Ann Rehabil Med.
2011 Jun;35(3):441-444. 10.5535/arm.2011.35.3.441.
Deep Vein Thrombosis Associated with May-Thurner Syndrome in an Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Patient: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Gangneung Asan Hospital, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Gangneung 210-711, Korea. mdjhkoo@gnah.co.kr
- 2Department of Radiology, Gangneung Asan Hospital, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Gangneung 210-711, Korea.
- KMID: 2266867
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2011.35.3.441
Abstract
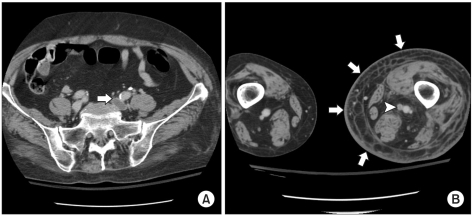
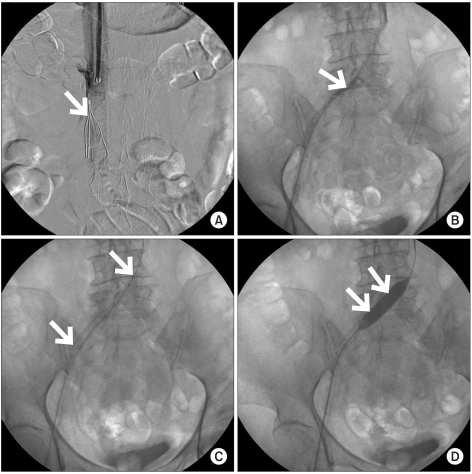
- There have been a few reports on deep vein thrombosis (DVT) associated with compression of the left common iliac vein by the right common iliac artery, referred to as May-Thurner syndrome (MTS). However, there have been no reports on DVT associated with MTS in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) patients exhibiting similar clinical features to paraplegic spinal cord injury patients. We hereby report a case of DVT associated with MTS in an ALS patient, who was treated successfully.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. May R, Thurner J. The cause of the predominantly occurrence of thrombosis of the pelvic veins. Angiology. 1957; 8:419–427. PMID: 13478912.2. Shin JC, Kim EJ, Park CI, Jeon SC, Yoo JH, Lee DY. Iliac vein compression syndrome in spinal cord injury. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 2005; 29:266–271.3. Murphy EH, Davis CM, Journeycake JM, DeMuth RP, Arko FR. Symptomatic ileofemoral DVT after onset of oral contraceptive use in women with previously undiagnosed May-Thurner syndrome. J Vasc Surg. 2009; 49:697–703. PMID: 19135831.
Article4. Acharya G, Singh K, Hansen JB, Kumar S, Maltau JM. Catheter-directed thrombolysis for the management of postpartum deep venous thrombosis. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2005; 84:155–158. PMID: 15683376.
Article5. Heniford BT, Senler SO, Olsofka JM, Carrillo EH, Bergamini TM. May-Thurner syndrome: management by endovascular surgical techniques. Ann Vasc Surg. 1998; 12:482–486. PMID: 9732429.
Article6. Chapman NH, Brighton T, Harris MF, Caplan GA, Braithwaite J, Chong BH. Venous thromboembolism - management in general practice. Aust Fam Physician. 2009; 38:36–40. PMID: 19283234.7. Patel NH, Stookey KR, Ketcham DB, Cragg AH. Endovascular management of acute extensive iliofemoral deep venous thrombosis caused by May-Thurner syndrome. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2000; 11:1297–1302. PMID: 11099239.
Article8. Ferris EJ, Lim WN, Smith PL, Casali R. May-Thuner syndrome. Radiology. 1983; 147:29–31. PMID: 6828755.9. Baron HC, Shams J, Wayne M. Iliac vein compression syndrome: a new method of treatment. Am Surg. 2000; 66:653–655. PMID: 10917476.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Perioperative Management for the Patient with May-Thurner Syndrome: A Case Report
- Deep Vein Thrombosis in May-Thurner Syndrome Patient after Operative Treatment of Acute Cauda Equina Syndrome: A Case Report
- May–Thurner Syndrome after Total Knee Arthroplasty
- Syndrome of Progressive Bulbar Palsy in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: A Case Report
- A Case of Left Iliac Vein Thrombosis with May-Thurner Syndrome