Ann Dermatol.
2010 Nov;22(4):482-485. 10.5021/ad.2010.22.4.482.
Vitiligo Coexistent with Nevus Depigmentosus: This Was Treated with Narrow-Band UVB and These Lesions Were Followed Using the Mexameter(R), a Pigment-Measuring Device
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, Busan Paik Hospital, College of Medicine, Inje University, Busan, Korea. btyouth@hanmail.net
- 2Department of Dermatology, Maryknoll Hospital, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 2266194
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2010.22.4.482
Abstract
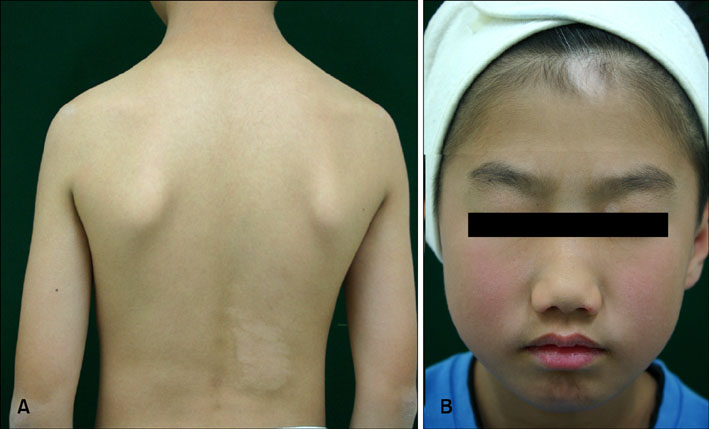
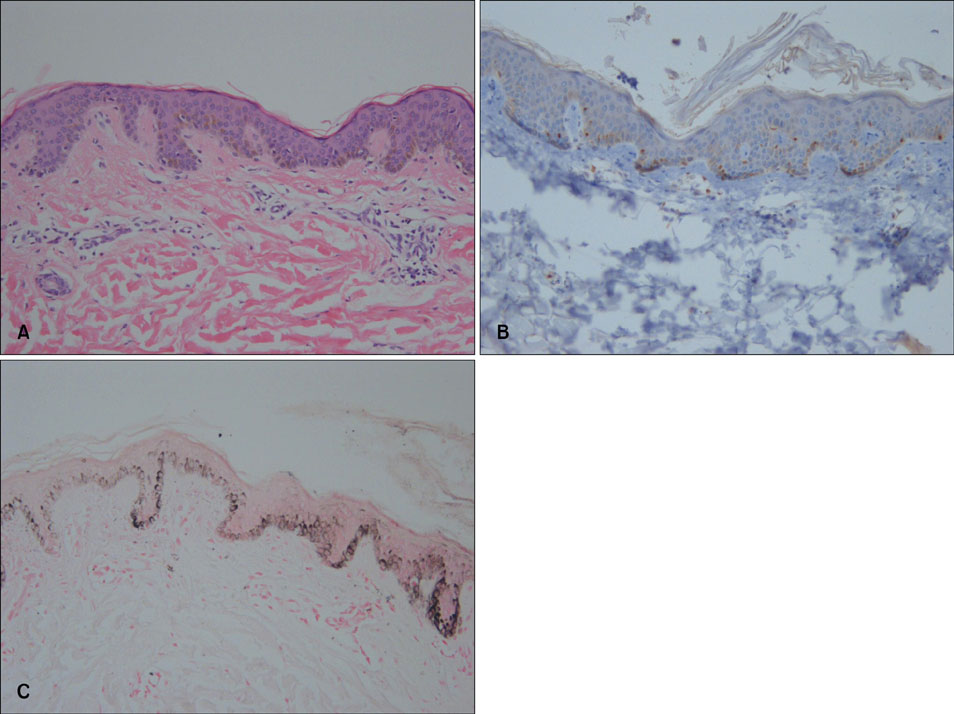
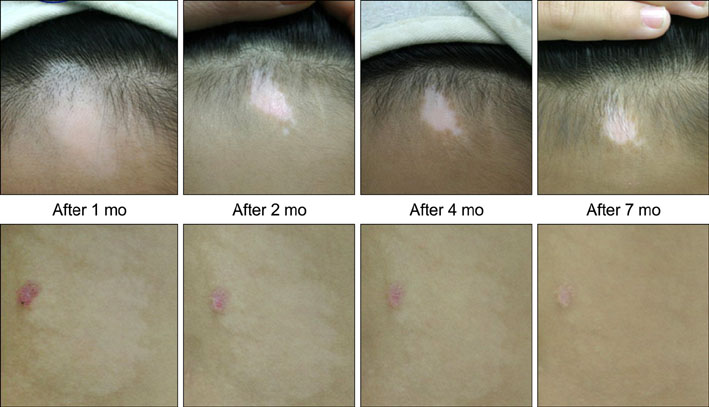
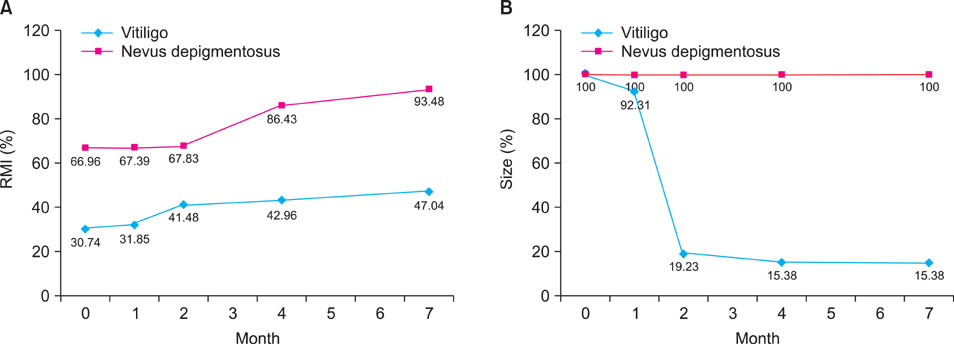
- Nevus depigmentosus (ND) is a congenital, non-progressive, hypopigmented lesion that is usually stable throughout an affected individual's lifetime. The clinical features of vitiligo are similar to those of ND, but the two diseases have different treatment responses and prognoses. We report here on a rare case of vitiligo that was coexistent with ND. Both conditions were treated with narrow-band UVB. An 11-year-old boy presented with two distinct types of hypopigmented lesions, one on the forehead and the other on his back. The first was a hypopigmented patch with leukotrichia, and it was incidentally discovered 3 months before the child was examined at our clinic and it had rapidly increased in size. The second hypopigmented patch was detected at birth and it had slowly been increasing in size. The hypopigmented lesion on the child's forehead was diagnosed as vitiligo, and the one on his back as ND. Once- or twice-weekly narrow-band UVB treatment was initiated. Improvements in the two lesions were assessed with clinical photography and using a Mexameter(R) (Courage-Khazaka Electronic, Germany), which is a pigment-measuring device.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lee HS, Chun YS, Hann SK. Nevus depigmentosus: clinical features and histopathologic characteristics in 67 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1999. 40:21–26.
Article2. Park ES, Na JI, Kim SO, Huh CH, Youn SW, Park KC. Application of a pigment measuring device-Mexameter-for the differential diagnosis of vitiligo and nevus depigmentosus. Skin Res Technol. 2006. 12:298–302.
Article3. Yoshimura K, Harii K, Masuda Y, Takahashi M, Aoyama T, Iga T. Usefulness of a narrow-band reflectance spectrophotometer in evaluating effects of depigmenting treatment. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2001. 25:129–133.
Article4. Clarys P, Alewaeters K, Lambrecht R, Barel AO. Skin color measurements: comparison between three instruments: the Chromameter®, the DermaSpetrometer® and the Mexameter®. Skin Res Technol. 2000. 6(230):238–.5. Gupta S, Goel A. Nevus depigmentosus needs transplant of epidermal sheets. Dermatol Surg. 2005. 31:1746–1747.6. Kim do Y, Lee KY, Park YK. Use of the 308-nm excimer laser for nevus depigmentosus: a promising treatment for either nevus depigmentosus or vitiligo. J Dermatol. 2007. 34:217–218.
Article7. Scott G, Deng A, Rodriguez-Burford C, Seiberg M, Han R, Babiarz L, et al. Protease-activated receptor 2, a receptor involved in melanosome transfer, is upregulated in human skin by ultraviolet irradiation. J Invest Dermatol. 2001. 117:1412–1420.
Article8. Kang IK, Hann SK. Vitiligo coexistent with nevus depigmentosus. J Dermatol. 1996. 187–190.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Efficacy of Narrow-Band UVB Phototherapy in Vitiligo Patients
- Narrow-band UVB as a Tool of Vitiligo Treatment
- Therapeutic Effects of Narrow-band UVB Phototherapy in the Treatment of Vitiligo
- Hypopigmentary Disorders Excluding Vitiligo : Clinical Features in 301 Patients
- Study of Vitiligo and Nevus Depigmentosus in Children by Clinical Evaluation and DOPA Staining