Allergy Asthma Respir Dis.
2013 Dec;1(4):391-394. 10.4168/aard.2013.1.4.391.
Chronic pulmonary complications due to toxic epidermal necrolysis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Inha University School of Medicine, Incheon, Korea. kimjhmd@inha.ac.kr
- KMID: 2262600
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aard.2013.1.4.391
Abstract
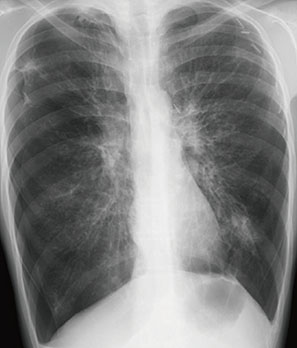
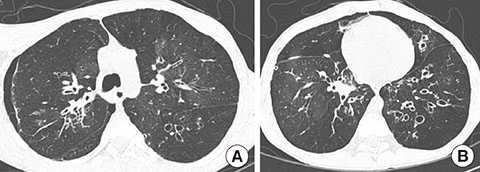
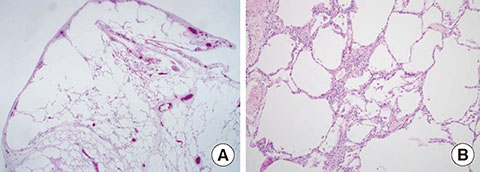
- Toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) is the most severe form of skin reactions caused by drugs or infection. Acute pulmonary complications in TEN are often observed. The mortality is especially high in those who suffer chronic pulmonary complications of TEN such as bronchiolitis obliterance, which occur as a consequence of bronchial epithelial injury. We report a case of a 16-year-old male who had required mechanical ventilation due to acute respiratory distress syndrome caused by TEN at 8 years of age. Although the patient initially recovered from acute respiratory distress syndrome, he required mechanical ventilation again due to severe chronic pulmonary complications of bronchiolitis obliterance and bronchiectasis caused by respiratory epithelial detachment. Thereafter, chronic bronchitis and chronic sinusitis has persisted due to mucosal ciliary dysfunction and several episodes of spontaneous pneumothorax has occurred. However, despite these persisting and serious sequelae of TEN, the patient has survived for 8 years. We report a rare case of a patient with long-term chronic pulmonary complications who had previously suffered TEN 8 years ago.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Finkelstein Y, Soon GS, Acuna P, George M, Pope E, Ito S, et al. Recurrence and outcomes of Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis in children. Pediatrics. 2011; 128:723–728.
Article2. Gerull R, Nelle M, Schaible T. Toxic epidermal necrolysis and Stevens-Johnson syndrome: a review. Crit Care Med. 2011; 39:1521–1532.
Article3. Kim HI, Kim SW, Park GY, Kwon EG, Kim HH, Jeong JY, et al. Causes and treatment outcomes of Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis in 82 adult patients. Korean J Intern Med. 2012; 27:203–210.
Article4. Harr T, French LE. Toxic epidermal necrolysis and Stevens-Johnson syndrome. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2010; 5:39.
Article5. Lebargy F, Wolkenstein P, Gisselbrecht M, Lange F, Fleury-Feith J, Delclaux C, et al. Pulmonary complications in toxic epidermal necrolysis: a prospective clinical study. Intensive Care Med. 1997; 23:1237–1244.
Article6. Woo T, Saito H, Yamakawa Y, Komatsu S, Onuma S, Okudela K, et al. Severe obliterative bronchitis associated with Stevens-Johnson syndrome. Intern Med. 2011; 50:2823–2827.
Article7. Edwards C, Penny M, Newman J. Mycoplasma pneumonia, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, and chronic obliterative bronchitis. Thorax. 1983; 38:867–869.
Article8. Kamata T, Sakamaki F, Fujita H, Urano T, Mori M, Yamaguchi K, et al. Toxic epidermal necrolysis with tracheobronchial and pulmonary complications. Intern Med. 1994; 33:252–255.
Article9. Virant FS, Redding GJ, Novack AH. Multiple pulmonary complications in a patient with Stevens-Johnson syndrome. Clin Pediatr (Phila). 1984; 23:412–414.
Article10. Reyes de la Rocha S, Leonard JC, Demetriou E. Potential permanent respiratory sequela of Stevens-Johnson syndrome in an adolescent. J Adolesc Health Care. 1985; 6:220–223.
Article11. Kim MJ, Lee KY. Bronchiolitis obliterans in children with Stevens-Johnson syndrome: follow-up with high resolution CT. Pediatr Radiol. 1996; 26:22–25.
Article12. McIvor RA, Zaidi J, Peters WJ, Hyland RH. Acute and chronic respiratory complications of toxic epidermal necrolysis. J Burn Care Rehabil. 1996; 17:237–240.
Article13. Kumar S, Tefferi A. Spontaneous pneumomediastinum and subcutaneous emphysema complicating bronchiolitis obliterans after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation: case report and review of literature. Ann Hematol. 2001; 80:430–435.
Article14. Kamada N, Kinoshita K, Togawa Y, Kobayashi T, Matsubara H, Kohno M, et al. Chronic pulmonary complications associated with toxic epidermal necrolysis: report of a severe case with anti-Ro/SS-A and a review of the published work. J Dermatol. 2006; 33:616–622.
Article15. Roujeau JC, Chosidow O, Saiag P, Guillaume JC. Toxic epidermal necrolysis (Lyell syndrome). J Am Acad Dermatol. 1990; 23(6 Pt 1):1039–1058.
Article16. Namdar T, Stang FH, Siemers F, Stollwerck PL, Wild Tv, Mailänder P, et al. [Mechanical ventilation in toxic epidermal necrolysis]. Handchir Mikrochir Plast Chir. 2011; 43:125–128.17. Correia O, Delgado L, Barbosa IL, Campilho F, Fleming-Torrinha J. Increased interleukin 10, tumor necrosis factor alpha, and interleukin 6 levels in blister fluid of toxic epidermal necrolysis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002; 47:58–62.
Article18. Chadwick C, Marven SM, Vora AJ. Autologous blood pleurodesis for pneumothorax complicating graft-versus-host disease-related bronchiolitis obliterans. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2004; 33:451–453.
Article19. Matsumoto K, Yamauchi T, Ichikawa M, Masuda Y, Ogawa K, Arai T, et al. Bronchiolitis obliterans in a patient with chronic graft-versus-host disease after bone marrow transplantation. Nihon Kyobu Shikkan Gakkai Zasshi. 1996; 34:345–349.20. Date H, Sano Y, Aoe M, Goto K, Tedoriya T, Sano S, et al. Living-donor lobar lung transplantation for bronchiolitis obliterans after Stevens-Johnson syndrome. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2002; 123:389–391.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis Associated with Chronic Pulmonary Complications
- A Case of Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis and Review of Literatures
- A Case of Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis Due to Contact of Paraquat(Gramoxone(R))
- A Case of Carbamazepine- Induced- Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis
- A Case of Complete Vaginal Ostruction Following Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis