Ann Surg Treat Res.
2014 Nov;87(5):265-272. 10.4174/astr.2014.87.5.265.
Validation of the Korean version Moorehead-Ardelt quality of life questionnaire II
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Family Medicine, Inha University School of Medicine, Incheon, Korea.
- 2National Evidence-Based Healthcare Collaborating Agency, Seoul, Korea. gshur@inha.ac.kr
- 3School of Pharmacy, Sungkyunkwan University, Suwon, Korea.
- 4Department of Surgery, Inha University School of Medicine, Incheon, Korea.
- 5College of Pharmacy, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea.
- 6Department of Surgery, Chung-Ang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 7Department of Surgery, The Catholic University of Korea School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2266886
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/astr.2014.87.5.265
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To investigate the weight loss effects with higher sensitivity, disease specific quality of life (QoL) instruments were important. The Moorehead-Ardelt quality of life questionnaire II (MA-II) is widely used, because it was simple and validated the several languages. The aims of present study was performed the translation of MA-II Korean version and the validation compared with EuroQol-5 dimension (EQ-5D), obesity-related problems scale (OP-scale), and impact of weight quality of life-lite (IWQoL-Lite).
METHODS
The study design was a multicenter, cross-sectional survey and this study was included the postoperative patients. The validation procedure is translation-back translation procedure, pilot study, and field study. The instruments of measuring QoL included the MA-II, EQ-5D, OP-scale, and IWQoL-lite. The reliability was checked through internal consistency using Cronbach alpha coefficients. The construct validity was assessed the Spearman rank correlation between 6 domains of MA-II and EQ-5D, OP-scale, and 5 domains of IWQoL-Lite.
RESULTS
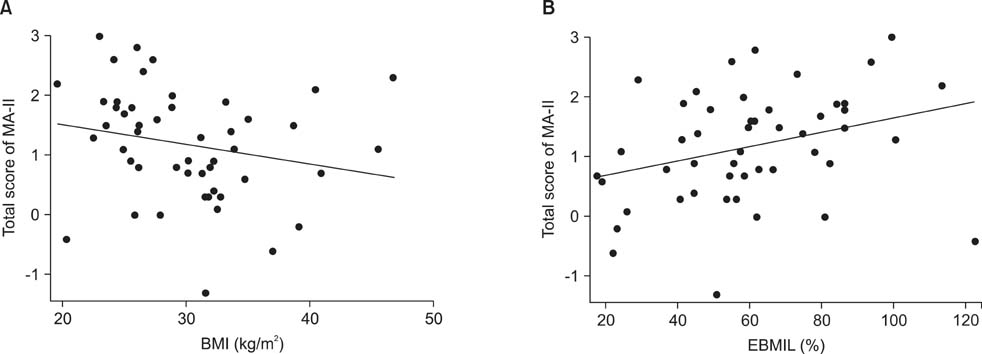
The Cronbach alpha of MA-II was 0.763, so the internal consistency was confirmed. The total score of MA-II was significantly correlated with all other instruments; EQ-5D, OP-scale, and IWQoL-Lite. IWQoL-lite (rho = 0.623, P < 0.001) was showed the strongest correlation compared with MA-II, followed by OP-scale (rho = 0.588, P < 0.001) and EQ-5D (rho = 0.378, P < 0.01).
CONCLUSION
The Korean version MA-II was valid instrument of measuring the obesity-specific QoL. Through the present study, the MA-II was confirmed to have good reliability and validity and it was also answered simple for investigating. Thus, MA-II could be estimated sensitive and exact QoL in obesity patients.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence. Obesity: the prevention, identification, assessment and management of overweight and obesity in adults and children. NICE Clinical Guidelines, No. 43. London: National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (UK);2006.2. Korean Endocrine Society. Korean Society for the Study of Obesity. Management of obesity, 2010 recommendation. Endocrinol Metab. 2010; 25:301–304.3. Carpenter KM, Hasin DS, Allison DB, Faith MS. Relationships between obesity and DSM-IV major depressive disorder, suicide ideation, and suicide attempts: results from a general population study. Am J Public Health. 2000; 90:251–257.4. McElroy SL, Kotwal R, Malhotra S, Nelson EB, Keck PE, Nemeroff CB. Are mood disorders and obesity related? A review for the mental health professional. J Clin Psychiatry. 2004; 65:634–651.5. Chang CY, Hung CK, Chang YY, Tai CM, Lin JT, Wang JD. Health-related quality of life in adult patients with morbid obesity coming for bariatric surgery. Obes Surg. 2010; 20:1121–1127.6. Karlsen TI, Lund RS, Roislien J, Tonstad S, Natvig GK, Sandbu R, et al. Health related quality of life after gastric bypass or intensive lifestyle intervention: a controlled clinical study. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2013; 11:17.7. Lier HO, Biringer E, Hove O, Stubhaug B, Tangen T. Quality of life among patients undergoing bariatric surgery: associations with mental health- A 1 year follow-up study of bariatric surgery patients. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2011; 9:79.8. Lee SK. The current status of bariatric surgery in South Korea. In : Korean Society for the Study of Obesity 33th Conference; 2010 Oct 31; Seoul, Korea. Seoul: Korean Society for the Study of Obsity;2010.9. Moorehead MK, Ardelt-Gattinger E, Lechner H, Oria HE. The validation of the Moorehead-Ardelt Quality of Life Questionnaire II. Obes Surg. 2003; 13:684–692.10. Chang CY, Huang CK, Chang YY, Tai CM, Lin JT, Wang JD. Cross-validation of the Taiwan version of the Moorehead-Ardelt quality of life questionnaire II with WHOQOL and SF-36. Obes Surg. 2010; 20:1568–1574.11. Sauerland S, Weiner S, Hausler E, Dolezalova K, Angrisani L, Noguera CM, et al. Validity of the Czech, German, Italian, and Spanish version of the Moorehead-Ardelt II questionnaire in patients with morbid obesity. Obes Facts. 2009; 2:Suppl 1. 57–62.12. Sullivan M, Karlsson J, Sjostrom L, Taft C. Why quality-of-life measures should be used in the treatment of patients with obesity. In : Bjorntorp P, editor. International textbook in obesity. New York: Wiley;2001. p. 237–240.13. Oria HE, Moorehead MK. Bariatric analysis and reporting outcome system (BAROS). Obes Surg. 1998; 8:487–499.14. EuroQol Group. EuroQol: a new facility for the measurement of health-related quality of life. Health Policy. 1990; 16:199–208.15. Lee YK, Nam HS, Chuang LH, Kim KY, Yang HK, Kwon IS, et al. South Korean time trade-off values for EQ-5D health states: modeling with observed values for 101 health states. Value Health. 2009; 12:1187–1193.16. Hurst NP, Kind P, Ruta D, Hunter M, Stubbings A. Measuring health-related quality of life in rheumatoid arthritis: validity, responsiveness and reliability of EuroQol (EQ-5D). Br J Rheumatol. 1997; 36:551–559.17. Sullivan M, Karlsson J, Sjostrom L, Backman L, Bengtsson C, Bouchard C, et al. Swedish obese subjects (SOS): an intervention study of obesity. Baseline evaluation of health and psychosocial functioning in the first 1743 subjects examined. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 1993; 17:503–512.18. Karlsson J, Taft C, Sjostrom L, Torgerson JS, Sullivan M. Psychosocial functioning in the obese before and after weight reduction: construct validity and responsiveness of the Obesity-related Problems scale. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 2003; 27:617–630.19. Kolotkin RL, Crosby RD, Kosloski KD, Williams GR. Development of a brief measure to assess quality of life in obesity. Obes Res. 2001; 9:102–111.20. Kolotkin RL, Norquist JM, Crosby RD, Suryawanshi S, Teixeira PJ, Heymsfield SB, et al. One-year health-related quality of life outcomes in weight loss trial participants: comparison of three measures. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2009; 7:53.21. Lee YJ, Moon KH, Choi JH, Cho MJ, Shin SH, Heo Y. Validation of the Korean translation of obesity-related problems scale assessing the quality of life in obese Korean. J Korean Surg Soc. 2013; 84:140–153.22. Jo MW, Lee SI. Validity and reliability of korean EQ-5D valuationstudy using the time-trade off method. Korean J Health Promot Dis Prev. 2007; 7:96–103.23. Kolotkin RL, Head S, Brookhart A. Construct validity of the Impact of weight on quality of life questionnaire. Obes Res. 1997; 5:434–441.24. Oh SH, Song HJ, Kwon JW, Park DJ, Lee YJ, Chun H, et al. The improvement of quality of life in patients treated with bariatric surgery in Korea. J Korean Surg Soc. 2013; 84:131–139.25. Nunnally JC, Berstein IR. Psychometric theory. 3rd ed. McGraw-Hill: New York;1994.26. Crandall CS. Prejudice against fat people: ideology and self-interest. J Pers Soc Psychol. 1994; 66:882–894.27. Moore ME, Stunkard A, Srole L. Obesity, social class, and mental illness. JAMA. 1962; 181:962–966.28. Korean Ministry of Health and Welfare Affairs. Korean National Health and Nutritional Examination Survey IV 2007-2009. Seoul: Korean Ministry of Health and Welfare Affairs;2010.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Revisional Bariatric Surgery: Focus on Quality of Life
- Translation and Linguistic Validation of the Korean Version of the Wisconsin Stone Quality of Life Questionnaire
- Translation and linguistic validation of Korean version of short form of pelvic floor distress inventory-20, pelvic floor impact questionnaire-7
- Development of Korean Version of Quality of Life Questionnaire in Patients with Erectile Dysfunction
- Translation and Linguistic Validation of Korean Version of the Expanded Prostate Cancer Index Composite for Clinical Practice for Patients With Prostate Cancer