Ann Rehabil Med.
2011 Dec;35(6):939-943. 10.5535/arm.2011.35.6.939.
Lance-Adams Syndrome
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Gachon University of Medicine and Science, Incheon 405-760, Korea. pm@gilhospital.com
- KMID: 2266822
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2011.35.6.939
Abstract
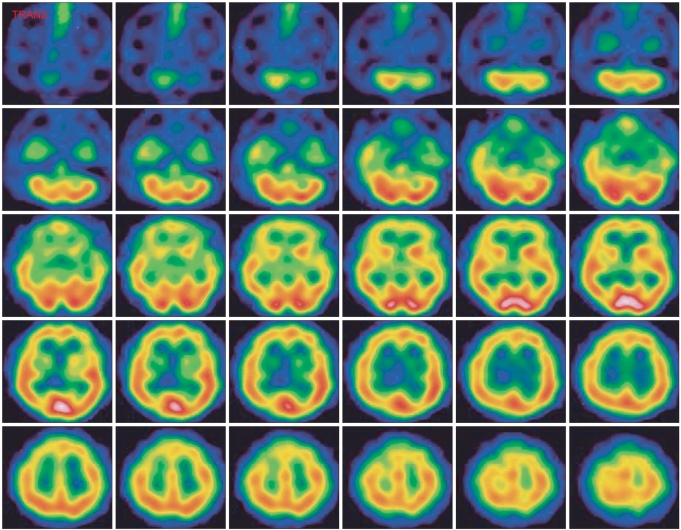
- Lance-Adams syndrome (LAS) is a rare complication of successful cardiopulmonary resuscitation and is often accompanied by action myoclonus. LAS is seen in patients who have undergone a cardiorespiratory arrest, later regained consciousness, and then developed myoclonus days or weeks after the event. Less than 150 cases of LAS have been reported in the worldwide medical literature. Here, we present a 32-year-old man who suffered from myoclonus after hypoxic brain damage due to hanging himself. This case was diagnosed as Lance-Adams syndrome according to a history of hypoxic brain damage, the clinical features, and the neuroimages such as brain SPECT. Making an early diagnosis and properly managing LAS is positively related to improving the patient's functional outcome. If patients have posthypoxic myoclonus after successful cardiopulmonary resuscitation, we should consider the diagnosis of LAS and initiate a proper rehabilitation program.
MeSH Terms
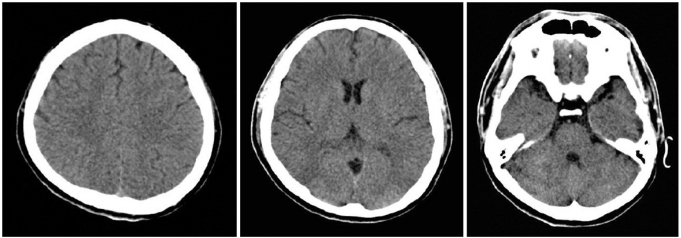
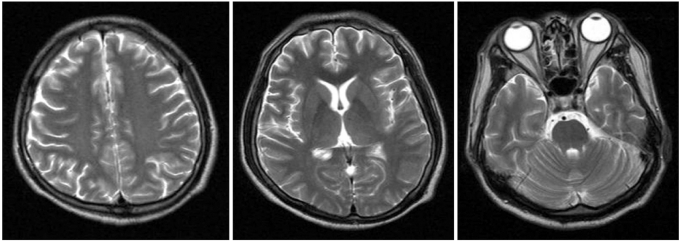
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lance JW, Adams RD. The syndrome of intention or action myoclonus as a sequel to hypoxic encephalopathy. Brain. 1963; 86:111–136. PMID: 13928398.
Article2. English WA, Giffin NJ, Nolan JP. Myoclonus after cardiac arrest: pitfalls in diagnosis and prognosis. Anaesthesia. 2009; 64:908–911. PMID: 19604197.
Article3. Werhahn KJ, Brown P, Thompson PD, Marsden CD. The clinical features and prognosis of chronic posthypoxic myoclonus. Mov Disord. 1997; 12:216–220. PMID: 9087980.
Article4. Frucht SJ, Trost M, Ma Y, Eidelberg D. The metabolic topography of posthypoxic myoclonus. Neurology. 2004; 62:1879–1881. PMID: 15159501.
Article5. Zhang YX, Liu JR, Jiang B, Liu HQ, Ding MP, Song SJ, Zhang BR, Zhang H, Xu B, Chen HH, et al. Lance-Adams syndrome : a report of two cases. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2007; 8:715–720. PMID: 17910113.6. Welsh JP, Placantonakis DG, Warsetsky SI, Marquez RG, Bernstein L, Aicher SA. The serotonin hypothesis of myoclonus from the perspective of neuronal rhythmicity. Adv Neurol. 2002; 89:307–329. PMID: 11968457.7. Matsumoto RR, Truong DD, Nguyen KD, Dang AT, Hoang TT, Vo PQ, Sandroni P. Involvement of GABA(A) receptors in myoclonus. Mov Disord. 2000; 15(Suppl 1):47–52. PMID: 10755272.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Lance-Adams Syndrome
- A Case of The Successful Treatment of Pentobarbital for Posthypoxic Action Myoclonus(Lance-Adams Syndrome) with Refractory Status Epilepticus
- An Exploration of the Neural Network of Lance-Adams Syndrome: a Case Report
- Acute onset Lance-Adams syndrome following brief exposure to severe hypoxia without cardiac arrest: a case report
- A Case of Corrosive Gastritis Caused by Salt-fermented Northern Sand Lance