Ann Dermatol.
2014 Aug;26(4):524-525. 10.5021/ad.2014.26.4.524.
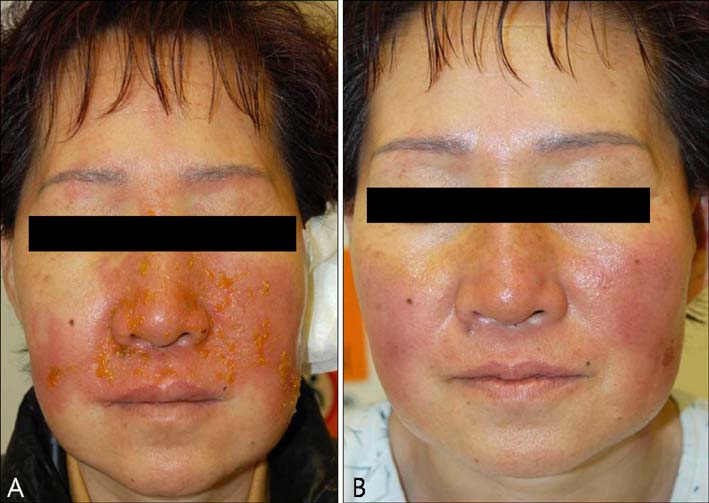
Benzoin Spray: Cause of Allergic Contact Dermatitis due to Its Rosin Content
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. uucm79@gmail.com
- 2Department of Otolaryngology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2265600
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2014.26.4.524
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Downs AM, Sansom JE. Colophony allergy: a review. Contact Dermatitis. 1999; 41:305–310.
Article2. Fiebach K, Grimm D. Resins, natural. Ullmann's encyclopedia of industrial chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA;2000.3. Wilkinson DS, Budden MG, Hambly EM. A 10-year review of an industrial dermatitis clinic. Contact Dermatitis. 1980; 6:11–17.
Article4. Fischer T, Bohlin S, Edling C, Rystedt I, Wieslander G. Skin disease and contact sensitivity in house painters using water-based paints, glues and putties. Contact Dermatitis. 1995; 32:39–45.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Allergic Contact Dermatitis due to Propolis Tincture
- A Case of Allergic Contact Dermatitis to Budesonide in a Nasal Spray
- A Case of Allergic Contact Dermatitis from Duoderm Hydrocolloid Dressing
- A Case of Allergic Contact Dermatitis Due to DuoDERM Extrathin(R)
- Patch Test in the Suspected Cosmetic Contact Dermatitis