Brain Neurorehabil.
2013 Mar;6(1):1-8. 10.12786/bn.2013.6.1.1.
Effects of Ankle Foot Orthosis on Post-stroke Hemiplegic Gait -A Meta-analysis-
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department and Research Institute of Rehabilitation Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Korea. kimdy@yuhs.ac
- KMID: 2270733
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12786/bn.2013.6.1.1
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
The aim of this meta-analysis was to investigate the effects of ankle foot orthosis on adult post-stroke hemiplegic patients' walking ability and pattern. METHOD: We searched for the case controlled clinical trials about the effects of ankle foot orthosis (AFO) for walking ability and pattern using quantitative gait analysis in adult post-stroke patients, which published between January 1950 and July 2012 in PubMed, and searching engine of Journal of Korean Academy of Rehabilitation Medicine. The mean standardized difference (MSD) and a 95% confidence interval (CI) were estimated for gait ability and pattern using fixed effect models.
RESULTS
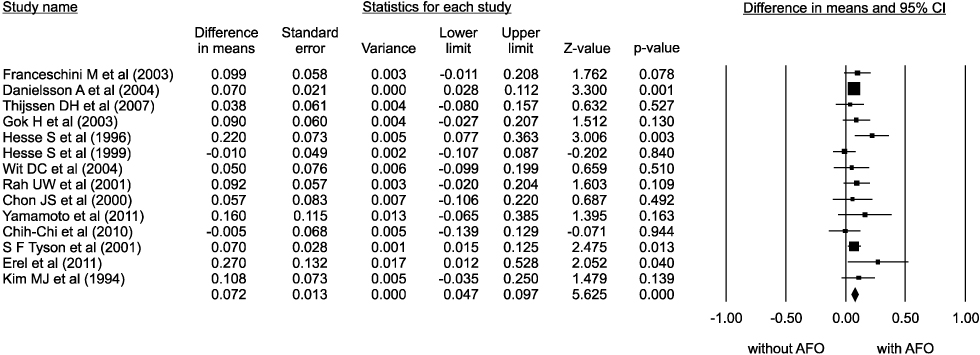
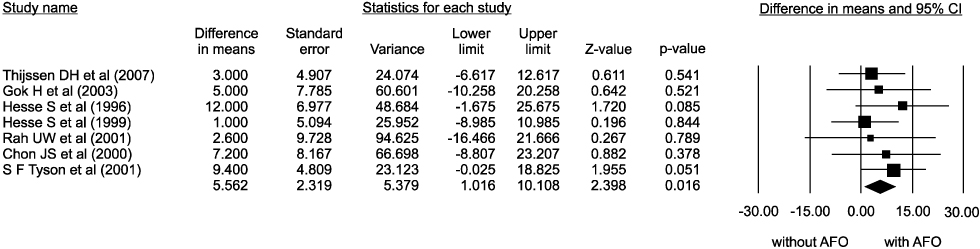
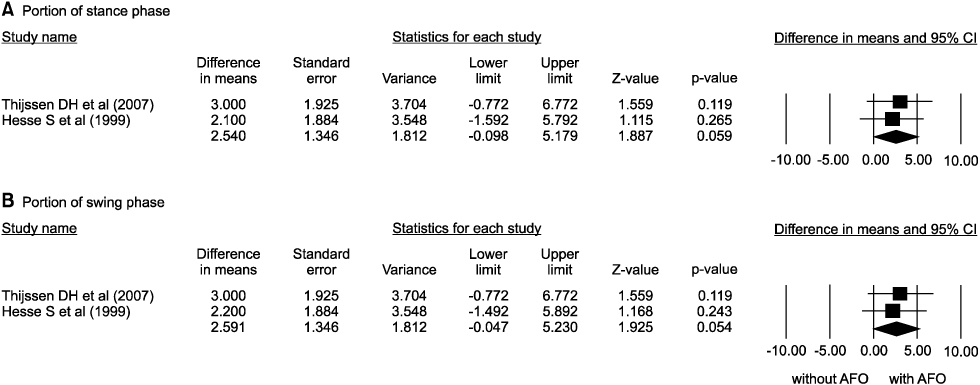
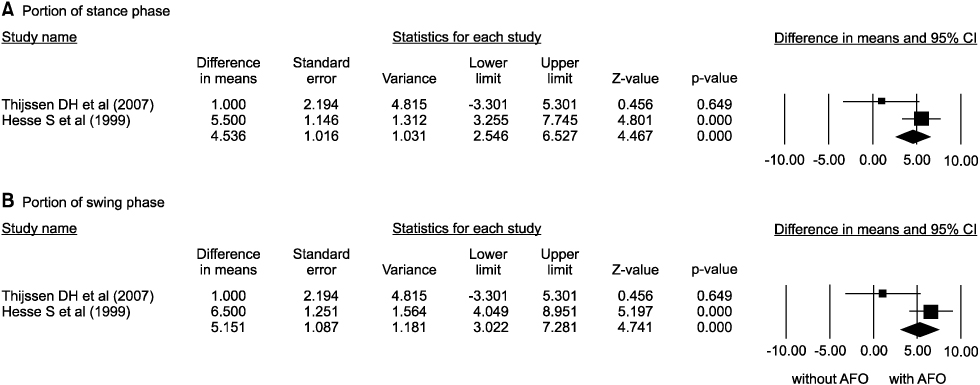
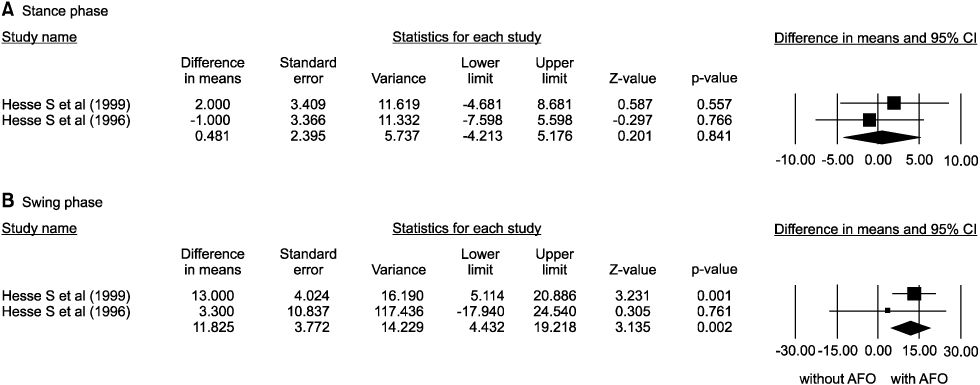
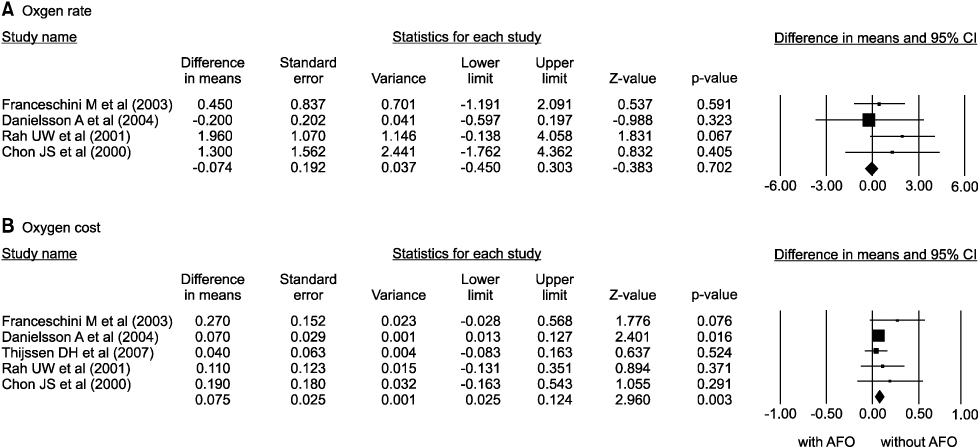
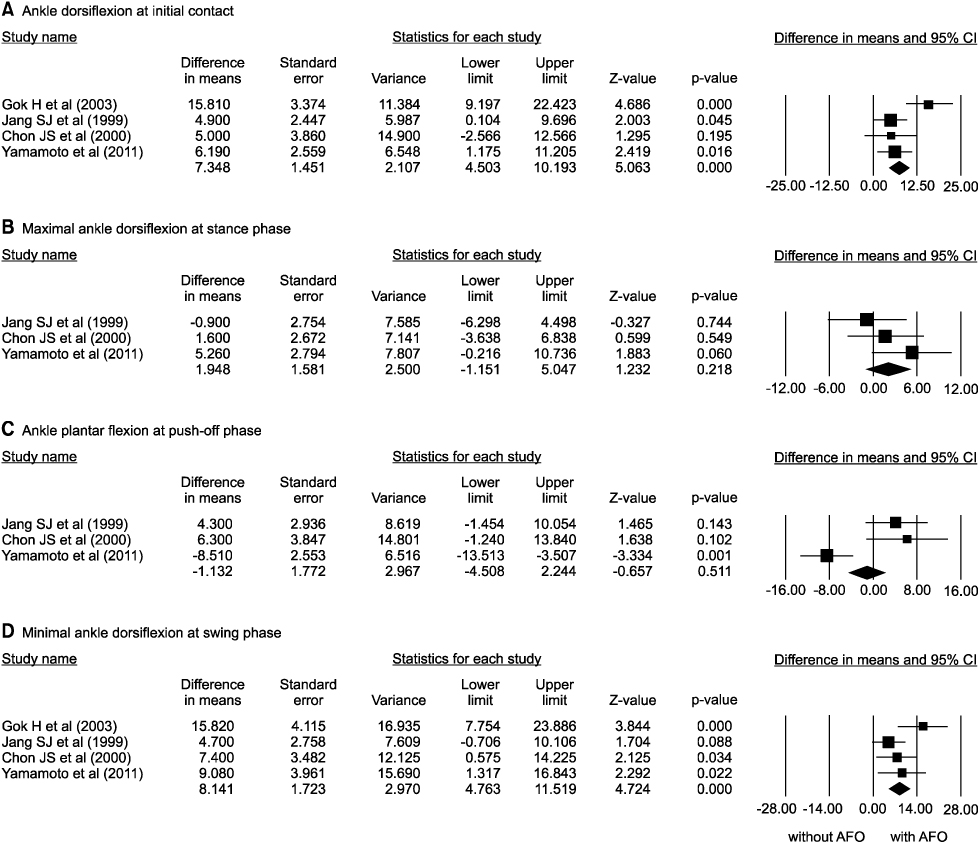
Sixteen of the 56 articles were included in this analysis. The selected studies involved a total of 274 patients. The walking speed, cadence, the portion of double limb supporting, stride length on affected side, the portion of swing period on unaffected side, and symmetry of swing period were improved by AFO. The oxygen cost was decreased by AFO. The AFO did improve ankle dorsiflexion at initial contact, maximal ankle dorsiflexion at swing phase, but the ankle plantar flexion at push-off did not.
CONCLUSION
The ankle foot orthosis has some evidence to improve the walking ability and gait pattern in post-stroke hemiplegic patients.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Braddom RL. Harvey RL, Roth EJ, Yu DT, Celnick P, editors. Stroke syndromes. Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation. 2010. Philadelphia: Saunders;1177–1213.2. Kim DY, Park CI, Jang YW, Ahn SY, Na SI, Park YS. The relationship between weight-bearing and stiff-knee gait in hemiplegic patients. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 2004. 28:20–25.3. Waters RL, Garland DE, Perry J, Habig T, Slabaugh P. Stiff-legged gait in hemiplegia: Surgical correction. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1979. 61:927–933.4. Brandstater ME, de Bruin H, Gowland C, Clark BM. Hemiplegic gait: analysis of temporal variables. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1983. 64:583–587.5. Brunnstrom S. Recording gait patterns of adult hemiplegic patients. Phys Ther. 1964. 44:11–18.6. Lehmann JF, Condon SM, Price R, deLateur BJ. Gait abnormalities in hemiplegia: their correction by ankle-foot orthoses. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1987. 68:763–771.7. Wagenaar RC, Beek WJ. Hemiplegic gait: a kinematic analysis using walking speed as a basis. J Biomech. 1992. 25:1007–1015.8. Olney SJ, Griffin MP, Monga TN, McBride ID. Work and power in gait of stroke patients. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1991. 72:309–314.9. Perry J. The mechanics of walking in hemiplegia. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1969. 63:23–31.10. Kim BO. Methods in clinical gait analysis. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 1994. 18:191–202.11. Yune SH, Kim BO, Lee JW, Park SK, Kim CJ, Park SJ. Analysis of normal gait with a 3-dimensional motion analyzer. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 1992. 16:399–406.12. Perry J, Burnfield JM. Perry J, Burnfield JM, editors. Gait analysis system. Gait Analysis: Normal and Pathological Function. 2010. Thorofare: SLACK;403–406.13. Hesse S, Luecke D, Jahnke MT, Mauritz KH. Gait function in spastic hemiparetic patients walking barefoot, with firm shoes, and with ankle-foot orthosis. Int J Rehabil Res. 1996. 19:133–141.14. Corcoran PJ, Jebsen RH, Brengelmann GL, Simons BC. Effects of plastic and metal leg braces on speed and energy cost of hemiparetic ambulation. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1970. 51:69–77.15. Kim MJ, Lee SA, Kim SK, Sung IY. The study for gait speed of stroke patients: Comfortable versus maximum safe speed. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 1994. 18:736–741.16. Kim YH, Chang IS, Kim BO. Plastic ankle-foot orthosis (afo) for hemiplegic ambulation. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 1984. 8:50–54.17. Yamamoto S, Ebina M, Kubo S, Kawai H, Hayashi T, Iwasaki M, Kubota T, Miyazaki S. Quantification of the effect of dorsi-/ plantarflexibility of ankle-foot orthoses on hemiplegic gait: a preliminary report. J Prosthet Orthot. 1993. 5:88–94.18. Chen CC, Hong WH, Wang CM, Chen CK, Wu KP, Kang CF, Tang SF. Kinematic features of rear-foot motion using anterior and posterior ankle-foot orthoses in stroke patients with hemiplegic gait. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2010. 91:1862–1868.19. Danielsson A, Sunnerhagen KS. Energy expenditure in stroke subjects walking with a carbon composite ankle foot orthosis. J Rehabil Med. 2004. 36:165–168.20. de Wit DC, Buurke JH, Nijlant JM, Ijzerman MJ, Hermens HJ. The effect of an ankle-foot orthosis on walking ability in chronic stroke patients: a randomized controlled trial. Clin Rehabil. 2004. 18:550–557.21. Erel S, Uygur F, Engin Simsek I, Yakut Y. The effects of dynamic ankle-foot orthoses in chronic stroke patients at three-month follow-up: a randomized controlled trial. Clin Rehabil. 2011. 25:515–523.22. Franceschini M, Massucci M, Ferrari L, Agosti M, Paroli C. Effects of an ankle-foot orthosis on spatiotemporal parameters and energy cost of hemiparetic gait. Clin Rehabil. 2003. 17:368–372.23. Gok H, Kucukdeveci A, Altinkaynak H, Yavuzer G, Ergin S. Effects of ankle-foot orthoses on hemiparetic gait. Clin Rehabil. 2003. 17:137–139.24. Hesse S, Werner C, Matthias K, Stephen K, Berteanu M. Non-velocity-related effects of a rigid double-stopped ankle-foot orthosis on gait and lower limb muscle activity of hemiparetic subjects with an equinovarus deformity. Stroke. 1999. 30:1855–1861.25. Pohl M, Mehrholz J. Immediate effects of an individually designed functional ankle-foot orthosis on stance and gait in hemiparetic patients. Clin Rehabil. 2006. 20:324–330.26. Thijssen DH, Paulus R, van Uden CJ, Kooloos JG, Hopman MT. Decreased energy cost and improved gait pattern using a new orthosis in persons with long-term stroke. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2007. 88:181–186.27. Tyson SF, Thornton HA. The effect of a hinged ankle foot orthosis on hemiplegic gait: Objective measures and users' opinions. Clin Rehabil. 2001. 15:53–58.28. Yamamoto S, Fuchi M, Yasui T. Change of rocker function in the gait of stroke patients using an ankle foot orthosis with an oil damper: Immediate changes and the short-term effects. Prosthet Orthot Int. 2011. 35:350–359.29. Chon JS, Chun Sl, Kim DA, Yoon TJ, Seo CH, Seok H, Ohn SH, Chang YC. Comparison of gait analysis and energy consumption between various types of plastic ankle foot orthoses in hemiplegic patients. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 2000. 24:1046–1054.30. Jang SJ, Kim BJ, Kim CW, Kang MJ, Kim BS. Effect of plastic ankle foot orthosis and functional electrical stimulation on hemiplegic gait. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 1999. 23:853–860.31. Rah UW, Yang JI, Lee IY, Park HK, Park SI, Im SH, Moon HW, Cho JR. Effects of plastic ankle-foot orhtosis on hemiplegic ambulation. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 2001. 25:836–841.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effect of Plastic Ankle Foot Orthosis and Functional Electrical Stimulation on Hemiplegic Gait
- Effects of Plastic Ankle-Foot Orhtosis on Hemiplegic Ambulation
- Effect of Torque Heel on Excessive External Rotation of Hemiplegic Foot: Three Dimensional Gait Analysis
- A novel hinged ankle foot orthosis for gait performance in chronic hemiplegic stroke survivors: a feasibility study
- Effects on Foot External Rotation of the Modified Ankle-Foot Orthosis on Post-Stroke Hemiparetic Gait