Comparison of the Efficacy of Caudal, Interlaminar, and Transforaminal Epidural Injections in Managing Lumbar Disc Herniation: Is One Method Superior to the Other?
- Affiliations
-
- 1Pain Management Center of Paducah, Paducah, USA. drlm@thepainmd.com
- 2Pain Management Center of University of Louisville, Louisville, KY, USA.
- 3Spine Pain Diagnostics Associates, Niagara, WI, USA.
- 4Mid Atlantic Spine & Pain Physicians, Newark, DE, USA.
- 5Temple University Hospital, Philadelphia, PA, 5Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA.
- KMID: 2278248
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2015.28.1.11
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Epidural injections are performed utilizing 3 approaches in the lumbar spine: caudal, interlaminar, and transforaminal. The literature on the efficacy of epidural injections has been sporadic. There are few high-quality randomized trials performed under fluoroscopy in managing disc herniation that have a long-term follow-up and appropriate outcome parameters. There is also a lack of literature comparing the efficacy of these 3 approaches.
METHODS
This manuscript analyzes data from 3 randomized controlled trials that assessed a total of 360 patients with lumbar disc herniation. There were 120 patients per trial either receiving local anesthetic alone (60 patients) or local anesthetic with steroids (60 patients).
RESULTS
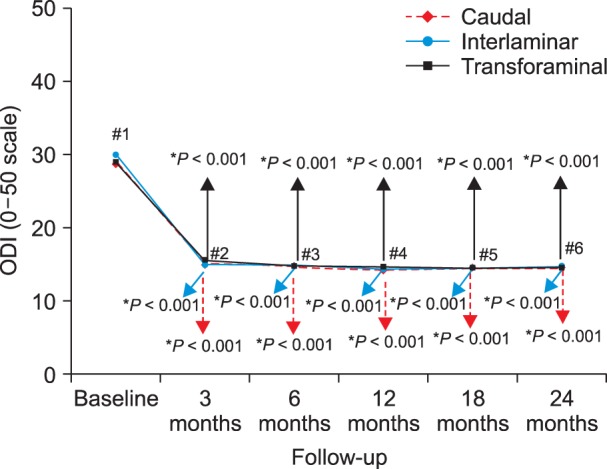
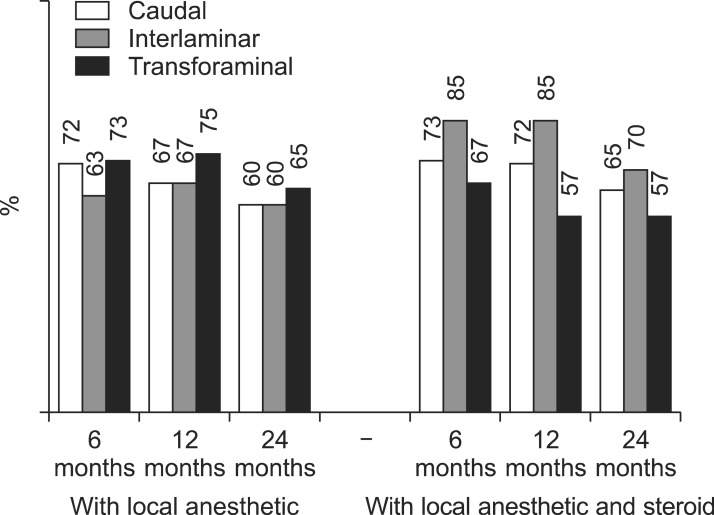
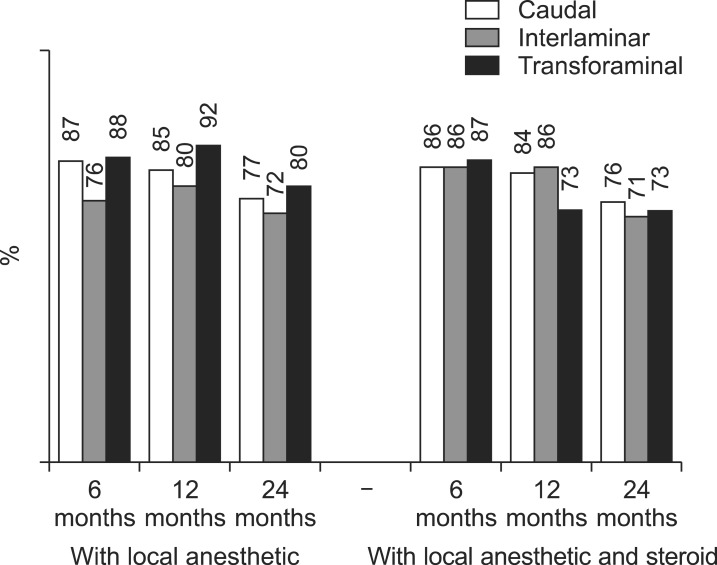
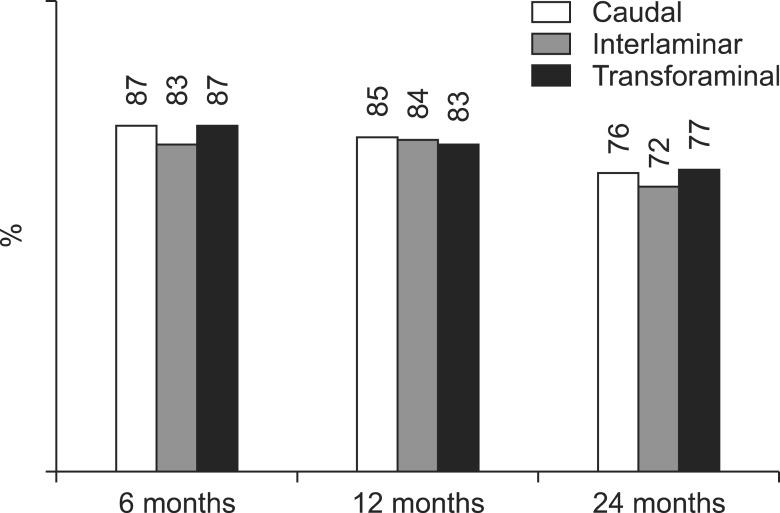
Analysis showed similar efficacy for caudal, interlaminar, and transforaminal approaches in managing chronic pain and disability from disc herniation. The analysis of caudal epidural injections showed the potential superiority of steroids compared with local anesthetic alone a 2-year follow-up, based on the average relief per procedure. In the interlaminar group, results were somewhat superior for pain relief in the steroid group at 6 months and functional status at 12 months. Interlaminar epidurals provided improvement in a significantly higher proportion of patients. The proportion of patients nonresponsive to initial injections was also lower in the group for local anesthetic with steroid in the interlaminar trial.
CONCLUSIONS
The results of this assessment show significant improvement in patients suffering from chronic lumbar disc herniation with 3 lumbar epidural approaches with local anesthetic alone, or using steroids with long-term follow-up of up to 2 years, in a contemporary interventional pain management setting.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 8 articles
-
In Response to Risks and Pitfalls of Epidural Injections during Management of Lumbar Disc Herniation: Few Comments
Laxmaiah Manchikanti, Joshua A. Hirsch
Korean J Pain. 2015;28(3):219-220. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2015.28.3.219.Risks and Pitfalls of Epidural Injections during Management of Lumbar Disc Herniation: Few Comments
Mohammad Sadegh Sanie, Mohamed Amin Ghobadifar
Korean J Pain. 2015;28(3):217-218. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2015.28.3.217.What is the Role of Epidural Injections in the Treatment of Lumbar Discogenic Pain: A Systematic Review of Comparative Analysis with Fusion
Laxmaiah Manchikanti, Peter S. Staats, Devi E. Nampiaparampil, Joshua A. Hirsch
Korean J Pain. 2015;28(2):75-87. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2015.28.2.75.Comparison of clinical efficacy in epidural steroid injections through transforaminal or parasagittal approaches
Ji Hee Hong, Eun Kyul Park, Ki Bum Park, Ji Hoon Park, Sung Won Jung
Korean J Pain. 2017;30(3):220-228. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2017.30.3.220.Effect of epidural corticosteroid injection on magnetic resonance imaging findings
Min Soo Kim, Tae Yoon Jeong, Yu Seon Cheong, Young Wook Jeon, So Young Lim, Seong Sik Kang, In Nam Kim, Tsong Bin Chang, Hyun Ho Seong, Byeong Mun Hwang
Korean J Pain. 2017;30(4):281-286. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2017.30.4.281.Therapeutic lumbar facet joint nerve blocks in the treatment of chronic low back pain: cost utility analysis based on a randomized controlled trial
Laxmaiah Manchikanti, Vidyasagar Pampati, Alan D. Kaye, Joshua A. Hirsch
Korean J Pain. 2018;31(1):27-38. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2018.31.1.27.Effect of needle type on intravascular injection in transforaminal epidural injection: a meta-analysis
Jae Yun Kim, Soo Nyoung Kim, Chulmin Park, Ho Young Lim, Jae Hun Kim
Korean J Pain. 2019;32(1):39-46. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2019.32.1.39.Digital subtraction angiography vs. real-time fluoroscopy for detection of intravascular injection during transforaminal epidural block
Kibeom Park, Saeyoung Kim
Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2019;36(2):109-114. doi: 10.12701/yujm.2019.00122.
Reference
-
1. Birkmeyer NJ, Weinstein JN, Tosteson AN, Tosteson TD, Skinner JS, Lurie JD, et al. Design of the Spine Patient outcomes Research Trial (SPORT). Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2002; 27:1361–1372. PMID: 12065987.
Article2. Radcliff K, Hilibrand A, Lurie JD, Tosteson TD, Delasotta L, Rihn J, et al. The impact of epidural steroid injections on the outcomes of patients treated for lumbar disc herniation: a subgroup analysis of the SPORT trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012; 94:1353–1358. PMID: 22739998.
Article3. Lurie JD, Tosteson TD, Tosteson AN, Zhao W, Morgan TS, Abdu WA, et al. Surgical versus nonoperative treatment for lumbar disc herniation: eight-year results for the spine patient outcomes research trial. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2014; 39:3–16. PMID: 24153171.4. Mixter WJ, Barr JS. Rupture of the intervertebral disc with involvement of the spinal canal. N Engl J Med. 1934; 211:210–215.
Article5. Manson NA, McKeon MD, Abraham EP. Transforaminal epidural steroid injections prevent the need for surgery in patients with sciatica secondary to lumbar disc herniation: a retrospective case series. Can J Surg. 2013; 56:89–96. PMID: 23351495.
Article6. Manchikanti L, Falco FJ, Singh V, Pampati V, Parr AT, Benyamin RM, et al. Utilization of interventional techniques in managing chronic pain in the Medicare population: analysis of growth patterns from 2000 to 2011. Pain Physician. 2012; 15:E969–E982. PMID: 23159982.7. Manchikanti L, Helm Ii S, Singh V, Hirsch JA. Accountable interventional pain management: a collaboration among practitioners, patients, payers, and government. Pain Physician. 2013; 16:E635–E670. PMID: 24284849.8. Manchikanti L, Abdi S, Atluri S, Benyamin RM, Boswell MV, Buenaventura RM, et al. An update of comprehensive evidence-based guidelines for interventional techniques in chronic spinal pain. Part II: guidance and recommendations. Pain Physician. 2013; 16:S49–283. PMID: 23615883.9. Benyamin RM, Manchikanti L, Parr AT, Diwan S, Singh V, Falco FJ, et al. The effectiveness of lumbar interlaminar epidural injections in managing chronic low back and lower extremity pain. Pain Physician. 2012; 15:E363–E404. PMID: 22828691.10. Parr AT, Manchikanti L, Hameed H, Conn A, Manchikanti KN, Benyamin RM, et al. Caudal epidural injections in the management of chronic low back pain: a systematic appraisal of the literature. Pain Physician. 2012; 15:E159–E198. PMID: 22622911.11. Manchikanti L, Buenaventura RM, Manchikanti KN, Ruan X, Gupta S, Smith HS, et al. Effectiveness of therapeutic lumbar transforaminal epidural steroid injections in managing lumbar spinal pain. Pain Physician. 2012; 15:E199–E245. PMID: 22622912.12. Pinto RZ, Maher CG, Ferreira ML, Hancock M, Oliveira VC, McLachlan AJ, et al. Epidural corticosteroid injections in the management of sciatica: a systematic review and metaanalysis. Ann Intern Med. 2012; 157:865–877. PMID: 23362516.
Article13. Manchikanti L, Benyamin RM, Falco FJ, Kaye AD, Hirsch JA. Do epidural injections provide short- and long-term relief for lumbar disc herniation? A systematic review. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014; [in press].
Article14. Manchikanti L, Singh V, Cash KA, Pampati V, Damron KS, Boswell MV. Effect of fluoroscopically guided caudal epidural steroid or local anesthetic injections in the treatment of lumbar disc herniation and radiculitis: a randomized, controlled, double blind trial with a two-year follow-up. Pain Physician. 2012; 15:273–286. PMID: 22828681.15. Manchikanti L, Singh V, Cash KA, Pampati V, Falco FJ. A randomized, double-blind, active-control trial of the effectiveness of lumbar interlaminar epidural injections in disc herniation. Pain Physician. 2014; 17:E61–E74. PMID: 24452658.16. Manchikanti L, Cash KA, Pampati V, Falco FJ. Transforaminal epidural injections in chronic lumbar disc herniation: a randomized, double-blind, active-control trial. Pain Physician. 2014; 17:E489–E501. PMID: 25054399.17. Manchikanti L, Falco FJ, Pampati V, Cash KA, Benyamin RM, Hirsch JA. Cost utility analysis of caudal epidural injections in the treatment of lumbar disc herniation, axial or discogenic low back pain, central spinal stenosis, and post lumbar surgery syndrome. Pain Physician. 2013; 16:E129–E143. PMID: 23703415.18. Martin BI, Deyo RA, Mirza SK, Turner JA, Comstock BA, Hollingworth W, et al. Expenditures and health status among adults with back and neck problems. JAMA. 2008; 299:656–664. PMID: 18270354.
Article19. US Burden of Disease Collaborators. The state of US health, 1990-2010: burden of diseases, injuries, and risk factors. JAMA. 2013; 310:591–608. PMID: 23842577.20. Rajaee SS, Bae HW, Kanim LE, Delamarter RB. Spinal fusion in the United States: analysis of trends from 1998 to 2008. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2012; 37:67–76. PMID: 21311399.21. Manchikanti L, Cash KA, McManus CD, Pampati V, Fellows B. Results of 2-year follow-up of a randomized, double-blind, controlled trial of fluoroscopic caudal epidural injections in central spinal stenosis. Pain Physician. 2012; 15:371–384. PMID: 22996849.22. Manchikanti L, Cash KA, McManus CD, Pampati V. Fluoroscopic caudal epidural injections in managing chronic axial low back pain without disc herniation, radiculitis, or facet joint pain. J Pain Res. 2012; 5:381–390. PMID: 23091395.
Article23. Manchikanti L, Singh V, Cash KA, Pampati V, Datta S. Fluoroscopic caudal epidural injections in managing post lumbar surgery syndrome: two-year results of a randomized, double-blind, active-control trial. Int J Med Sci. 2012; 9:582–591. PMID: 23028241.
Article24. Manchikanti L, Cash KA, McManus CD, Pampati V, Benyamin RM. A randomized, double-blind, active-controlled trial of fluoroscopic lumbar interlaminar epidural injections in chronic axial or discogenic low back pain: results of 2-year follow-up. Pain Physician. 2013; 16:E491–E504. PMID: 24077199.25. Manchikanti L, Cash KA, McManus CD, Damron KS, Pampati V, Falco FJ. Lumbar interlaminar epidural injections in central spinal stenosis: preliminary results of a randomized, double-blind, active control trial. Pain Physician. 2012; 15:51–63. PMID: 22270738.26. Manchikanti L, Cash KA, Pampati V, Malla Y. Two-year follow-up results of fluoroscopic cervical epidural injections in chronic axial or discogenic neck pain: a randomized, double-blind, controlled trial. Int J Med Sci. 2014; 11:309–320. PMID: 24578607.
Article27. Manchikanti L, Malla Y, Cash KA, McManus CD, Pampati V. Fluoroscopic epidural injections in cervical spinal stenosis: preliminary results of a randomized, double-blind, active control trial. Pain Physician. 2012; 15:E59–E70. PMID: 22270749.28. Manchikanti L, Malla Y, Cash KA, McManus CD, Pampati V. Fluoroscopic cervical interlaminar epidural injections in managing chronic pain of cervical postsurgery syndrome: preliminary results of a randomized, double-blind, active control trial. Pain Physician. 2012; 15:13–25. PMID: 22270734.29. Bicket MC, Gupta A, Brown CH 4th, Cohen SP. Epidural injections for spinal pain: a systematic review and metaanalysis evaluating the "control" injections in randomized controlled trials. Anesthesiology. 2013; 119:907–931. PMID: 24195874.30. National Institutes of Health, Warren Grant Magnuson Clinical Center (US). Pain intensity instruments July 2003. 0-10 Numeric rating scale [Internet]. Bethesda (MA): Warren Grant Magnuson Clinical Center;2003. Available at http://www.mvltca.net/Presentations/mvltca.pdf.31. Fairbank JC, Pynsent PB. The oswestry disability index. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2000; 25:2940–2952. PMID: 11074683.
Article32. Manchikanti L, Falco FJ, Benyamin RM, Helm S 2nd, Singh V, Hirsch JA. Value-based interventional pain management: a review of medicare national and local coverage determination policies. Pain Physician. 2013; 16:E145–E180. PMID: 23703416.33. Chou R, Atlas SJ, Loeser JD, Rosenquist RW, Stanos SP. Guideline warfare over interventional therapies for low back pain: can we raise the level of discourse? J Pain. 2011; 12:833–839. PMID: 21742563.
Article34. Manchikanti L, Benyamin RM, Falco FJ, Caraway DL, Datta S, Hirsch JA. Guidelines warfare over interventional techniques: is there a lack of discourse or straw man? Pain Physician. 2012; 15:E1–26. PMID: 22270745.35. Ackerman WE 3rd, Ahmad M. The efficacy of lumbar epidural steroid injections in patients with lumbar disc herniations. Anesth Analg. 2007; 104:1217–1222. PMID: 17456677.
Article36. Tunis SR, Stryer DB, Clancy CM. Practical clinical trials: increasing the value of clinical research for decision making in clinical and health policy. JAMA. 2003; 290:1624–1632. PMID: 14506122.37. ICH Expert Working Group (CH). International conference on harmonisation of technical requirements for registration of pharmaceuticals for human use. ICH harmonised tripartite guideline. Choice of control group and related issues in clinical trials E10 [Internet]. Geneva: ICH Expert Working Group;2000. 7. 20. Available at http://www.ich.org/fileadmin/Public_Web_Site/ICH_Products/Guidelines/Efficacy/E10/Step4/E10_Guideline.pdf.38. Ghahreman A, Ferch R, Bogduk N. The efficacy of transforaminal injection of steroids for the treatment of lumbar radicular pain. Pain Med. 2010; 11:1149–1168. PMID: 20704666.
Article39. Karppinen J, Malmivaara A, Kurunlahti M, Kyllönen E, Pienimäki T, Nieminen P, et al. Periradicular infiltration for sciatica: a randomized controlled trial. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001; 26:1059–1067. PMID: 11337625.40. Iversen T, Solberg TK, Romner B, Wilsgaard T, Twisk J, Anke A, et al. Effect of caudal epidural steroid or saline injection in chronic lumbar radiculopathy: multicentre, blinded, randomised controlled trial. BMJ. 2011; 343:d5278. PMID: 21914755.
Article41. Gerdesmeyer L, Wagenpfeil S, Birkenmaier C, Veihelmann A, Hauschild M, Wagner K, et al. Percutaneous epidural lysis of adhesions in chronic lumbar radicular pain: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Pain Physician. 2013; 16:185–196. PMID: 23703406.42. Arden NK, Price C, Reading I, Stubbing J, Hazelgrove J, Dunne C, et al. A multicentre randomized controlled trial of epidural corticosteroid injections for sciatica: the WEST study. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2005; 44:1399–1406. PMID: 16030082.
Article43. Dilke TF, Burry HC, Grahame R. Extradural corticosteroid injection in management of lumbar nerve root compression. Br Med J. 1973; 2:635–637. PMID: 4577015.
Article44. Carette S, Leclaire R, Marcoux S, Morin F, Blaise GA, St-Pierre A, et al. Epidural corticosteroid injections for sciatica due to herniated nucleus pulposus. N Engl J Med. 1997; 336:1634–1640. PMID: 9171065.
Article45. Hróbjartsson A, Gøtzsche PC. Placebo interventions for all clinical conditions. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010; CD003974. PMID: 20091554.
Article46. Howick J, Bishop FL, Heneghan C, Wolstenholme J, Stevens S, Hobbs FD, et al. Placebo use in the United kingdom: results from a national survey of primary care practitioners. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e58247. PMID: 23526969.
Article47. Manchikanti L, Giordano J, Fellows B, Hirsch JA. Placebo and nocebo in interventional pain management: a friend or a foe-or simply foes? Pain Physician. 2011; 14:E157–E175. PMID: 21412379.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of Two Methods of Epidural Steroid Injection in the Treatment of Recurrent Lumbar Disc Herniation
- Comparison of the Effects between Interlaminar Epidural Block and Transforaminal Epidural Block under C-arm Guide in Lumbar Disc Herniated Radiculopathy
- Oblique interlaminar lumbar epidural steroid injection for management of low back pain with lumbosacral radicular pain: A case report
- What is the Role of Epidural Injections in the Treatment of Lumbar Discogenic Pain: A Systematic Review of Comparative Analysis with Fusion
- Inadvertent discogram during transforaminal epidural injection in patients with lumbar disc herniation: A report of 2 cases