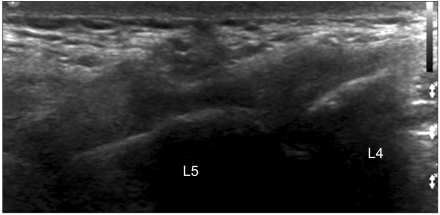
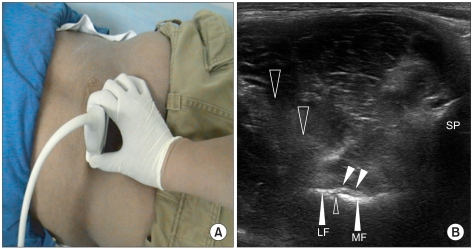
Ann Rehabil Med.
2012 Feb;36(1):66-71. 10.5535/arm.2012.36.1.66.
Efficacy of Ultrasonography-Guided Injections in Patients with Facet Syndrome of the Low Lumbar Spine
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, College of Medicine, Kyung Hee University, Seoul 130-702, Korea. pk9282@naver.com
- KMID: 2266782
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2012.36.1.66
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To investigate the efficacy of ultrasonography (US)-guided injections in patients with low lumbar facet syndrome, compared with that in patients who received fluoroscopy (FS)-guided injections. METHOD: Fifty-seven subjects with facet syndrome of the lumbar spine of the L4-5 and L5-S1 levels were randomly divided into two groups to receive intraarticular injections into the facet joint. One group received FS-guided facet joint injections and the other group received US-guided facet joint injections. Treatment effectiveness was assessed using a visual analogue scale (VAS), physician's and patient's global assessment (PhyGA, PaGA), and the modified Oswestry Disability Index (MODI). All parameters were evaluated four times: before injections, and at a week, a month, and three months after injections. We also measured, in both groups, how long it took to complete the whole procedure.
RESULTS
Each group showed significant improvement from the facet joint injections on the VAS, PhyGA, PaGA, and MODI (p<0.05). However at a week, a month, and three months after injections, no significant differences were observed between the groups with regard to VAS, PhyGA, PaGA, and MODI (p>0.05). Statistically significant differences in procedure time were observed between groups (FS: 248.7+/-6.5 sec; US: 263.4+/-5.9 sec; p=0.023).
CONCLUSION
US-guided injections in patients with lumbar facet syndrome are as effective as FS-guided injections for pain relief and improving activities of daily living.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Boswell MV, Colson JD, Spillane WF. Therapeutic facet joint interventions in chronic spinal pain: a systematic review of effectiveness and complications. Pain Physician. 2005; 8:101–114. PMID: 16850048.2. Sehgal N, Shah RV, McKenzie-Brown AM, Everett CR. Diagnostic utility of facet (zygapophysial) joint injections in chronic spinal pain: a systematic review of evidence. Pain Physician. 2005; 8:211–224. PMID: 16850075.3. Joy H, Ha SK, Kim SH, Lim DJ, Park JY, Suh JK. Prognostic factors of percutaneous radiofrequency neurotomy on the posterior primary ramus. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2003; 33:51–55.4. Bogduk N. International Spinal Injections Society guidelines for the performance of spinal injections procedures. Part I: Zygapophysial joint blocks. Clin J Pain. 1997; 13:285–302. PMID: 9430809.5. Greher M, Kirchmair L, Enna B, Kovacs P, Gustorff B, Kapral S, Moriggl B. Ultrasound-guided lumbar facet nerve block: accuracy of a new technique confirmed by computed tomography. Anesthesiology. 2004; 101:1195–1200. PMID: 15505456.6. Greher M, Kapral S. Is regional anesthesia simply an exercise in appliedsonoanatomy?: aiming at higher frequencies of ultrasonographic imaging. Anesthesiology. 2003; 99:250–251. PMID: 12883395.7. Galiano K, Obwegeser AA, Walch C, Schatzer R, Ploner F, Gruber H. Ultrasound-guided versus computed tomography-controlled facet joint injections in the lumbar spine: a prospective randomized clinical trial. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2007; 32:317–322. PMID: 17720116.
Article8. Manchikanti L, Manchikanti KN, Manchukonda R, Cash KA, Damron KS, Pampati V, McManus CD. Evaluation of lumbar facet joint nerve blocks in the management of chronic low back pain: preliminary report of a randomized, double-blind controlled trial: clinical trial NC T00355914. Pain Physician. 2007; 10:425–440. PMID: 17525777.9. Galiano K, Obwegeser AA, Bodner G, Freund M, Maurer H, Kamelger FS, Schatzer R, Ploner F. Ultrasound guidance for facet joint injections in the lumbar spine: a computed tomography-Controlled feasibility study. Anesth Analg. 2005; 101:579–583. PMID: 16037179.
Article10. Aguirre DA, Bermudez S, Diaz OM. Spinal CT-guided interventional procedures for management of chronic back pain. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2005; 16:689–697. PMID: 15872324.
Article11. Wagner LK, Eifel PJ, Geise RA. Potential biological effects following high X-ray dose interventional procedures. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 1994; 5:71–84. PMID: 8136601.
Article12. Kim HS, Ahn KH, Yun DH, Oh JJ, Jeong YS, Kim DH. Skin lesion after repeated fluoroscopically guided procedures: a case report. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 2001; 25:729–733.13. Nelemans PJ, deBie RA, deVet HC, Sturmans F. Injections therapy for subacute and chronic benign low back pain. Spine. 2001; 26:501–515. PMID: 11242378.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Lumbar Facet Joint Injection: A Review of Efficacy and Safety
- Degenerative Diseases and Ultrasound-guided Intervention in Lumbar Spine
- Ultrasound-Guided Injections in the Lumbar and Sacral Spine
- Comprasion of Effectiveness of CT vs C-arm Guided Percutaneous Radiofrequency Lumbar Facet Rhizotomy
- The Effect of Intra-articular Hyaluronic Acid in Facet Syndrome of the Lumbar Spine