Anat Cell Biol.
2013 Sep;46(3):198-202. 10.5115/acb.2013.46.3.198.
Analysis of the morphometry and variations in the extensor digitorum brevis muscle: an anatomic guide for muscle flap and tendon transfer surgical dissection
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anatomy, Melaka Manipal Medical College, Manipal University, Manipal, Karnataka, India. ravindrammmc@gmail.com
- 2Department of Anatomy, Kasturba Medical College, Manipal University, Manipal, Karnataka, India.
- KMID: 2263146
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5115/acb.2013.46.3.198
Abstract
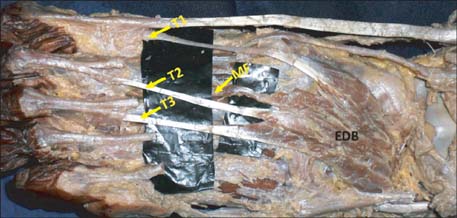
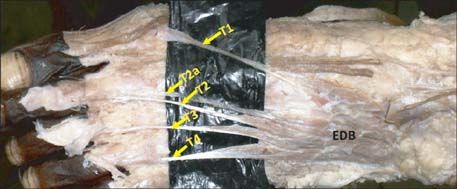
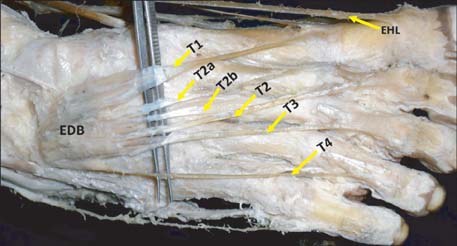
- The extensor digitorum brevis muscle (EDB) is a practical option for use as an island flap or free flap when reconstructing soft tissue defects in the ankle as well as in the entire lower limb. It is frequently used to correct crossover toe deformity and other painful toe disorders. We evaluated the morphometry of the EDB in 44 formalin-fixed limbs. Length and width of the muscles were measured. Surface area was calculated as the product of length and width of the muscle. The length of each tendon was also measured from its origin to the point of distal attachment. Presence of any additional tendons was noted. Mean length, width, and surface area of the muscle were 7.39+/-0.71 cm, 4.1+/-0.37 cm, and 30.5+/-4.78 cm2 on the right side and 7.2+/-0.84 cm, 3.9+/-0.37 cm, and 28.4+/-5.35 cm2 on the left side, respectively. Morphometry of the tendons revealed that the tendon of the great toe had the highest mean length (9.5 cm) and the tendon of the fourth toe had the lowest mean length (6.3 cm). Four of the limbs studied (9.09%) had only three tendons. Three of the limbs studied (6.81%) had five tendons, and in one exceptional case (2.27%), six tendons were detected. These observations have significant value and are applicable to plastic and orthopedic surgery.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Muscular Variations of Extensor Digitorum Brevis Muscle Related with Anterior Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome
Hyung-Jin Won, Chang-Seok Oh
Korean J Phys Anthropol. 2018;31(1):35-39. doi: 10.11637/kjpa.2018.31.1.35.
Reference
-
1. Standring S. Gray's anatomy: the anatomical basis of clinical practice. 39th ed. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone;2005. p. 1536–1537.2. Moore KL, Dalley AF, Agur AM. Clinically oriented anatomy. 6th ed. Philadelphia: Lippencott, Williams & Wilkins;2009. p. 612–614.3. Moore KL, Persaud TV. The developing human: clinically oriented embryology. 6th ed. Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders;2002. p. 612–614.4. Baltensperger MM, Ganzoni N, Jirecek V, Meyer VE. The extensor digitorum brevis island flap: possible applications based on anatomy. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1998; 101:107–113.5. del Piñal F, Herrero F. Extensor digitorum brevis free flap: anatomic study and further clinical applications. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2000; 105:1347–1356.6. Westlin NE, Vogler HW, Albertsson MP, Arvidsson T, Montgomery F. Treatment of lateral ankle instability with transfer of the extensor digitorum brevis muscle. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2003; 42:183–192.7. Haddad SL, Sabbagh RC, Resch S, Myerson B, Myerson MS. Results of flexor-to-extensor and extensor brevis tendon transfer for correction of the crossover second toe deformity. Foot Ankle Int. 1999; 20:781–788.8. Lui TH, Chan KB. Technique tip: modified extensor digitorum brevis tendon transfer for crossover second toe correction. Foot Ankle Int. 2007; 28:521–523.9. Bergman RA, Afifi AK, Miyauchi R. Extensor Digitorum Brevis (Pedis). Illustrated encyclopedia of human anatomic variation: Opus I: Muscular system: alphabetical listing of muscles: E. Anatomy Atalases. cited 2013 Sep 1. Available from: http://www.anatomyatlases.org/AnatomicVariants/MuscularSystem/Text/E/19Extensor.shtml.10. Anson BJ. Morris' human anatomy. 12th ed. New York: McGrawHill Book Co.;1966.11. Henle J. Handbuch der Muskellehre des Menschen, in Handbuch der systematischen Anatomie des Menschen. Braunschweig: Verlag von Friedrich Vieweg und Sohn;1871.12. Macalister A. Additional observation on muscular anomalies in human anatomy (third series), with a catalogue of the principal muscular variations hitherto published. Trans R Ir Acad. 1875; 25:1–134.13. Cihák R. Ontogenesis of the skeleton and intrinsic muscles of the human hand and foot. Ergeb Anat Entwicklungsgesch. 1972; 46:5–194.14. Grim M. Ultrastructure of the ulnar portion of the contrahent muscle layer in the embryonic human hand. Folia Morphol (Praha). 1972; 20:113–115.15. Kopuz C, Tetik S, Ozbenli S. A rare anomaly of the abductor digiti minimi muscle of the foot. Cells Tissues Organs. 1999; 164:174–176.16. Crocker AD, Moss AL. The extensor hallucis brevis muscle flap. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1989; 71:532.17. Chattar-Cora D, Pederson WC. Experience with the extensor digitorum brevis muscle flap for foot and ankle reconstruction. Ann Plast Surg. 2006; 57:289–294.18. Landi A, Soragni O, Monteleone M. The extensor digitorum brevis muscle island flap for soft-tissue loss around the ankle. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1985; 75:892–897.19. Leitner DW, Gordon L, Buncke HJ. The extensor digitorum brevis as a muscle island flap. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1985; 76:777–780.20. Martinet X, Forli A, Guinard D, Corcella D, Moutet F. Extensor digitorum muscle flap: its position in ankle and foot coverage. Report of 15 cases. Ann Chir Plast Esthet. 2003; 48:159–166.21. Chateau F, Chabas JF, Niddam J, Guinard D, Legré R. Use of Extensor digitorum brevis flap in routine reconstructive surgery of lower limbs. Report of more than 50 cases. Ann Chir Plast Esthet. 2012; 57:600–605.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Muscular Variations of Extensor Digitorum Brevis Muscle Related with Anterior Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome
- An Extensor Digitorum Muscle for Index Finger Originated from the Extensor Carpi Radialis Brevis
- Extensor Indicis Brevis: A Case Report
- Separated muscle belly of the flexor digitorum brevis for the fifth toe: a case report
- Reconstruction of Soft Tissue Defect on Distal Leg with Extensor Digitorum Brevis Myo-Cutaneous Flap