Ann Dermatol.
2012 Nov;24(4):438-443. 10.5021/ad.2012.24.4.438.
The Clinical Efficacy, Safety and Functionality of Anion Textile in the Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, Busan Paik Hospital, College of Medicine, Inje University, Busan, Korea. karrot75@hanmail.net
- 2Dr Park's Dermatologic Clinic, Busan, Korea.
- 3Department of Laboratory Medicine, Busan Paik Hospital, College of Medicine, Inje University, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 2266039
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2012.24.4.438
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Several previous studies have suggested the improvement of atopic dermatitis (AD) in response to special fabrics. In particular, beneficial effects have been reported, following the use of anion textiles.
OBJECTIVE
The purpose of this study is to evaluate the effectiveness and safety of an anion textile in patients suffering from AD.
METHODS
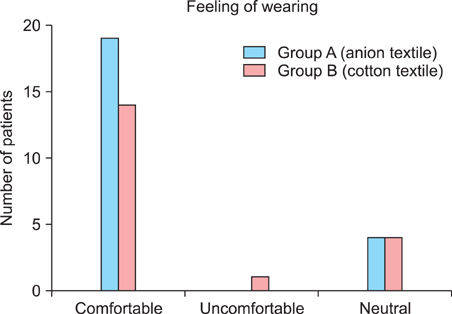
We compared an anion textile with a pure cotton textile. Fifty-two atopic patients (n=52) were enrolled and divided into two groups. The patients in the test (n=25) and control (n=19) groups wore undergarments made of an anion textile or pure cotton over a period of 4 weeks. The overall severity of disease was evaluated using the SCORing atopic dermatitis (SCORAD) index, whereas, the treatment efficacy was measured using a Tewameter(R) (Courage & Khazaka, Cologne, Germany), Mexameter(R) (Courage & Khazaka) and Corneo meter(R) (Courage & Khazaka).
RESULTS
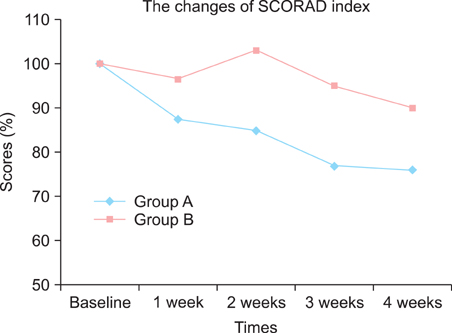
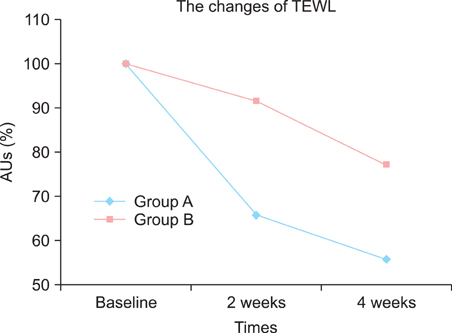
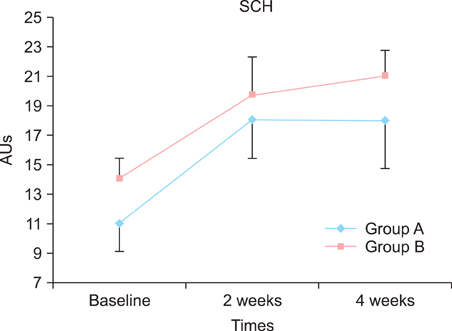
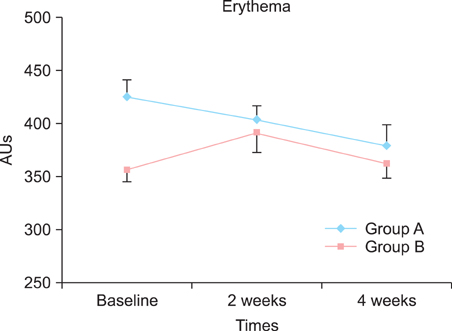
At the end of the study, a significant decrease in the SCORAD index was observed among the patients with AD in the test group (mean SCORAD decreased from 47.2 to 36.1). Similarly, improvements in the mean transepidermal water loss, skin erythema and stratum corneum hydration were significantly greater among the patients with AD in the test group than in the control group.
CONCLUSION
Anion textiles may be used to significantly improve the objective and subjective symptoms of AD, and are similar in terms of comfort to cotton textiles. The use of anion textiles may be beneficial in the management of patients with AD.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Williams JR, Burr ML, Williams HC. Factors influencing atopic dermatitis-a questionnaire survey of schoolchildren's perceptions. Br J Dermatol. 2004. 150:1154–1161.
Article2. Roll A, Cozzio A, Fischer B, Schmid-Grendelmeier P. Microbial colonization and atopic dermatitis. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004. 4:373–378.
Article3. Baker BS. The role of microorganisms in atopic dermatitis. Clin Exp Immunol. 2006. 144:1–9.
Article4. Hermanns JF, Goffin V, Arrese JE, Rodriguez C, Piérard GE. Beneficial effects of softened fabrics on atopic skin. Dermatology. 2001. 202:167–170.
Article5. Ricci G, Patrizi A, Mandrioli P, Specchia F, Medri M, Menna G, et al. Evaluation of the antibacterial activity of a special silk textile in the treatment of atopic dermatitis. Dermatology. 2006. 213:224–227.
Article6. Gauger A. Silver-coated textiles in the therapy of atopic eczema. Curr Probl Dermatol. 2006. 33:152–164.
Article7. Ricci G, Patrizi A, Bellini F, Medri M. Use of textiles in atopic dermatitis: care of atopic dermatitis. Curr Probl Dermatol. 2006. 33:127–143.8. Juenger M, Ladwig A, Staecker S, Arnold A, Kramer A, Daeschlein G, et al. Efficacy and safety of silver textile in the treatment of atopic dermatitis (AD). Curr Med Res Opin. 2006. 22:739–750.
Article9. Gauger A, Fischer S, Mempel M, Schaefer T, Foelster-Holst R, Abeck D, et al. Efficacy and functionality of silver-coated textiles in patients with atopic eczema. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2006. 20:534–541.
Article10. Hipler UC, Elsner P, Fluhr JW. Antifungal and antibacterial properties of a silver-loaded cellulosic fiber. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2006. 77:156–163.
Article11. Ricci G, Patrizi A, Bendandi B, Menna G, Varotti E, Masi M. Clinical effectiveness of a silk fabric in the treatment of atopic dermatitis. Br J Dermatol. 2004. 150:127–131.
Article12. Gauger A, Mempel M, Schekatz A, Schäfer T, Ring J, Abeck D. Silver-coated textiles reduce Staphylococcus aureus colonization in patients with atopic eczema. Dermatology. 2003. 207:15–21.
Article13. Hanifin JM, Rajka G. Diagnostic features of atopic dermatitis. Acta Derm Venereol Suppl (Stockh). 1980. 92:44–47.14. Severity scoring of atopic dermatitis: the SCORAD index. Consensus Report of the European Task Force on Atopic Dermatitis. Dermatology. 1993. 186:23–31.15. Rogiers V. EEMCO Group. EEMCO guidance for the assessment of transepidermal water loss in cosmetic sciences. Skin Pharmacol Appl Skin Physiol. 2001. 14:117–128.
Article16. Berardesca E. European Group for Efficacy Measurements on Cosmetics and Other Topical Products (EEMCO). EEMCO guidance for the assessment of stratum corneum hydration: electrical methods. Skin Res Technol. 1997. 3:126–132.
Article17. Fluhr JW, Kuss O, Diepgen T, Lazzerini S, Pelosi A, Gloor M, et al. Testing for irritation with a multifactorial approach: comparison of eight non-invasive measuring techniques on five different irritation types. Br J Dermatol. 2001. 145:696–703.
Article18. Clarys P, Alewaeters K, Lambrecht R, Barel AO. Skin color measurements: comparison between three instruments: the Chromameter(R), the DermaSpectrometer(R) and the Mexameter( R). Skin Res Technol. 2000. 6:230–238.
Article19. Hatch KL, Maibach HI. Textile fiber dermatitis. Contact Dermatitis. 1985. 12:1–11.
Article20. Senti G, Steinmann LS, Fischer B, Kurmann R, Storni T, Johansen P, et al. Antimicrobial silk clothing in the treatment of atopic dermatitis proves comparable to topical corticosteroid treatment. Dermatology. 2006. 213:228–233.
Article21. Ring J, Brockow K, Abeck D. The therapeutic concept of "patient management" in atopic eczema. Allergy. 1996. 51:206–215.
Article22. Niwa Y, Iizawa O, Ishimoto K, Jiang X, Kanoh T. Electromagnetic wave emitting products and "Kikoh" potentiate human leukocyte functions. Int J Biometeorol. 1993. 37:133–138.
Article23. Dover JS, Phillips TJ, Arndt KA. Cutaneous effects and therapeutic uses of heat with emphasis on infrared radiation. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1989. 20:278–286.
Article24. Meng J, Jin W, Liang J, Ding Y, Gan K, Yuan Y. Effects of particle size on far infrared emission properties of tourmaline superfine powders. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2010. 10:2083–2087.
Article25. Ju K, Kubo T. Power spectral analysis of autonomic nervous activity in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Biomed Sci Instrum. 1997. 33:338–343.26. Yoo BH, Park CM, Oh TJ, Han SH, Kang HH, Chang IS. Investigation of jewelry powders radiating far-infrared rays and the biological effects on human skin. J Cosmet Sci. 2002. 53:175–184.27. Suzuki S, Yanagita S, Amemiya S, Kato Y, Kubota N, Ryushi T, et al. Effects of negative air ions on activity of neural substrates involved in autonomic regulation in rats. Int J Biometeorol. 2008. 52:481–489.
Article28. Watanabe I, Noro H, Ohtsuka Y, Mano Y, Agishi Y. Physical effects of negative air ions in a wet sauna. Int J Biometeorol. 1997. 40:107–112.
Article29. Abeck D, Strom K. Optimal management of atopic dermatitis. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2000. 1:41–46.
Article30. Borelli S, Stern A, Wüthrich B. A silk cardigan inducing asthma. Allergy. 1999. 54:900–901.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Superoxide Anion Generation of Neutrophils in Patients with Atopic Dermatitis
- Measurement of Atopic Dermatitis Disability
- Improvement of Post-inflammatory Hyperpigmentation, Subsequent to Cold Atmospheric Plasma Treatment, in a Patient with Atopic Dermatitis
- Tacrolimus ointment: An Open study for Effects on Severe Facial Atopic Dermatitis in Korean
- Efficacy of 0.1% Tacrolimus Ointment in Korean Patients with Atopic Dermatitis