Korean J Pain.
2014 Jan;27(1):72-76. 10.3344/kjp.2014.27.1.72.
Radiofrequency Thermal Ablation in Painful Myeloma of the Clavicle
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Amirmomenin Hospital, Tehran Azad Islamic University of Medical Science, Tehran, Iran. helengharaee@yahoo.com
- 2Anesthesiology and Pain Department, Rasoul-Akram Hospital, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran.
- 3Hematology and Oncology Department, Rasoul-Akram Hospital, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran.
- KMID: 2278206
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2014.27.1.72
Abstract
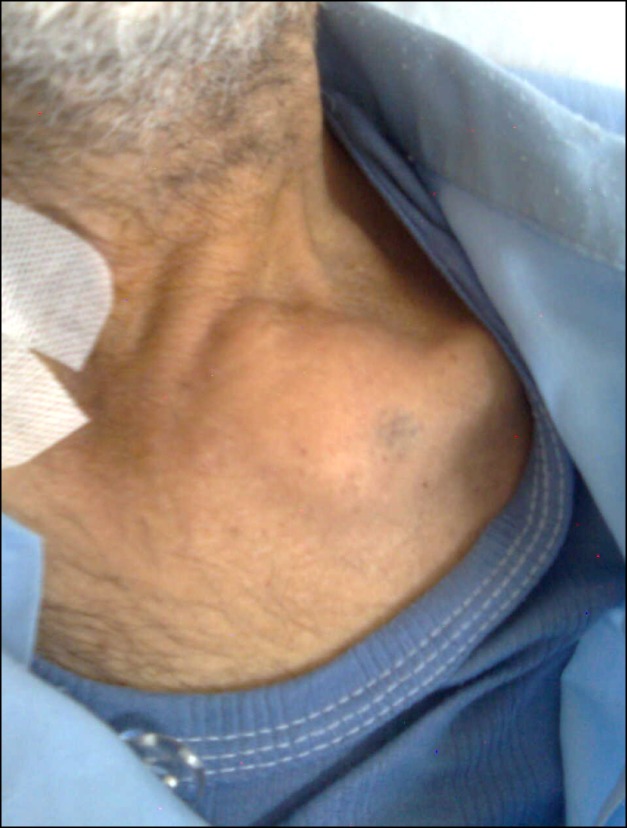
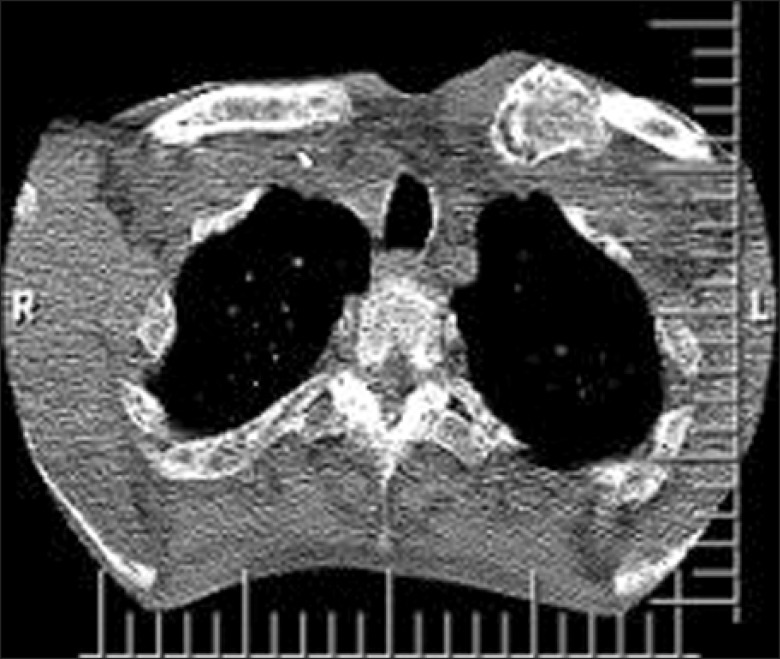
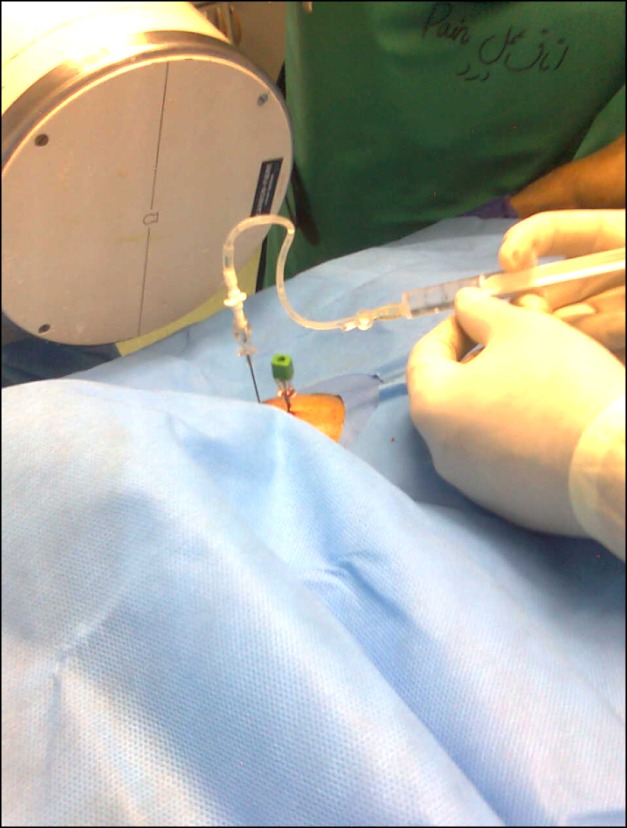
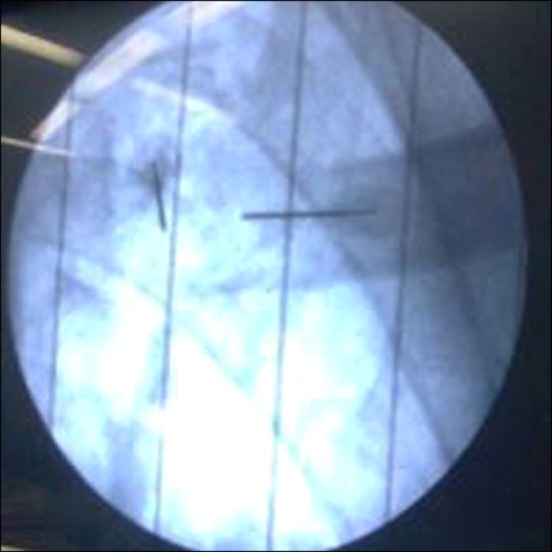
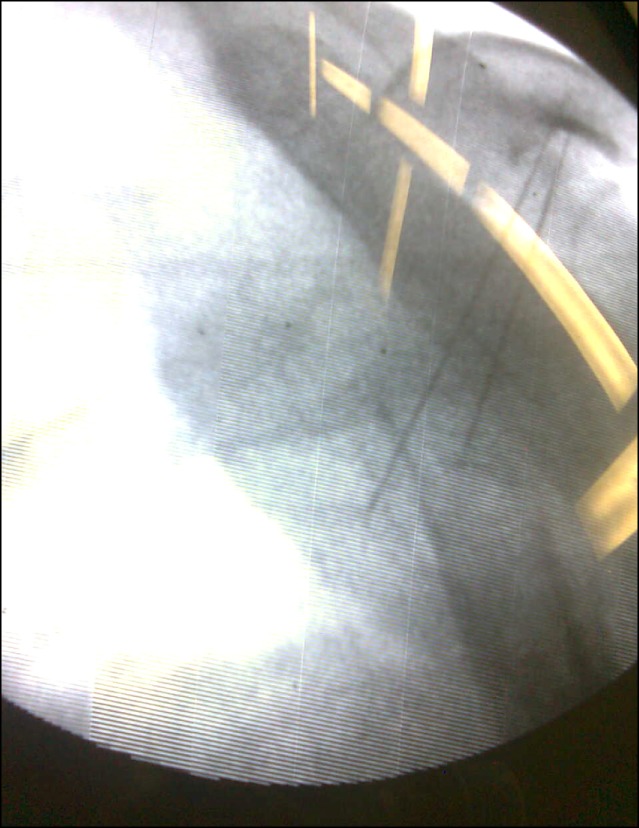
- A 57-year-old male patient had myeloma. He had severe pain in the left clavicle that did not respond to radiotherapy; therefore, it was treated with radiofrequency thermal ablation (RFTA). Under fluoroscopic guidance, two RF needles at a distance of 1.5 cm from each other were inserted into the mass and conventional radiofrequency (90degrees C and 60 seconds) at two different depths (1 cm apart) was applied. Then, 2 ml of 0.5% ropivacaine along with triamcinolone 40 mg was injected in each needle. The visual analogue pain score (VAS from 0 to 10) was decreased from 8 to 0. In the next 3 months of follow-up, the patient was very satisfied with the procedure and the mass gradually became smaller. There were no complications. This study shows that RFTA could be a useful method for pain management in painful osteolytic myeloma lesions in the clavicle.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Rajkumar SV. Plasma cell disorders. In : Goldman L, Schafer AI, editors. Goldman's cecil medicine. 24th ed. Philadelphia (PA): Elsevier Saunders;2012. p. 1237–1240.2. Munshi NC, Longo DL, Anderson KC. Plasma cell disorders. In : Longo DL, Fauci AS, Kasper DL, Hauser SL, Jameson JL, Loscalzo J, editors. Harrison's principle of internal medicine. 18th ed. New York (NY): McGraw-Hill, Medical;2012. p. 941–942.3. Janjan NA. Radiation for bone metastases: conventional techniques and the role of systemic radiopharmaceuticals. Cancer. 1997; 80(8 Suppl):1628–1645. PMID: 9362430.4. Tharmalingam S, Chow E, Harris K, Hird A, Sinclair E. Quality of life measurement in bone metastases: a literature review. J Pain Res. 2008; 1:49–58. PMID: 21197288.5. Schaefer O, Lohrmann C, Herling M, Uhrmeister P, Langer M. Combined radiofrequency thermal ablation and percutaneous cementoplasty treatment of a pathologic fracture. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2002; 13:1047–1050. PMID: 12397128.
Article6. Jeremic B, Shibamoto Y, Acimovic L, Milicic B, Milisavljevic S, Nikolic N, et al. A randomized trial of three single-dose radiation therapy regimens in the treatment of metastatic bone pain. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1998; 42:161–167. PMID: 9747834.
Article7. Helmberger TK. Radiofrequency ablation. In : Vogl TJ, Helmberger TK, Mack MG, Reiser MF, editors. Percutaneous tumor ablation in medical radiology. Berlin: Springer;2008. p. 7–11.8. de Baere T, Elias D, Dromain C, Din MG, Kuoch V, Ducreux M, et al. Radiofrequency ablation of 100 hepatic metastases with a mean follow-up of more than 1 year. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2000; 175:1619–1625. PMID: 11090390.
Article9. Oprée A, Kress M. Involvement of the proinflammatory cytokines tumor necrosis factor-alpha, IL-1 beta, and IL-6 but not IL-8 in the development of heat hyperalgesia: effects on heat-evoked calcitonin gene-related peptide release from rat skin. J Neurosci. 2000; 20:6289–6293. PMID: 10934280.
Article10. Mantyh PW, Clohisy DR, Koltzenburg M, Hunt SP. Molecular mechanisms of cancer pain. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002; 2:201–209. PMID: 11990856.
Article11. Caraceni A, Martini C, Zecca E, Portenoy RK, Ashby MA, Hawson G, et al. Breakthrough pain characteristics and syndromes in patients with cancer pain. An international survey. Palliat Med. 2004; 18:177–183. PMID: 15198130.
Article12. Delaney A, Fleetwood-Walker SM, Colvin LA, Fallon M. Translational medicine: cancer pain mechanisms and management. Br J Anaesth. 2008; 101:87–94. PMID: 18492671.
Article13. Colvin L, Fallon M. Challenges in cancer pain management--bone pain. Eur J Cancer. 2008; 44:1083–1090. PMID: 18439817.
Article14. Smith HS, Mohsin I. Painful boney metastases. Korean J Pain. 2013; 26:223–241. PMID: 23861996.
Article15. Callstrom MR, Charboneau JW. Image-guided palliation of painful metastases using percutaneous ablation. Tech Vasc Interv Radiol. 2007; 10:120–131. PMID: 18070690.
Article16. Dupuy DE, Liu D, Hartfeil D, Hanna L, Blume JD, Ahrar K, et al. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of painful osseous metastases: a multicenter American College of Radiology Imaging Network trial. Cancer. 2010; 116:989–997. PMID: 20041484.
Article17. Simon CJ, Dupuy DE. Percutaneous minimally invasive therapies in the treatment of bone tumors: thermal ablation. Semin Musculoskelet Radiol. 2006; 10:137–144. PMID: 16598666.
Article18. Goetz MP, Callstrom MR, Charboneau JW, Farrell MA, Maus TP, Welch TJ, et al. Percutaneous image-guided radiofrequency ablation of painful metastases involving bone: a multicenter study. J Clin Oncol. 2004; 22:300–306. PMID: 14722039.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Radiofrequency Thermal Ablation of Hepatocellular Carcinomas
- Skin Burn after Laparoscopic Radiofrequency Thermal Ablation for Uterine Myoma : A case report
- A Case of Multiple Myeolma with Huge Tumor Mass in Clavicle
- Short-Term Results of Radiofrequency Thermal Ablation Using VENISTAR Ⓡ in Treatment of Varicose Veins
- Completely Ablated Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Percutaneous Radiofrequency Thermal Ablation