Korean J Obstet Gynecol.
2011 Jul;54(7):377-380. 10.5468/KJOG.2011.54.7.377.
A case of full term delivery after selective fetocide with potassium chloride in heterotopic cornual pregnancy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Bundang Cha Women's Hospital, CHA University College of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea. mmj33@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2274053
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5468/KJOG.2011.54.7.377
Abstract
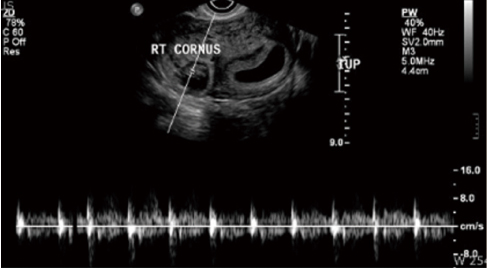
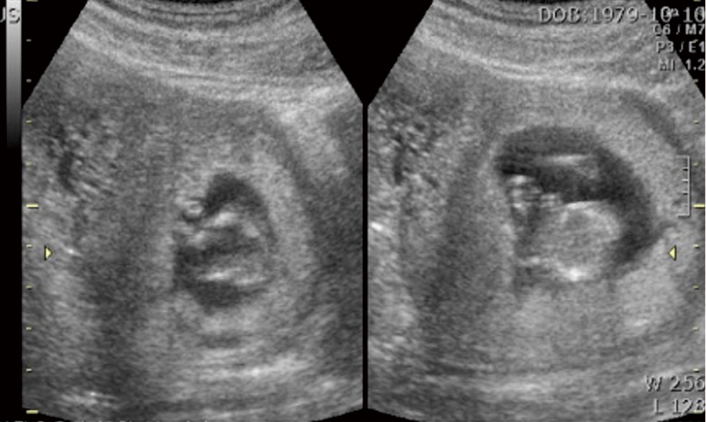
- Heterotopic pregnancy is the simultaneous occurrence of intrauterine and ectopic gestations. Possible risk factors include past pelvic inflammatory disease, previous pelvic surgery, or uterine anomalies. Its incidence is very rare, 1 in 30,000 in natural pregnancies but it has been increased in frequency by the advent of assisted reproductive technology. In cases of heterotopic pregnancy with intrauterine pregnancy and ectopic pregnancy, the diagnosis can be even more difficult. And the management of heterotopic pregnancy still remains controversial. We have experienced a case of heterotopic pregnancy with cornual pregnancy after in vitro fertilization and embryo transfer. which was successfully treated by selective fetocide with ultrasonographically guided potassium chloride injection of cornual pregnancy while maintaining the viabillity of the intrauterine gestation.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Steadman HE. Combined intrauterine and extrauterine pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol. 1953. 2:277–280.2. Lee DH, Kim SJ, Ryu Y, Whang HK, Lee SY. A case of combined pregnancy. Korean J Obstet Gynecol. 1971. 14:39–40.3. Kim JU, Park KZ, Chang SS, Ahn MO, Hwang DH. A case of combined intra-and extrauterine pregnancy. Korean J Obstet Gynecol. 1981. 24:1245–1248.4. Kim EI, Song JS, Yoo JJ, Mok YJ. A case of combined pregnancy following GIFT with microsurgery. Korean J Fertil Steril. 1989. 16:103–107.5. Park MC, Ahn CS, Kim SH, Moon SY, Lee JY, Chang YS. A case of combined pregnancy following IVF-ET. Korean J Obstet Gynecol. 1991. 34:1457–1462.6. DeVoe RW, Pratt JH. Simultaneous intrauterine and extrauterine pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1948. 56:1119–1126.7. Tal J, Haddad S, Gordon N, Timor-Tritsch I. Heterotopic pregnancy after ovulation induction and assisted reproductive technologies: a literature review from 1971 to 1993. Fertil Steril. 1996. 66:1–12.8. Lau S, Tulandi T. Conservative medical and surgical management of interstitial ectopic pregnancy. Fertil Steril. 1999. 72:207–215.9. Dor J, Seidman DS, Levran D, Ben-Rafael Z, Ben-Shlomo I, Mashiach S. The incidence of combined intrauterine and extrauterine pregnancy after in vitro fertilization and embryo transfer. Fertil Steril. 1991. 55:833–834.10. Rizk B, Tan SL, Morcos S, Riddle A, Brinsden P, Mason BA, et al. Heterotopic pregnancies after in vitro fertilization and embryo transfer. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1991. 164:161–164.11. Louis-Sylvestre C, Morice P, Chapron C, Dubuisson JB. The role of laparoscopy in the diagnosis and management of heterotopic pregnancies. Hum Reprod. 1997. 12:1100–1102.12. Chandra PC, Schiavello HJ, Briggs SL, Samuels JD. Heterotopic pregnancy with term delivery after rupture of a first-trimester tubal pregnancy. A case report. J Reprod Med. 1999. 44:556–558.13. Wright A, Kowalczyk CL, Quintero R, Leach RE. Selective embryo reduction in a heterotopic pregnancy using potassium chloride injection resulting in a hematosalpinx. Fertil Steril. 1996. 66:1028–1030.14. Ghazeeri GS, Phillips OP, Emerson DS, Kutteh WH, Ke RW. Live birth after treatment of a heterotopic cornual pregnancy with fetal intrathoracic KCI. A case report. J Reprod Med. 2002. 47:1038–1040.15. Ozgur K, Isikoglu M. Cornual heterotopic pregnancy: conservative treatment with transvaginal embryo reduction. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2005. 271:73–75.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Full-term delivery in patient with heterotopic cornual pregnancy via selective fetal reduction with potassium chloride
- Ultrasound-guided local injection of potassium chloride (KCl) and methotrexate (MTX) in the treatment of cornual pregnancy
- Successful Full-term Live Birth after Selective Fetal Reduction Procedure in Patient with Heterotopic Cornual Pregnancy
- Interstitial heterotopic pregnancy by in vitro fertilization and embryo transfer after bilateral salpingectomy
- A live birth after laparoscopic cornual resection for cornual heterotopic pregnancy after IVF-ET