Ultrasonography of Median Nerve and Electrophysiologic Severity in Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Gangwon-do Rehabilitation Hospital, Chuncheon 200-853, Korea.
- 2Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul 136-705, Korea. hkkwon@korea.ac.kr
- 3Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, SahmYook Medical Center, Seoul 130-711, Korea.
- KMID: 2266783
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2012.36.1.72
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
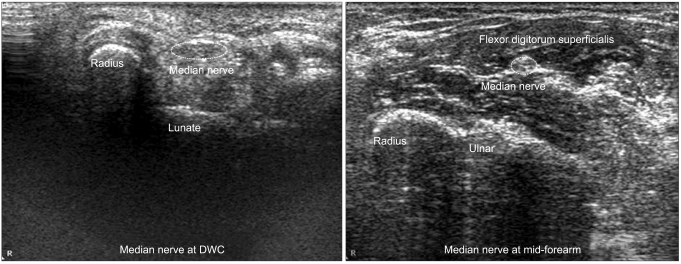
To investigate the correlation of the ultrasonographic wrist-to-forearm median nerve area ratio (WFR) and cross sectional area of median nerve at the wrist (CSA-W) to the electrophysiologic severity in patients with carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS). METHOD: One hundred and ten wrists electrophysiologically graded as mild, moderate, and severe CTS and 38 healthy controls underwent ultrasonography of median nerve at the distal wrist crease and mid-forearm. WFR and CSA-W were analyzed according to the severity of CTS.
RESULTS
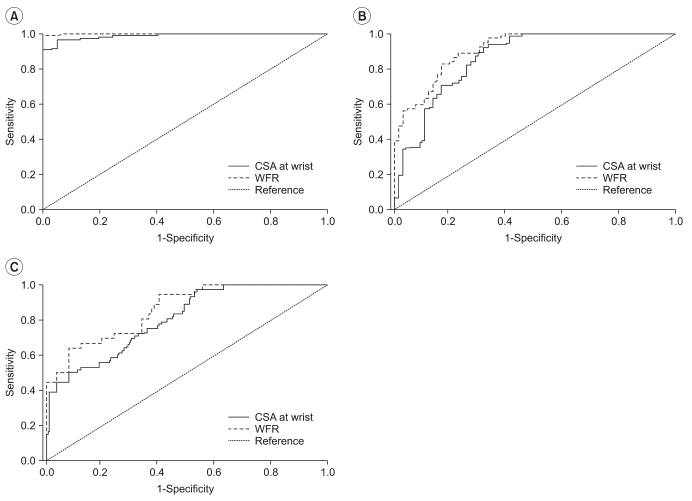
WFR was 1.12+/-0.14, 1.91+/-0.33, 2.27+/-0.47 and 3.02+/-0.97 and the CSAs-W was 7.23+/-1.67 mm2, 13.51+/-3.72 mm2, 14.67+/-2.93 mm2, and 18.74+/-6.01 mm2 in controls, mild (n=28), moderate (n=46), and severe (n=36) CTS, respectively. CSA-W displayed significant differences between the control and the mild CTS, moderate CTS and severe CTS groups. However, there was no significant difference between mild CTS and moderate CTS groups. WFR revealed significant difference between all groups. The sensitivity and specificity of the WFR in grading the severity of CTS were higher than those of the CSA-W.
CONCLUSION
Ultrasonography is a useful complementary tool for the evaluation of CTS. Both WFR and CSA-W are highly correlated with severity grade of CTS. However, WFR is superior to CSA-W for diagnosis and grading of the severity of CTS.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 4 articles
-
Analysis of Sonographic Measurement by Anatomical Area in Carpal Tunnel Syndrome and Correlation the Measurement with Electrodiagnostic Study
JungWoo Park
Arch Hand Microsurg. 2020;25(1):8-16. doi: 10.12790/ahm.19.0062.Diagnostic Significance of Ultrasonographic Measurements and Median-Ulnar Ratio in Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: Correlation with Nerve Conduction Studies
Ozan Volkan Yurdakul, Nilgün Mesci, Yilmaz Çetinkaya, Duygu Geler Külcü
J Clin Neurol. 2016;12(3):289-294. doi: 10.3988/jcn.2016.12.3.289.Diagnostic Cutoff Value for Ultrasonography of the Common Fibular Neuropathy at the Fibular Head
Ji Yeon Kim, Seojin Song, Hye Jung Park, Won Ihl Rhee, Sun Jae Won
Ann Rehabil Med. 2016;40(6):1057-1063. doi: 10.5535/arm.2016.40.6.1057.Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Assessment With Ultrasonography: A Comparison Between Non-diabetic and Diabetic Patients
Chung Ho Lee, Hanboram Choi, Joon Shik Yoon, Seok Kang
Ann Rehabil Med. 2018;42(1):85-91. doi: 10.5535/arm.2018.42.1.85.
Reference
-
1. Jablecki CK, Andary MT, Floeter MK, Miller RG, Qartly CA, Vennix MJ, Wilson JR. Practice parameter: electrodiagnostic studies in carpal tunnel syndrome. Report of the American Association of Electrodiagnostic Medicine, American Academy of Neurology, and the American Academy of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. Neurology. 2002; 58:1589–1592. PMID: 12058083.
Article2. Buchberger W, Schon G, Strasser K, Jungwirth W. High-resolution ultrasonography of the carpal tunnel. J Ultrasound Med. 1991; 10:531–537. PMID: 1942218.
Article3. Wong SM, Griffith JF, Hui AC, Lo SK, Fu M, Wong KS. Carpal tunnel syndrome: diagnostic usefulness of sonography. Radiology. 2004; 232:93–99. PMID: 15155897.
Article4. Yoon JS, Kim BJ, Kim SJ, Kim JM, Sim KH, Hong SJ, Walker FO, Cartwright MS. Ultrasonographic measurements in cubital tunnel syndrome. Muscle Nerve. 2007; 36:853–855. PMID: 17879384.
Article5. Yoon JS, Walker FO, Cartwright MS. Ultrasonographic swelling ratio in the diagnosis of ulnar neuropathy at the elbow. Muscle Nerve. 2008; 38:1231–1235. PMID: 18785184.
Article6. Tuncali D, Barutcu AY, Terzioglu A, Aslan G. Carpal tunnel syndrome: comparison of intraoperative structural changes with clinical and electrodiagnostic severity. Br J Plast Surg. 2005; 58:1136–1142. PMID: 16054604.
Article7. Hammer HB, Hovden IA, Haavardsholm EA, Kvien TK. Ultrasonography shows increased cross-sectional area of the median nerve in patients with arthritis and carpal tunnel syndrome. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2006; 45:584–588. PMID: 16332951.
Article8. Beekman R, Visser LH. Sonography in the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome: a critical review of the literature. Muscle Nerve. 2003; 27:26–33. PMID: 12508291.
Article9. Peeters EY, Nieboer KH, Osteaux MM. Sonography of the normal ulnar nerve at Guyon's canal and of the common peroneal nerve dorsal to the fibular head. J Clin Ultrasound. 2004; 32:375–380. PMID: 15372443.
Article10. Cartwright MS, Shin HW, Passmore LV, Walker FO. Ultrasonographic findings of the normal ulnar nerve in adults. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2007; 88:394–396. PMID: 17321837.
Article11. Martinoli C, Schenone A, Bianchi S, Mandich P, Caponetto C, Abbruzzese M, Derchi LE. Sonography of the median nerve in Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2002; 178:1553–1556. PMID: 12034637.
Article12. Cho JM, Yoon JS, Kim SJ, Park BK, Lee GH, Jeong JS. Feasibility of ultrasonographic area ratio of median nerve in the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome in Korea. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 2009; 33:627–631.13. Cartwright MS, Shin HW, Walker FO. Ultrasonographic characteristics of the normal median nerve. Neurology. 2006; 66(Suppl 2):A83.14. Hobson-Webb LD, Massey JM, Juel VC, Sanders DB. The ultrasonographic wrist-to-forearm median nerve area ratio in carpal tunnel syndrome. Clin Neurophysiol. 2008; 119:1353–1357. PMID: 18387336.
Article15. American Association of Electrodiagnostic Medicine. Guidelines in electrodiagnostic medicine. Practice parameter for electrodiagnostic studies in carpal tunnel syndrome. Muscle Nerve Suppl. 1999; 8:S141–S167. PMID: 16921633.16. Bland JD. A neurophysiological grading scale for carpal tunnel syndrome. Muscle Nerve. 2000; 23:1280–1283. PMID: 10918269.
Article17. Giannini F, Cioni R, Mondelli M, Padua R, Gregori B, D'Amico P, Padua L. A new clinical scale of carpal tunnel syndrome: validation of the measurement and clinical-neurophysiological assessment. Clin Neurophysiol. 2002; 113:71–77. PMID: 11801427.
Article18. Padua L. A new approach to carpal tunnel syndrome: multicenter studies with multiperspective assessment. AAEM Course H. 2003. 2003 Sep 16-20; San Francisco, USA. Rochester: American Association of Electrodiagnostic Medicine.19. Stevens JC. AAEM minimonograph #26: the electrodiagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome American Association of Electrodiagnostic Medicine. Muscle Nerve. 1997; 20:1477–1486. PMID: 9390659.20. Wee AS. Carpal tunnel syndrome: a system for categorizing and grading electrophysiologic abnormalities. Electromyogr Clin Neurophysiol. 2001; 41:281–288. PMID: 11572189.21. El Miedany YM, Aty SA, Ashour S. Ultrasonography versus nerve conduction study in patients with carpal tunnel syndrome: substantive or complementary tests? Rheumatology (Oxford). 2004; 43:887–895. PMID: 15100417.
Article22. Lee HJ, Kwon HK. Electrophysiologic classification of severity of carpal tunnel syndrome. J Korean Assoc EMG-Electrodiagn Med. 2004; 6:1–3.23. Cho YS, Lee SH, Kwon HK, Lee HJ. Reappraisal of nerve conduction studies in carpal tunnel syndrome. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 1998; 22:861–865.24. Kotevoglu N, Gulbahce-Saglam S. Ultrasound imaging in the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome and its relevance to clinical evaluation. Joint Bone Spine. 2005; 72:142–145. PMID: 15797494.
Article25. Buchberger W, Judmaier W, Birbamer G, Lener M, Schmidauer C. Carpal tunnel syndrome: diagnosis with high-resolution sonography. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1992; 159:793–798. PMID: 1529845.
Article26. Lee CH, Kim TK, Yoon ES, Dhong ES. Correlation of high-resolution ultrasonographic findings with the clinical symptoms and electrodiagnostic data in carpal tunnel syndrome. Ann Plast Surg. 2005; 54:20–23. PMID: 15613877.
Article27. Bayrak IK, Bayrak AO, Tilki HE, Nural MS, Sunter T. Ultrasonography in carpal tunnel syndrome: comparison with electrophysiological stage and motor unit number estimate. Muscle Nerve. 2007; 35:344–348. PMID: 17143879.
Article28. Padua L, Pazzaglia C, Caliandro P, Granata G, Foschini M, Briani C, Martinoli C. Carpal tunnel syndrome: ultrasound, neurophysiology, clinical and patient-oriented assessment. Clin Neurophysiol. 2008; 119:2064–2069. PMID: 18620908.
Article29. Park JY, Park SR, Lee SH, Choi KH. The ultrasonographic findings of the median nerve in the carpal tunnel according to age and sex of normal Korean adults. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 2008; 32:564–569.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Ultrasonographic Study of Median Nerve after Carpal Tunnel Release
- The Abnormal Ultrasonographic Findings of Carpal Tunnel in Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
- The Correlation Between Electrodiagnostic Results and Ultrasonographic Findings in the Severity of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome in Females
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
- A Comparison of Diagnostic Usefulness of Sonography and Electrophysiologic Study in Patients with Carpal Tunnel Syndrome