Ann Rehabil Med.
2012 Aug;36(4):556-560. 10.5535/arm.2012.36.4.556.
Alien Hand Syndrome in Stroke: Case Report & Neurophysiologic Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Inha University College of Medicine, Incheon 400-711, Korea. rmjung@inha.ac.kr
- KMID: 2266728
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2012.36.4.556
Abstract
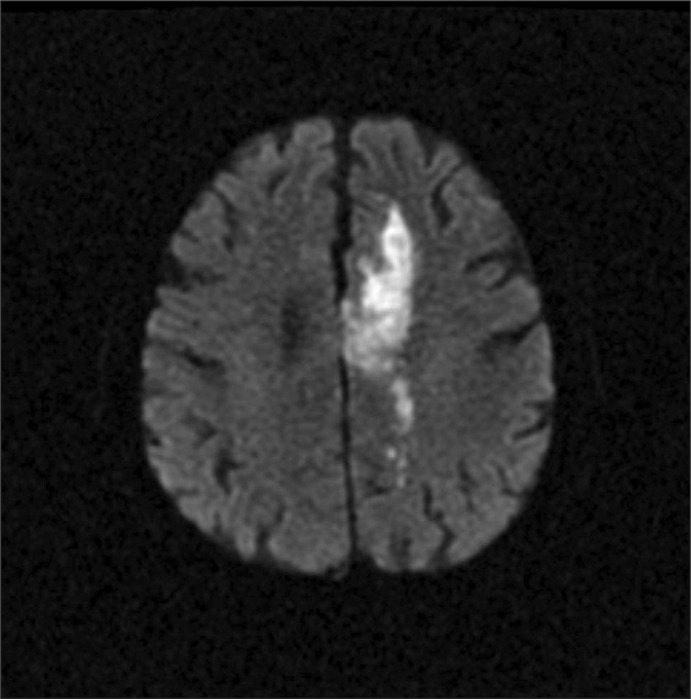
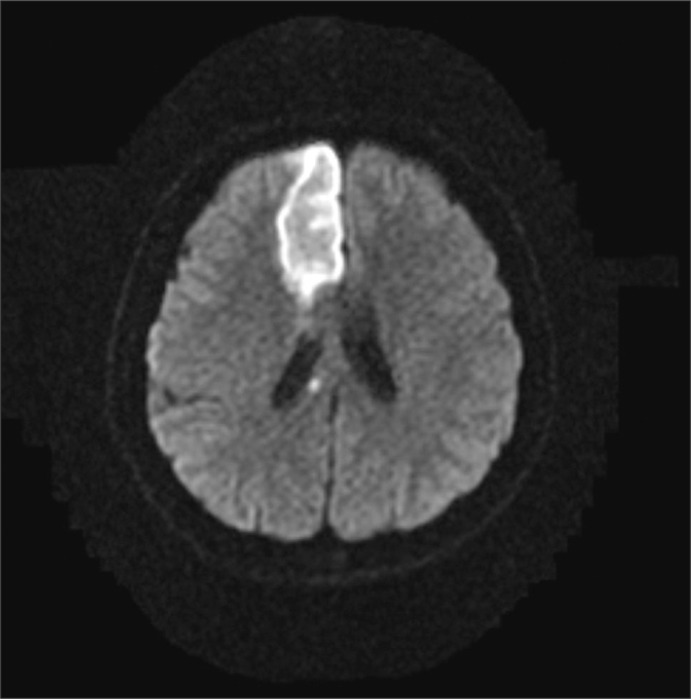
- Alien Hand Syndrome is defined as unwilled, uncontrollable, but seemingly purposeful movements of an upper limb. Two major criteria for the diagnosis are complaint of a foreign limb and complex, autonomous, involuntary motor activity that is not part of an identifiable movement disorder. After a cerebrovascular accident in the corpus callosum, the parietal, or frontal regions, various abnormal involuntary motor behaviors may follow. Although different subtypes of Alien Hand Syndrome have been distinguished, this classification clearly does not cover the wide clinical variety of abnormal motor behaviors of the upper extremity. And there are few known studies about the neurophysiology of this syndrome using transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS). We recently experienced 2 rare cases of Alien Hand Syndrome which occurred after anterior cerebral artery (ACA) infarction. A 72 year-old male with right hemiplegia following a left ACA infarct had difficulty with voluntarily releasing an object from his grasp. A 47 year-old female with left hemiplegia following a right ACA infarct had a problem termed 'intermanual conflict' in which the two hands appear to be directed at opposing purposes. Both of them had neurophysiologic studies done, and showed reduced amplitude by single pulse MEP and a lack of intracortical inhibition (ICI) by paired pulse TMS. No abnormalities were found in SSEP.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kikkert MA, Ribbers GM, Koudstaal PJ. Alien hand syndrome in stroke: a report of 2 cases and review of the literature. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2006; 87:728–732. PMID: 16635638.
Article2. Dolado AM, Castrillo C, Urra DG, Varela de Seijas E. Alien hand sign or alien hand syndrome? J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1995; 59:100–101. PMID: 7608695.
Article3. Ay H, Buonanno FS, Price BH, Le DA, Koroshetz WJ. Sensory alien handsyndrome: case report and review of the literature. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1998; 65:366–369. PMID: 9728952.4. Marey-Lopez J, Rubio-Nazabal E, Alonso-Magdalena L, Lopez-Facal S. Posterior alien hand syndrome after a right thalamic infarct. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2002; 73:447–479. PMID: 12235318.
Article5. McNabb AW, Carroll WM, Mastaglia FL. "Alien hand" and loss of bimanual coordination after dominant anterior cerebral artery territory infarction. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1988; 51:218–222. PMID: 3346686.
Article6. Chen R, Tam A, Butefisch C, Corwell B, Ziemann U, Rothwell JC, Cohen LG. Intracortical inhibition and facilitation in different representations of the human motor cortex. J Neurophysiol. 1998; 80:2870–2881. PMID: 9862891.
Article7. Ridding MC, Sheean G, Rothwell JC, Inzelberg R, Kujirai T. Changes in the balance between motor cortical excitation and inhibition in focal, task specific dystonia. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1995; 59:493–498. PMID: 8530933.
Article8. Oh BM, Kim DY, Paik NJ. The relationship between the severity of motor impairment and motor cortical excitability in the unaffected hemisphere after unilateral stroke. Int Congr Ser. 2005; 1278:291–294.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Right Sensory Alien Hand Phenomenon from a Left Pontine Hemorrhage
- Hemichoreoballism with Anterior Cerebral Artery Territory Infarction
- Pure Posterior Alien Hand Syndrome Following a Cerebrovascular Lesion: Clinicoradiological Correlates
- A Case with the Alien Hand Sign
- Two Cases of Callosal Disconnection Syndrome: Impaired Body Cognition of Nondominant Limbs