Korean J Nutr.
2009 Oct;42(7):615-621. 10.4163/kjn.2009.42.7.615.
A Study on the Nutritional Status in Hospitalized Patients with Pulmonary Tuberculosis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Graduate School of Clinical Health Sciences, Ewha Womans University, Seoul 120-750, Korea.
- 2Department of Nutritional Science and Food Management, Ewha Womans University, Seoul 120-750, Korea. yhmoon@ewha.ac.kr
- KMID: 2267340
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4163/kjn.2009.42.7.615
Abstract
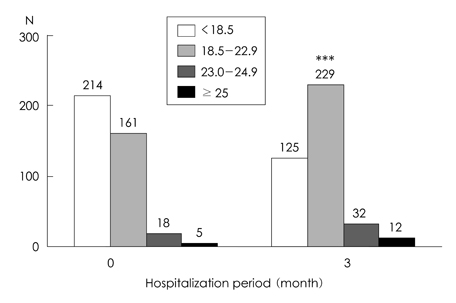
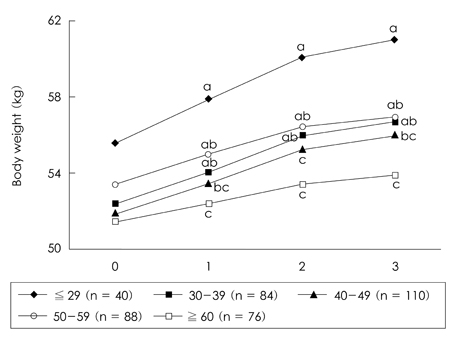
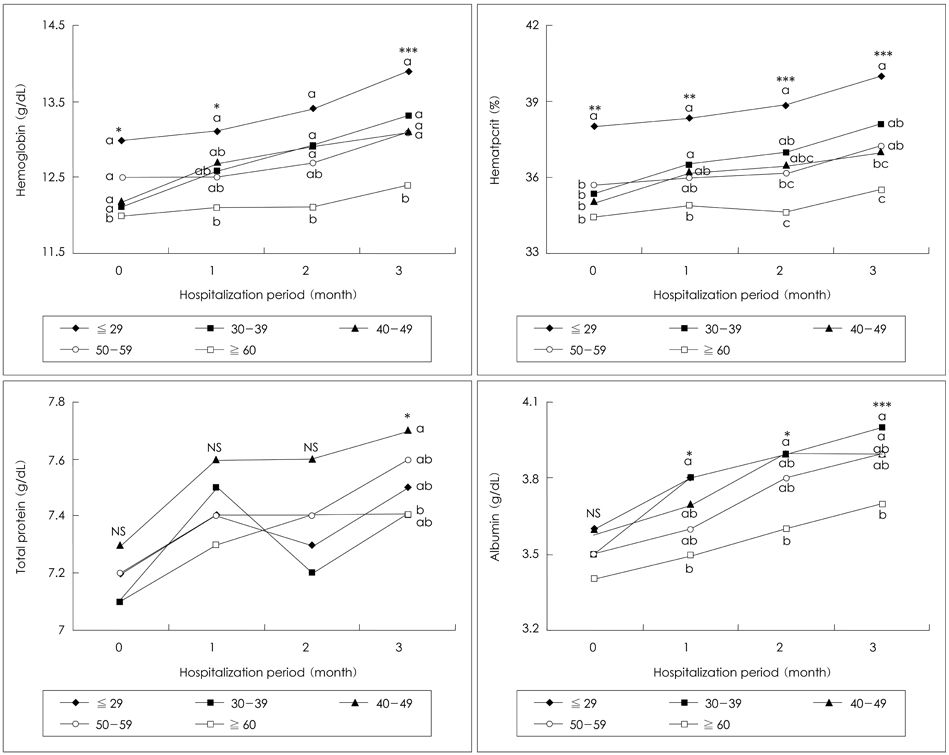
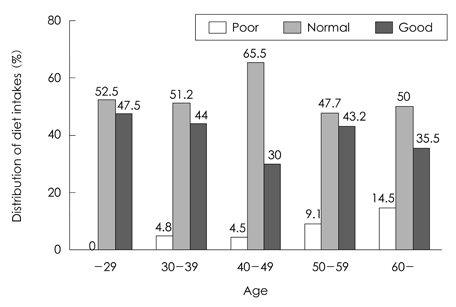
- This study was conducted to evaluate the change of nutritional status and to analyze related factors in hospitalized tuberculosis (TB) patients during their hospitalization. The subjects were 398 men patients (mean age: 47.3 +/- 14.4 y) who had hospitalized more than 3 months at TB hospital located in Seoul. The anthropometric and blood biochemical indices were measured, and dietary intakes were assessed. At the time of admission the body weight of subjects was about 76% of the average body weight of Korean men with same age, Body mass index (BMI) of subjects was 18.5 kg/m2, and 53.8% of subjects were under weight status. Average level of blood hemoglobin and hematocrit of subjects was lower than the normal value. After 3 months of hospitalization period, the body weight and body mass index were significantly increased compared to admission by 3.9 kg (7.41%) and 1.4 kg/m2 (7.61%)(p<0.001), respectively. Blood levels of hemoglobin, hematocrit, albumin, and total protein were also significantly increased after 3 months of hospitalization period compared to admission (p<0.001). The increment in the body weight and blood indices was significantly higher in below 29 years group than over 60 years group (p<0.05). The increment in the body weight and body mass index was significantly higher in the under-body weight group compared to the normal-body weight group (p<0.05). In conclusion the body weight and body mass index of subjects were significantly increased after 3 months of hospitalization period, and the age and body weight of subjects at admission were supposed to influence the degree of change in the nutritional status.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Corbett Elizabeth L. The Growing burden of tuberculosis: Global trends and interactions with HIV epidemic. Arch Intern Med. 2003. 163:1009–1102.2. WHO. TB global burden update. Stop TB Annual Report. 2001.3. The korean national tuberculosis association. Tuberculosis management. 2001.4. Choi SI, Lee J, Kong SJ, Park JH. The survey for clinical course of intractable pulmonary tuberculosis. Korean J Med. 2005. 69(6):590–600.5. Park YM, Yoon HI, Shon CM, Choue RW. Nutritional Status of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Patients according to the severity of Disease. Korean J Nutr. 2008. 41(4):307–316.6. Schols AM, Slangen J, Volovics L, Wouters EF. Weight loss is a reversible factor in the prognosis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998. 157(6 Pt 1):1791–1797.
Article7. Lee KH. Nutritional Assessment in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Tuberc Respir Dis. 2005. 59:242–249.
Article8. Wilson DO, Rogers RM, Openbrier D. Nutritional aspects of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Clin Chest Med. 1996. 7:643–656.
Article9. Donahoe MD, Rogers RM. Nutritional assessment and support in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Clin Chest Med. 1990. 11:487–492.
Article10. Whittaker JS, Ryan CF, Buckley PA, Road JD. The effects of refeeding on peripheral and respiratory muscle function in malnourished chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients. Am Rev Repair Dis. 1990. 142(2):283–288.
Article11. Ferreira IM, Borrks D, Lacasse Y, Goldstein RS. Nutritional support for individuals with COPD: a meta-analysis. Chest. 2000. 117:672–678.12. Schols AM, Slangen J, Volovics L, Wouters EF. Weight loss is a reversible factor in the prognosis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998. 157:1791–1797.
Article13. Korean Society for The Study of Obesity. WHO. IASO. IOTF. The Asia-Pacific Perspective: Redefinding obesity and it's treatment. 2000.14. Kim HJ. Tuberculosis prevalence survey in Korea. 2008. The Korean National Tuberculosis Association.15. Lee JH, Jang TW, Kim HK, KIM NH, Yang SW, Kim SJ, Ok CH, Jung MH. Active Pulmonary Tuberculosis in Patients with Lung Cancer. Kosin Medical J. 2005. 20(1):57–62.16. Kim KS, Jo YH, Chun JH, Cho EH, Eun CK. The prognostic factor affecting outcomes in primary treatment for pulmonary tuberculosis patients. Inje Medical J. 2002. 23(3):529–537.17. Korean Agency for Technology and Standards. Report of Size Korea 5th. 2004.18. Ministry of health and welfare. Report on 2005 National health and nutrition survey. 2006.19. Calle EE, Thun MJ, Petrelli JM, Rodriguez C, Heath CW Jr. Body-mass index and mortality in a prospective cohort of U.S. adults. N Engl J Med. 1999. 341(15):1097–1105.
Article20. Schols A, Slangen J, Volovics L, Wouters EFM. Weight loss is a reversible factor in the prognosis of chronic obstructive of pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998. 157:1791–1797.
Article21. Lee JH, Park YK, Lim HS. Degree of enteral tube feeding in the intensive care unit and change in Nutritional status. J Korean Dietetic Assoc. 2001. 7(3):217–226.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Nutritional Status of the Hospitalized Patients with High Risk of Dysphagia in Korea
- A survey of deaths in hospitalized patients for pulmonary tuberculosis
- Assessment of Nutritional Status in Hospitalized Pediatric Patients
- Prediction Model for Health-Related Quality of Life in Hospitalized Patients with Pulmonary Tuberculosis
- The Differences in Resting Pulmonary Function in Relation to the Nutritional status of Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease