Ann Rehabil Med.
2015 Apr;39(2):313-317. 10.5535/arm.2015.39.2.313.
Diagnosis of Spasmodic Dysphonia Manifested by Swallowing Difficulty in Videofluoroscopic Swallowing Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Dankook University College of Medicine, Cheonan, Korea. magnarbor@dankook.ac.kr
- 2Nanobiomedical Science & WCU Research Center, Dankook University, Cheonan, Korea.
- 3Institute of Tissue Regeneration Engineering (ITREN), Dankook University, Cheonan, Korea.
- KMID: 2273055
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2015.39.2.313
Abstract
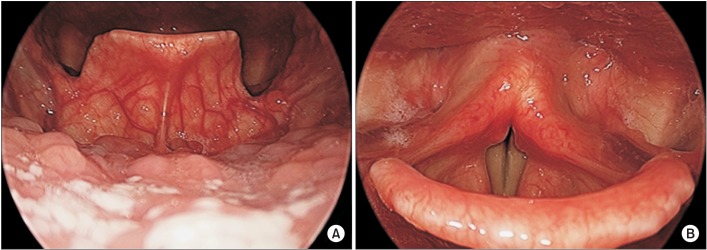
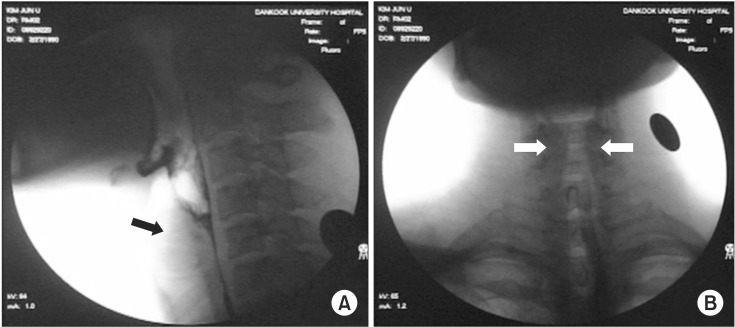
- Spasmodic dysphonia is defined as a focal laryngeal disorder characterized by dystonic spasms of the vocal cord during speech. We described a case of a 22-year-old male patient who presented complaining of idiopathic difficulty swallowing that suddenly developed 6 months ago. The patient also reported pharyngolaryngeal pain, throat discomfort, dyspnea, and voice change. Because laryngoscopy found no specific problems, an electrodiagnostic study and videofluoroscopic swallowing study (VFSS) were performed to find the cause of dysphagia. The VFSS revealed continuous twitch-like involuntary movement of the laryngeal muscle around the vocal folds. Then, he was diagnosed with spasmodic dysphonia by VFSS, auditory-perceptual voice analysis, and physical examination. So, we report the first case of spasmodic dysphonia accompanied with difficulty swallowing that was confirmed by VFSS.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ludlow CL, Adler CH, Berke GS, Bielamowicz SA, Blitzer A, Bressman SB, et al. Research priorities in spasmodic dysphonia. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2008; 139:495–505. PMID: 18922334.
Article2. Blitzer A, Brin MF. The dystonic larynx. J Voice. 1992; 6:294–297.
Article3. Miler RH. Technique of percutaneous EMG-guided botulinum toxin injection of the larynx for spasmodic dystonia. J Voice. 1992; 6:377–379.4. Davis PJ, Boone DR, Carroll RL, Darveniza P, Harrison GA. Adductor spastic dysphonia: heterogeneity of physiologic and phonatory characteristics. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1988; 97(2 Pt 1):179–185. PMID: 3355046.
Article5. Yu P, Ouaknine M, Revis J, Giovanni A. Objective voice analysis for dysphonic patients: a multiparametric protocol including acoustic and aerodynamic measurements. J Voice. 2001; 15:529–542. PMID: 11792029.6. Logemann JA. Evaluation and treatment of swallowing disorders. 2nd ed. Austin: Pro-Ed;1998.7. Blitzer A, Brin MF. Laryngeal dystonia: a series with botulinum toxin therapy. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1991; 100:85–89. PMID: 1992905.
Article8. Kieschnick CO, Powell TW. Treatment of spasmodic dysphonia: a brief overview for clinicians. Natl Stud Speech Lang Hear Assoc J. 1996; 23:14–18.
Article9. Banoub M, Rao U, Motta P, Tetzlaff JE, Eliachar I, Blitzer A. Recurrent postoperative stridor requiring tracheostomy in a patient with spasmodic dysphonia. Anesthesiology. 2000; 92:893–895. PMID: 10719977.
Article10. Pool KD, Freeman FJ, Finitzo T, Hayashi MM, Chapman SB, Devous MD Sr, et al. Heterogeneity in spasmodic dysphonia: neurologic and voice findings. Arch Neurol. 1991; 48:305–309. PMID: 2001189.