Ann Rehabil Med.
2014 Oct;38(5):698-701. 10.5535/arm.2014.38.5.698.
Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis and Venous Hemorrhagic Infarction in a Young Woman
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Physical & Rehabilitation Medicine, Regional Cardiocerebrovascular Center, Chonnam National University Hospital, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea. drchoiis@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2266506
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2014.38.5.698
Abstract
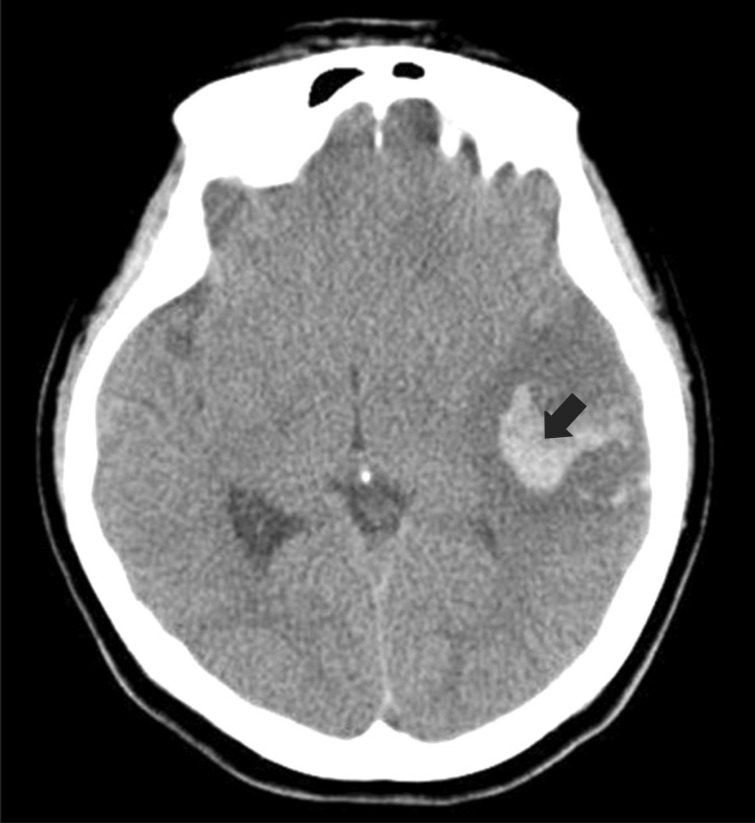
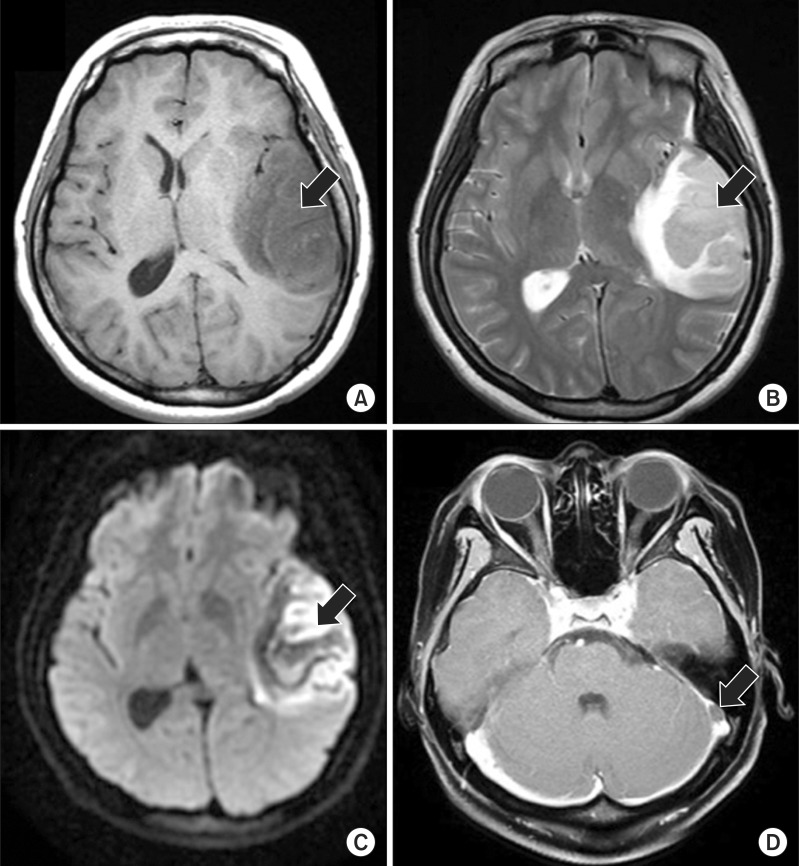
- Cerebral venous sinus thrombosis (CVST) is an uncommon cause of cerebral infarction, compared to arterial diseases. It is often unrecognized at initial presentation due to the diversity of causes and clinical manifestations. A 29-year-old female patient complained of severe headache and presented at the emergency room with altered consciousness. Brain computed tomography and brain magnetic resonance image revealed the left sigmoid sinus thrombosis with venous hemorrhagic infarction (VHI) in the left temporal lobe. The patient had no past medical and family history of bleeding diathesis. The laboratory finding at the admission showed severe iron-deficiency anemia (IDA), and protein C and S activities were decreased. After the neurosurgery, iron replacement, and neurorehabilitation, the patient had a good recovery. There has been no known recurrence. We report our therapeutic intervention on a very rare case of CVST and VHI, with IDA as a probable cause of cerebral thrombosis.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Saposnik G, Barinagarrementeria F, Brown RD Jr, Bushnell CD, Cucchiara B, Cushman M, et al. Diagnosis and management of cerebral venous thrombosis: a statement for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2011; 42:1158–1192. PMID: 21293023.
Article2. Ferro JM, Canhao P, Stam J, Bousser MG, Barinagarrementeria F. ISCVT Investigators. Prognosis of cerebral vein and dural sinus thrombosis: results of the International Study on Cerebral Vein and Dural Sinus Thrombosis (ISCVT). Stroke. 2004; 35:664–670. PMID: 14976332.3. Jalili M, Ghourchian S, Shahidi GA, Rohani M, Rezvani M, Zamani B. A study of factors associated with cerebral venous thrombosis. Neurol Sci. 2013; 34:321–326. PMID: 22395946.
Article4. Huang PH, Su JJ, Lin PH. Iron deficiency anemia: a rare etiology of sinus thrombosis in adults. Acta Neurol Taiwan. 2010; 19:125–130. PMID: 20714964.5. Coutinho JM, Zuurbier SM, Aramideh M, Stam J. The incidence of cerebral venous thrombosis: a cross-sectional study. Stroke. 2012; 43:3375–3377. PMID: 22996960.6. Bousser MG, Ferro JM. Cerebral venous thrombosis: an update. Lancet Neurol. 2007; 6:162–170. PMID: 17239803.
Article7. Liu K, Kaffes AJ. Iron deficiency anaemia: a review of diagnosis, investigation and management. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012; 24:109–116. PMID: 22157204.8. Cavenagh JD, Colvin BT. Guidelines for the management of thrombophilia. Postgrad Med J. 1996; 72:87–94. PMID: 8871458.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis Associated with Antithrombin III Deficiency: A Case Report
- A Case of Puerperal Cerebral Hemorrhagic Infarction with Venoue Thrombosis
- Cerebral Venous Thrombosis Complicated by Hemorrhagic Infarction Secondary to Ventriculoperitoneal Shunting
- A Case of Leptomeningeal Metastasis Associated with Cerebral Venous Thrombosis
- A Case of Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis Treated with Local Thrombolysis