Ann Dermatol.
2014 Dec;26(6):758-759. 10.5021/ad.2014.26.6.758.
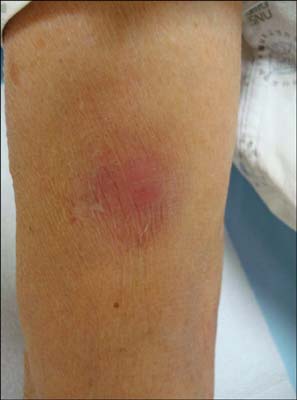
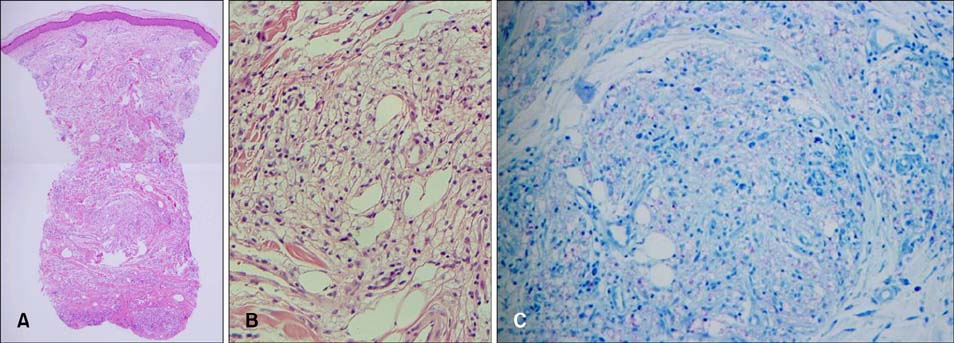
An Unsuspected Case of Relapsed Multibacillary Leprosy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, Seoul National University Boramae Hospital, Seoul, Korea. snuhdm@gmail.com
- 2Department of Dermatology, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2264875
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2014.26.6.758
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Sehgal VN. Leprosy. Dermatol Clin. 1994; 12:629–644.
Article2. Sehgal VN, Jain S, Charya SN. Persisters, relapse (reactivation), drug resistance and multidrug therapy (MDT): uniform diagnostic guidelines for leprosy are needed. J Dermatol. 1996; 23:905–907.
Article3. Kaimal S, Thappa DM. Relapse in leprosy. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2009; 75:126–135.
Article4. Lieberman J, Rea TH. Serum angiotensin-converting enzyme in leprosy and coccidioidomycosis. Ann Intern Med. 1977; 87:423–425.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Relapse in Two Couples Among Longterm Smear Negative Leprosy Patients
- A Case of Relapsed Lepromatous Leprosy Misdiagnosed as Granuloma Faciale
- A Case of Borderline Lepromatous Leprosy Masquerading as Chronic Eczema
- A Case of Borderline Lepromatous Leprosy Presenting in a Immigrant Woman
- 1 case of relapsed leprosy accompanied by multiple cranial nerve palsies