Ann Dermatol.
2015 Feb;27(1):79-81. 10.5021/ad.2015.27.1.79.
Novel Treatment of Neck Wrinkles with an Intradermal Radiofrequency Device
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, Chung-Ang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. beomjoon@unitel.co.kr
- 2Aesthetic Research Team, Amore Pacific Corporation Research and Development Center, Yongin, Korea.
- KMID: 2264842
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2015.27.1.79
Abstract
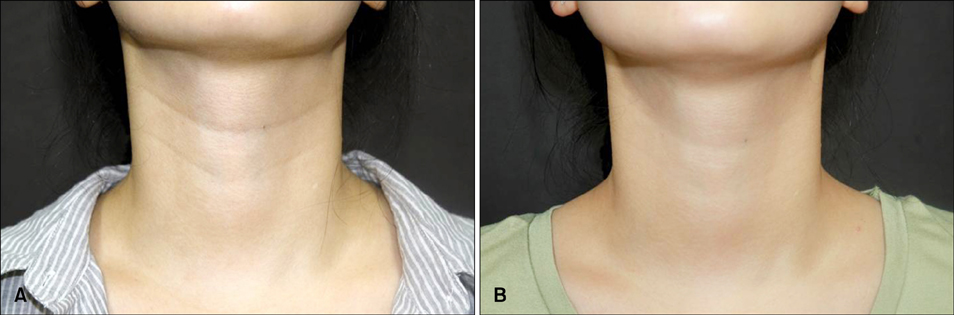
- Neck wrinkles commonly develop owing to the aging process. However, recently, the number of patients with neck wrinkles has been increasing. Also, an increasing number of young patients have presented with this condition, possibly because of the effect of the head-down posture that they adopt when using their computer or smartphone. We report two cases of young adults with a prominent neck wrinkle. In case 1, a 29-year-old woman with a neck wrinkle was treated with six intradermal radiofrequency (RF) procedures. Her neck wrinkle was significantly improved with the RF treatment. In case 2, a 32-year-old woman with a wrinkle and generalized light brownish tiny papules on the neck was treated with three intradermal RF procedures simultaneously with 30% glycolic acid peeling. Her wrinkle and skin tone were improved dramatically. We conclude that intradermal RF has a considerable efficacy for reducing neck wrinkles.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Dayan SH, Arkins JP, Chaudhry R. Minimally invasive neck lifts: have they replaced neck lift surgery? Facial Plast Surg Clin North Am. 2013; 21:265–270.2. Hsu TS, Kaminer MS. The use of nonablative radiofrequency technology to tighten the lower face and neck. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2003; 22:115–123.
Article3. Finzi E, Spangler A. Multipass vector (mpave) technique with nonablative radiofrequency to treat facial and neck laxity. Dermatol Surg. 2005; 31:916–922.
Article4. Alster TS, Tanzi E. Improvement of neck and cheek laxity with a nonablative radiofrequency device: a lifting experience. Dermatol Surg. 2004; 30:503–507.
Article5. Elsaie ML, Choudhary S, Leiva A, Nouri K. Nonablative radiofrequency for skin rejuvenation. Dermatol Surg. 2010; 36:577–589.
Article6. Savoia A, Vannini F, Baldi A. Radiofrequency waves with filling and peeling substances: An innovative minimally invasive technique for facial rejuvenation. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2011; 1:2–10.
Article7. Kessler E, Flanagan K, Chia C, Rogers C, Glaser DA. Comparison of alpha- and beta-hydroxy acid chemical peels in the treatment of mild to moderately severe facial acne vulgaris. Dermatol Surg. 2008; 34:45–50.8. Takenaka Y, Hayashi N, Takeda M, Ashikaga S, Kawashima M. Glycolic acid chemical peeling improves inflammatory acne eruptions through its inhibitory and bactericidal effects on Propionibacterium acnes. J Dermatol. 2012; 39:350–354.
Article9. Tung RC, Bergfeld WF, Vidimos AT, Remzi BK. alpha-Hydroxy acid-based cosmetic procedures. Guidelines for patient management. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2000; 1:81–88.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Intradermal Injection of Botulinum Toxin: A Safer Treatment Modality for Forehead Wrinkles
- A Double-Blind, Split-Face, Randomized Study on the Effects and Safety of Intradermal Injection of Botulinum Toxin A (Incobotulinum Toxin A) in the Cheek
- Usefulness of Monopolar Thermal Radiofrequency Treatment for Periorbital Wrinkles
- Treatment of Skin Laxity and Facial Wrinkles with Combinationof Radiofrequency and Infrared Light
- Periorbital Skin Rejuvenation of Asian Skin Using Microneedle Fractional Radiofrequency