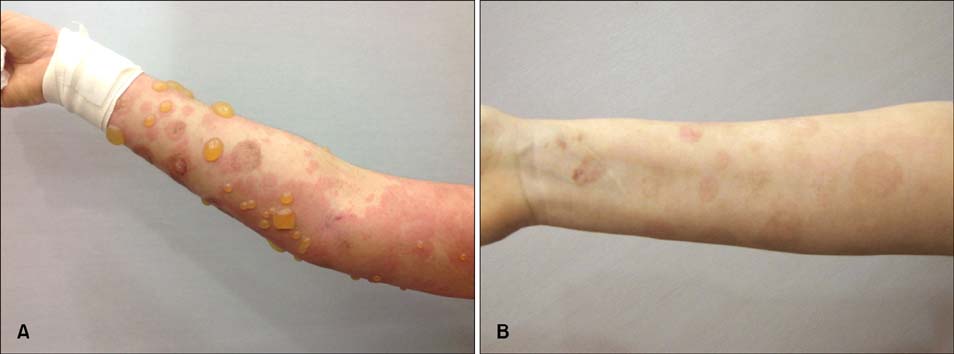
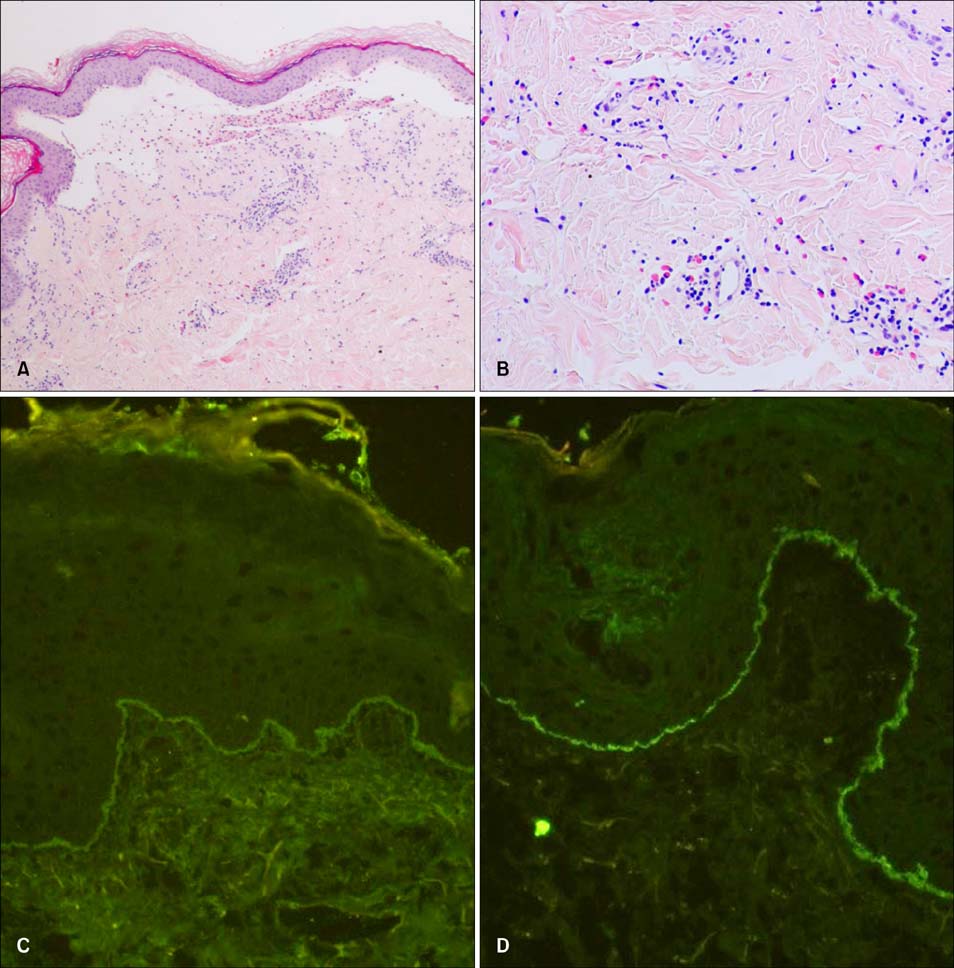
Ann Dermatol.
2014 Oct;26(5):661-663. 10.5021/ad.2014.26.5.661.
Intravenous Immunoglobulin Therapy for Persistent Pemphigoid Gestationis with Steroid Induced Iatrogenic Cushing's Syndrome
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, Soonchunhyang University, College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. snolomas@schmc.ac.kr
- KMID: 2265517
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2014.26.5.661
Abstract
- No abstract available.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Castro LA, Lundell RB, Krause PK, Gibson LE. Clinical experience in pemphigoid gestationis: report of 10 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006; 55:823–828.2. Harman KE, Black MM. High-dose intravenous immune globulin for the treatment of autoimmune blistering diseases: an evaluation of its use in 14 cases. Br J Dermatol. 1999; 140:865–874.
Article3. Czernik A, Toosi S, Bystryn JC, Grando SA. Intravenous immunoglobulin in the treatment of autoimmune bullous dermatoses: an update. Autoimmunity. 2012; 45:111–118.
Article4. Yang B, Wang C, Chen S, Chen X, Zhou G, Tian H, et al. Accuracy of indirect immunofluorescence on sodium chloride-split skin in the differential diagnosis of bullous pemphigoid and epidermolysis bullosa acquisita. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2011; 77:677–682.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Pemphigoid Gestationis with Involvement of the Face
- Two Cases of Bullous Pemphigoid Showing the Characteristics of Herpes Gestationis Autoantibodies
- A Case of Herpes Gestationis Treated with Cyclosporine
- Suspected Case of Iatrogenic Cushing Syndrome Due to Topical Steroid
- Dermatoses of Pregnancy: Clues to Diagnosis, Fetal Risk and Therapy