Korean J Pain.
2011 Mar;24(1):44-47. 10.3344/kjp.2011.24.1.44.
Epidural Catheter Malposition in a Failed Epidural Anesthesia Confirmed by Computed Tomography
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, College of Medicine, Soonchunhyang University, Seoul, Korea. pc@schmc.ac.kr
- KMID: 2278096
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2011.24.1.44
Abstract
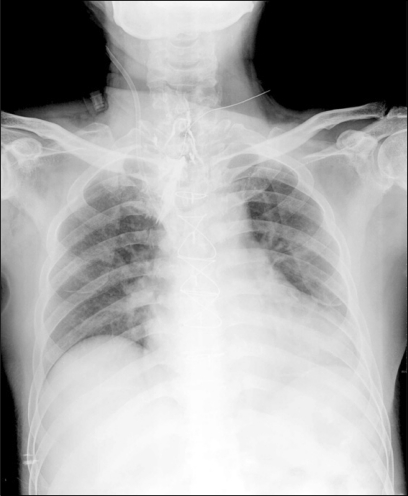
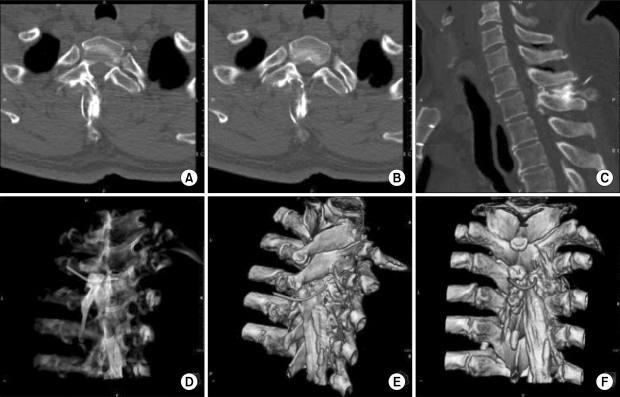
- We report a case of failed epidural anesthesia despite successful identification of the epidural space, loss of resistance technique, hanging drop method and drip infusion. This case evaluated the use of computed tomography to confirm epidural catheter position, which showed the catheter accidentally positioned at the T2 lamina. Because epidural anesthesia can even after successful procedure using standardized techniques such as loss of resistance, we recommend performing the procedure under fluoroscopic guidance to improve success rate and patient safety.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Howell TK, Prosser DP, Harmer M. A change in resistance? A survey of epidural practice amongst obstetric anaesthetists. Anaesthesia. 1998; 53:238–243. PMID: 9613268.
Article2. Kil HK, Cho JE, Kim WO, Koo BN, Han SW, Kim JY. Prepuncture ultrasound-measured distance: an accurate reflection of epidural depth in infants and small children. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2007; 32:102–106. PMID: 17350519.
Article3. Rapp HJ, Folger A, Grau T. Ultrasound-guided epidural catheter insertion in children. Anesth Analg. 2005; 101:333–339. PMID: 16037140.
Article4. Kim SH, Lee KH, Yoon KB, Park WY, Yoon DM. Sonographic estimation of needle depth for cervical epidural blocks. Anesth Analg. 2008; 106:1542–1547. PMID: 18420873.
Article5. Suwa T, Inomata S, Saito S, Toyooka H. Pressure-guided method for identification of the epidural space in children. Anesthesiology. 1998; 89:546–548. PMID: 9710427.
Article6. Matsuda K. Identification of the epidural space using a drip infusion set. Masui. 1977; 26:956–957. PMID: 916183.7. Yamashita M, Tsuji M. Identification of the epidural space in children. The application of a micro-drip infusion set. Anaesthesia. 1991; 46:872–874. PMID: 1952006.8. Yokoyama T, Ushida T, Yamasaki F, Inoue S, Sluka KA. Epidural puncture can be confirmed by the Queckenstedt-test procedure in patients with cervical spinal canal stenosis. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2008; 52:256–261. PMID: 17999711.
Article9. Lechner TJ, van Wijk MG, Maas AJ, van Dorsten FR, Drost RA, Langenberg CJ, et al. Clinical results with the acoustic puncture assist device, a new acoustic device to identify the epidural space. Anesth Analg. 2003; 96:1183–1187. PMID: 12651681.
Article10. Tsui BC, Gupta S, Finucane B. Confirmation of epidural catheter placement using nerve stimulation. Can J Anaesth. 1998; 45:640–644. PMID: 9717595.
Article11. Lee YB, Kim SY, Park JT, Han YK, Yoon KB. On the accuracy of cervicothoracic vertebral level determination by palpation of spinous processes. Korean J Anesthesiol. 1999; 37:608–612.
Article12. Uchino T, Hagiwara S, Iwasaka H, Kudo K, Takatani J, Mizutani A, et al. Use of imaging agent to determine postoperative indwelling epidural catheter position. Korean J Pain. 2010; 23:247–253. PMID: 21217888.
Article13. Rissanen PM. The surgical anatomy and pathology of the supraspinous and interspinous ligaments of the lumbar spine with special reference to ligament ruptures. Acta Orthop Scand Suppl. 1960; 46:1–100. PMID: 13741862.
Article14. Sharrock NE. Recordings of, and an anatomical explanation for, false positive loss of resistance during lumbar extradural analgesia. Br J Anaesth. 1979; 51:253–258. PMID: 435350.
Article15. Gupta B, Sharma S, D'souza N, Kaur M. Pseudo loss of resistance in epidural space localization. Saudi J Anaesth. 2010; 4:117–118. PMID: 20927275.
Article16. Lirk P, Kolbitsch C, Putz G, Colvin J, Colvin HP, Lorenz I, et al. Cervical and high thoracic ligamentum flavum frequently fails to fuse in the midline. Anesthesiology. 2003; 99:1387–1390. PMID: 14639154.
Article17. Yamashita M, Tsuji M. Identification of the epidural space in children. The application of a micro-drip infusion set. Anaesthesia. 1991; 46:872–874. PMID: 1952006.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Malposition of Epidural Catheter in Cancer Pain Control
- Misplacement of Epidural Catheter Confirmed by Epidurography
- Inadvertent Placement of Epidural Catheter in the Extra-epidural Space: Two case reports
- The Breakage of Epidural Catheter during Continuous Epidural Analgesia for Cancer Pain: A case report
- Etiology of Failure in Epidural Anesthesia: Transforaminal Escape of Epidural Catheter: Two cases