Allergy Asthma Respir Dis.
2013 Dec;1(4):344-349. 10.4168/aard.2013.1.4.344.
The investigation of hypoproteinemia in pediatric atopic dermatitis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Busan St. Mary's Hospital, Busan, Korea. sbdph1@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2262592
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aard.2013.1.4.344
Abstract
- PURPOSE
As a complication of atopic dermatitis (AD), the incidence of hypoproteinemia is increasing among infants with severe AD. It can be a life-threatening condition owing to hypovolemic shock as a result of hypoproteinemia. The aim of this study is to investigate the clinical feature and laboratory findings in pediatric AD patients with hypoproteinemia.
METHODS
Seventy-five patients who visited pediatric allergy clinic and diagnosed as AD by a physician from January 2005 to January 2012. Patients with low serum protein level were classified as group A (n=27) and those with normal serum protein level were classified as group B (n=48). Age, sex, and parental allergic history were studied. We examined serum protein and albumin, eosinophil count, C-reactive protein (CRP), serum eosinophil cationic protein (ECP), total IgE, specific IgE, skin culture and SCORing Atopic Dermatitis (SCORAD) score.
RESULTS
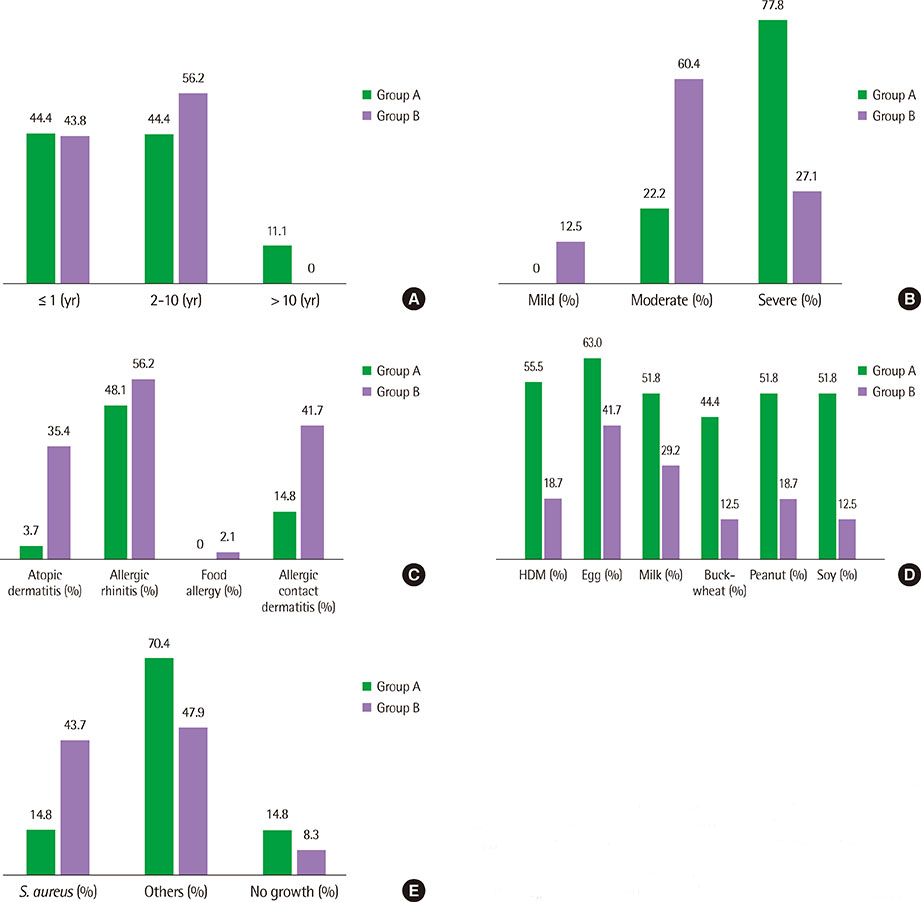
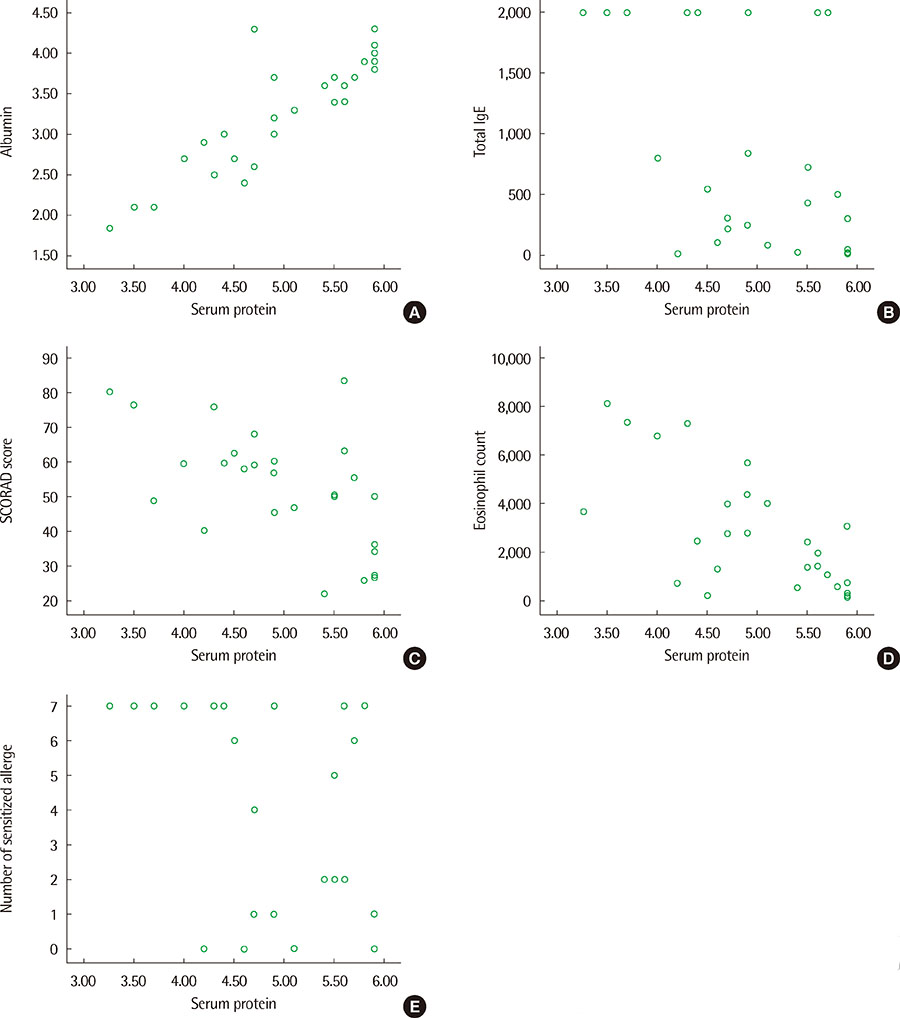
In group A, serum protein and albumin were lower and eosinophil count, CRP, ECP, total IgE and SCORAD score were higher than group B. Group A was sensitized more number of allergens than group B. In parental allergic history, allergic rhinitis was prominent in both group. In skin culture, other species than Staphylococcus aureus were prominent in group A. Egg sensitization was the most common in both group. Serum protein level was positively correlated with serum albumin and negatively correlated with eosinophil count, total IgE, SCORAD score and number of sensitized allergen.
CONCLUSION
Risk factors for hypoproteinemia in pediatric atopic dermatitis are considered infants, severe atopic dermatitis, increased number of sensitized allergens.
MeSH Terms
-
Allergens
C-Reactive Protein
Dermatitis, Atopic*
Eosinophil Cationic Protein
Eosinophils
Humans
Hypersensitivity
Hypoproteinemia*
Immunoglobulin E
Incidence
Infant
Ovum
Parents
Rhinitis
Risk Factors
Serum Albumin
Shock
Skin
Staphylococcus aureus
Allergens
C-Reactive Protein
Eosinophil Cationic Protein
Immunoglobulin E
Serum Albumin
Figure
Reference
-
1. Tay YK, Khoo BP, Goh CL. The epidemiology of atopic dermatitis at a tertiary referral skin center in Singapore. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol. 1999; 17:137–141.2. Kim BE, Leung DY. Epidermal barrier in atopic dermatitis. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2012; 4:12–16.
Article3. Barnetson RS, Rogers M. Childhood atopic eczema. BMJ. 2002; 324:1376–1379.
Article4. Ong PY, Leung DY. The infectious aspects of atopic dermatitis. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. 2010; 30:309–321.
Article5. Leung DY. Atopic dermatitis and the immune system: the role of superantigens and bacteria. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2001; 45:1 Suppl. S13–S16.
Article6. Novembre E, Leo G, Cianferoni A, Bernardini R, Pucci N, Vierucci A. Severe hypoproteinemia in infant with AD. Allergy. 2003; 58:88–89.
Article7. Nomura I, Katsunuma T, Tomikawa M, Shibata A, Kawahara H, Ohya Y, et al. Hypoproteinemia in severe childhood atopic dermatitis: a serious complication. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2002; 13:287–294.
Article8. Lee JH, Seo BO, Lee EY, Kim SW. The Investigation of hypoproteinemia in severe infantile atopic dermatitis. Pediatr Allergy Respir Dis. 2008; 18:316–325.9. Katoh N, Hosoi H, Sugimoto T, Kishimoto S. Features and prognoses of infantile patients with atopic dermatitis hospitalized for severe complications. J Dermatol. 2006; 33:827–832.
Article10. Chen CC, Huang JL, Yang KD, Chen HJ. Atopic cataracts in a child with atopic dermatitis: a case report and review of the literature. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol. 2000; 18:69–71.11. Tatham A. Atopic dermatitis, cutaneous steroids and cataracts in children: two case reports. J Med Case Rep. 2008; 2:124.
Article12. Kang KD, Kang SM, Yim HB. Herbal medication aggravates cataract formation: a case report. J Korean Med Sci. 2008; 23:537–539.
Article13. Moore MM, Rifas-Shiman SL, Rich-Edwards JW, Kleinman KP, Camargo CA Jr, Gold DR, et al. Perinatal predictors of atopic dermatitis occurring in the first six months of life. Pediatrics. 2004; 113(3 Pt 1):468–474.
Article14. Doull IJ. Maternal inheritance of atopy? Clin Exp Allergy. 1996; 26:613–615.
Article15. Sicherer SH, Sampson HA. 9. Food allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006; 117:2 Suppl Mini-Primer. S470–S475.
Article16. Sicherer SH, Sampson HA. Food hypersensitivity and atopic dermatitis: pathophysiology, epidemiology, diagnosis, and management. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1999; 104(3 Pt 2):S114–S122.
Article17. Sampson HA. Utility of food-specific IgE concentrations in predicting symptomatic food allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001; 107:891–896.
Article18. Kim HO, Cho SI, Kim JH, Chung BY, Cho HJ, Park CW, et al. Food hypersensitivity in patients with childhood atopic dermatitis in Korea. Ann Dermatol. 2013; 25:196–202.
Article19. Lee SY. IgE mediated food allergy in Korean children: focused on plant food allergy. Asia Pac Allergy. 2013; 3:15–22.
Article20. Park GH, Park JH, Hwang YH, Sung MS, Kim SW. The correlation between the severity of atopic dermatitis classified by SCORing atopic dermatitis index and the laboratory tests. Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2013; 1:79–83.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Investigation of Hypoproteinemia in Severe Infantile Atopic Dermatitis
- Measurement of Atopic Dermatitis Disability
- A Clinical Investigation of Patients with Atopic Dermatitis
- Serum IgE Level in Patients of Atopic Dermatitis and Atopic Dermatitis with Molluscum Contagiosum
- Nipple Involvement in Atopic Dermatitis: Report of 3 cases