Allergy Asthma Immunol Res.
2014 May;6(3):216-221. 10.4168/aair.2014.6.3.216.
Comparison of Diagnostic Criteria and Determination of Prognostic Factors for Drug Reaction With Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms Syndrome
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Allergy, Asthma and Clinical Immunology, Department of Internal Medicine, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea. yikoh@chonnam.ac.kr
- KMID: 2260683
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aair.2014.6.3.216
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) syndrome is characterized by prolonged clinical symptoms even after the withdrawal of the culprit drug. Different criteria to diagnose DRESS syndrome have been proposed; however, there have been limited studies on prognostic factors. We investigated appropriate criteria for the diagnosis of DRESS syndrome in practice and with associated prognostic factors.
METHODS
A total of 48 patients with DRESS syndrome that satisfied RegiSCAR possible (or more) criteria were retrospectively recruited. They were also analyzed according to Bocquet's criteria and Japanese drug-induced hypersensitivity syndrome (DIHS) criteria. The duration of clinical manifestations, requirement for steroids, and fatalities determined the severity of DRESS syndrome. Blood tests were performed at initial presentation to our hospital.
RESULTS
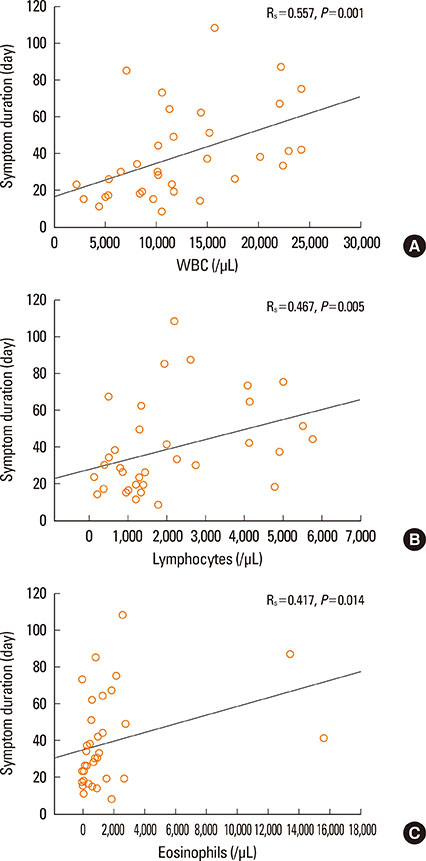
A total of 60.4% of patients satisfied RegiSCAR definite criteria and 77.1% satisfied Bocquet's criteria. Only 18.8% satisfied atypical DIHS criteria from the Japanese group. A total of 96.6% patients who fit the RegiSCAR definite criteria, 96.6% also satisfied Bocquet's criteria; reciprocally, 75.7% of patients who met Bocquet's criteria also satisfied RegiSCAR definite criteria. The duration of clinical symptoms positively correlated with leukocyte, lymphocyte, and eosinophil counts in non-fatal cases. Lymphocyte counts were higher in patients who used steroids compared to steroid-naive patients. Fatal cases showed higher serum creatinine and ferritin levels compared to non-fatal cases.
CONCLUSIONS
Bocquet's criteria is efficient and appropriate to diagnose DRESS syndrome in clinical practice. Lymphocyte and eosinophil counts as well as creatinine and ferritin levels could be useful early prognostic factors.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) syndrome in liver transplantation
Ara Cho, Jeong-Moo Lee, Kwangpyo Hong, Eui Soo Han, Suk Kyun Hong, YoungRok Choi, Nam-Joon Yi, Kwang-Woong Lee, Kyung-Suk Suh
Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2021;25(4):551-555. doi: 10.14701/ahbps.2021.25.4.551.
Reference
-
1. Wolf R, Orion E, Marcos B, Matz H. Life-threatening acute adverse cutaneous drug reactions. Clin Dermatol. 2005; 23:171–181.2. Tas S, Simonart T. Management of drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS syndrome): an update. Dermatology. 2003; 206:353–356.3. Cacoub P, Musette P, Descamps V, Meyer O, Speirs C, Finzi L, Roujeau JC. The DRESS syndrome: a literature review. Am J Med. 2011; 124:588–597.4. Bocquet H, Bagot M, Roujeau JC. Drug-induced pseudolymphoma and drug hypersensitivity syndrome (drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms: DRESS). Semin Cutan Med Surg. 1996; 15:250–257.5. Shiohara T, Inaoka M, Kano Y. Drug-induced hypersensitivity syndrome (DIHS): a reaction induced by a complex interplay among herpesviruses and antiviral and antidrug immune responses. Allergol Int. 2006; 55:1–8.6. Kardaun SH, Sidoroff A, Valeyrie-Allanore L, Halevy S, Davidovici BB, Mockenhaupt M, Roujeau JC. Variability in the clinical pattern of cutaneous side-effects of drugs with systemic symptoms: does a DRESS syndrome really exist? Br J Dermatol. 2007; 156:609–611.7. Walsh SA, Creamer D. Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS): a clinical update and review of current thinking. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2011; 36:6–11.8. Chiou CC, Yang LC, Hung SI, Chang YC, Kuo TT, Ho HC, Hu S, Hong HS, Chung WH. Clinicopathological features and prognosis of drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms: a study of 30 cases in Taiwan. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2008; 22:1044–1049.9. Shiohara T, Iijima M, Ikezawa Z, Hashimoto K. The diagnosis of a DRESS syndrome has been sufficiently established on the basis of typical clinical features and viral reactivations. Br J Dermatol. 2007; 156:1083–1084.10. Chen YC, Chiu HC, Chu CY. Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms: a retrospective study of 60 cases. Arch Dermatol. 2010; 146:1373–1379.11. Naranjo CA, Busto U, Sellers EM, Sandor P, Ruiz I, Roberts EA, Janecek E, Domecq C, Greenblatt DJ. A method for estimating the probability of adverse drug reactions. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1981; 30:239–245.12. Venulet J. Role and place of causality assessment. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 1992; 1:225–234.13. Cohen J. A coefficient of agreement for nominal scales. Educ Psychol Meas. 1960; 20:37–46.14. Wi JO, Jin NC, Han ER, Yoon BJ, Park SH, Koh YI. A case of DRESS syndrome accompanied by leukocytoclastic vasculitis. Korean J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010; 30:320–324.15. Landis JR, Koch GG. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics. 1977; 33:159–174.16. Ang CC, Wang YS, Yoosuff EL, Tay YK. Retrospective analysis of drug-induced hypersensitivity syndrome: a study of 27 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010; 63:219–227.17. Um SJ, Lee SK, Kim YH, Kim KH, Son CH, Roh MS, Lee MK. Clinical features of drug-induced hypersensitivity syndrome in 38 patients. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2010; 20:556–562.18. Jeung YJ, Lee JY, Oh MJ, Choi DC, Lee BJ. Comparison of the causes and clinical features of drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms and stevens-johnson syndrome. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2010; 2:123–126.19. Kano Y, Shiohara T. The variable clinical picture of drug-induced hypersensitivity syndrome/drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms in relation to the eliciting drug. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. 2009; 29:481–501.20. Wei CH, Chung-Yee Hui R, Chang CJ, Ho HC, Yang CH, Lin YJ, Chung WH. Identifying prognostic factors for drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS). Eur J Dermatol. 2011; 21:930–937.21. Camous X, Calbo S, Picard D, Musette P. Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms: an update on pathogenesis. Curr Opin Immunol. 2012; 24:730–735.22. Picard D, Janela B, Descamps V, D'Incan M, Courville P, Jacquot S, Rogez S, Mardivirin L, Moins-Teisserenc H, Toubert A, Benichou J, Joly P, Musette P. Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS): a multiorgan antiviral T cell response. Sci Transl Med. 2010; 2:46ra62.23. Choquet-Kastylevsky G, Intrator L, Chenal C, Bocquet H, Revuz J, Roujeau JC. Increased levels of interleukin 5 are associated with the generation of eosinophilia in drug-induced hypersensitivity syndrome. Br J Dermatol. 1998; 139:1026–1032.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptom Syndrome Due to Everolimus: A Case Report
- Rasagiline Induced Drug Rash with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms Syndrome: A Case Report
- Diagnosis and Management of DRESS (Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms) Syndrome
- Propylthiouracil Induced Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS) in Graves' Disease
- DRESS (drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms) syndrome induced by lamotrigine in a child