869.
Article10. Turan A, Memis D, Karamanlioglu B, Yagiz R, Pamukcu Z, Yavuz E. The analgesic effects of gabapentin in monitored anesthesia care for ear-nose-throat surgery. Anesth Analg. 2004; 8. 99(2):375–378. PMID: 15271709.
Article11. Reuben SS, Buvanendran A, Kroin JS, Raghunathan K. The analgesic efficacy of celecoxib, pregabalin, and their combination for spinal fusion surgery. Anesth Analg. 2006; 11. 103(5):1271–1277. PMID: 17056968.12. Freedman BM, O'Hara E. Pregabalin has opioid-sparing effects following augmentation mammaplasty. Aesthet Surg J. 2008; Jul-Aug. 28(4):421–424. PMID: 19083556.
Article13. Mathiesen O, Rasmussen ML, Dierking G, Lech K, Hilsted KL, Fomsgaard JS, et al. Pregabalin and dexamethasone in combination with paracetamol for postoperative pain control after abdominal hysterectomy: a randomized clinical trial. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2009; 2. 53(2):227–235. PMID: 19076108.
Article14. Mathiesen O, Moiniche S, Dahl JB. Gabapentin and postoperative pain: a qualitative and quantitative systematic review, with focus on procedure. BMC Anesthesiol. 2007; 7. 7:6. PMID: 17617920.
Article15. Tiippana EM, Hamunen K, Kontinen VK, Kalso E. Do surgical patients benefit from perioperative gabapentin/pregabalin? A systematic review of efficacy and safety. Anesth Analg. 2007; 6. 104(6):1545–1556. PMID: 17513656.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effects of pregabalin and gabapentin on postoperative pain and opioid consumption after laparoscopic cholecystectomy
- Pharmacotherapy of Generalized Anxiety Disorder and Pregabalin
- Effect of Preemptive vs Postoperative Continuous Epidural Analgesia on Postoperative Pain after Radical Gastrectomy
- A Study on Efficacy of Preemptive Analgesia: A Comparison on Efficacy of Preoperative and Postoperative Analgesic Administration
- Preemptive pregabalin for postoperative analgesia during minimally invasive hysterectomy: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials