Allergy Asthma Immunol Res.
2015 May;7(3):301-303. 10.4168/aair.2015.7.3.301.
Immunologic Evaluation of Patients with Cefotetan-Induced Anaphylaxis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, Dong-A University, Busan, Korea. skleeai@dau.ac.kr
- 2Department of Allergy & Clinical Immunology, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea.
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Yeungnam University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- KMID: 2260469
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aair.2015.7.3.301
Abstract
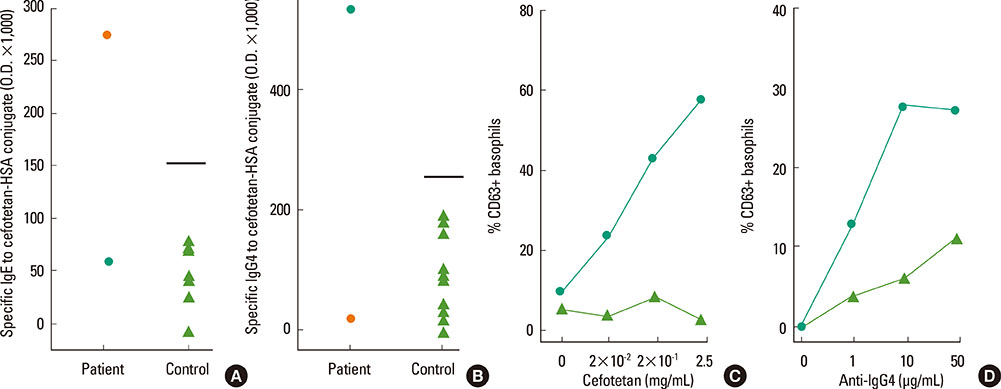
- Cefotetan is a commonly prescribed second-generation cephalosporin that acts against a wide range of bacteria. However, cefotetan-induced hypersensitivity has rarely been reported. We report 2 cases of cefotetan-induced anaphylaxis with immunologic evaluation. The first case was a 70-year-old asthmatic woman who had dyspnea and hypotension during administration of cefotetan, in which high serum-specific IgE to cefotetan-human serum albumin (HSA) conjugate was detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. The second case was a 63-year-old asthmatic woman who complained of chest tightness and dyspnea during cefotetan infusion, in which high serum-specific IgG1 and IgG4 with no serum specific IgE to cefotetan-HSA conjugate was detected. The basophil activation test using basophils from the patient showed a significant up-regulation of CD63 with the addition of anti-IgG4 antibody compared with that in non-atopic healthy controls. In conclusion, cefotetan can induce anaphylaxis, which may involve both IgE- and IgG4-mediated responses in the pathogenic mechanism.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
An Ofloxacin-Induced Anaphylaxis through an IgG4-Mediated but Not IgE-Mediated Basophil Activation Mechanism
Ji Hye Kim, Dae-Hong Seo, Ga-Young Ban, Eun-Mi Yang, Yoo Seob Shin, Young-Min Ye, Hae-Sim Park
Korean J Crit Care Med. 2017;32(3):302-305. doi: 10.4266/kjccm.2017.00108.
Reference
-
1. Kim JE, Kim SH, Jin HJ, Hwang EK, Kim JH, Ye YM, Park HS. IgE sensitization to cephalosporins in health care workers. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2012; 4:85–91.2. Suh YJ, Lee YM, Choi JH, Suh CH, Nahm DH, Park HS. Heterogeneity of IgE response to cefteram pivoxil was noted in 2 patients with cefteram-induced occupational asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003; 112:209–210.3. Kim JH, An S, Kim JE, Choi GS, Ye YM, Park HS. Beef-induced anaphylaxis confirmed by the basophil activation test. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2010; 2:206–208.4. Bloomberg RJ. Cefotetan-induced anaphylaxis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1988; 159:125–126.5. Lee MJ, Lim TH, Lee BJ, Yi JW, Park SH, Choi SK, Park SJ. Anaphylactic reaction to cefotetan during spinal anesthesia: a case report. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2005; 49:861–863.6. Blanca M, Romano A, Torres MJ, Férnandez J, Mayorga C, Rodriguez J, Demoly P, Bousquet PJ, Merk HF, Sanz ML, Ott H, Atanasković-Marković M. Update on the evaluation of hypersensitivity reactions to betalactams. Allergy. 2009; 64:183–193.7. Romano A, Guéant-Rodriguez RM, Viola M, Amoghly F, Gaeta F, Nicolas JP, Guéant JL. Diagnosing immediate reactions to cephalosporins. Clin Exp Allergy. 2005; 35:1234–1242.8. Antúnez C, Martín E, Cornejo-García JA, Blanca-Lopez N, R-Pena R, Mayorga C, Torres MJ, Blanca M. Immediate hypersensitivity reactions to penicillins and other betalactams. Curr Pharm Des. 2006; 12:3327–3333.9. Finkelman FD. Anaphylaxis: lessons from mouse models. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007; 120:506–515.10. Tsujimura Y, Obata K, Mukai K, Shindou H, Yoshida M, Nishikado H, Kawano Y, Minegishi Y, Shimizu T, Karasuyama H. Basophils play a pivotal role in immunoglobulin-G-mediated but not immunoglobulin-E-mediated systemic anaphylaxis. Immunity. 2008; 28:581–589.11. Ishizaka A, Sakiyama Y, Nakanishi M, Tomizawa K, Oshika E, Kojima K, Taguchi Y, Kandil E, Matsumoto S. The inductive effect of interleukin-4 on IgG4 and IgE synthesis in human peripheral blood lymphocytes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990; 79:392–396.12. de Haan P, Boorsma DM, Kalsbeek GL. Penicillin hypersensitivity. Determination and classification of anti-penicillin antibodies by the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Allergy. 1979; 34:111–119.13. Nam YH, Kim JE, Kim SH, Jin HJ, Hwang EK, Shin YS, Ye YM, Park HS. Identifying genetic susceptibility to sensitization to cephalosporins in health care workers. J Korean Med Sci. 2012; 27:1292–1299.14. Adkinson NF Jr, Swabb EA, Sugerman AA. Immunology of the monobactam aztreonam. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984; 25:93–97.15. Sánchez-Borges M, Thong B, Blanca M, Ensina LF, González-Díaz S, Greenberger PA, Jares E, Jee YK, Kase-Tanno L, Khan D, Park JW, Pichler W, Romano A, Jaén MJ. Hypersensitivity reactions to non beta-lactam antimicrobial agents, a statement of the WAO special committee on drug allergy. World Allergy Organ J. 2013; 6:18.16. Hausmann OV, Gentinetta T, Bridts CH, Ebo DG. The basophil activation test in immediate-type drug allergy. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. 2009; 29:555–566.17. Sanz ML, Gamboa PM, Mayorga C. Basophil activation tests in the evaluation of immediate drug hypersensitivity. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009; 9:298–304.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Anaphylactic Reaction to Cefotetan during Spinal Anesthesia: A case report
- Delayed Anaphylactic Shock to Intravenous Cefotetan in a Pregnant Woman: A Case Report
- A Case of Rifampicin-induced Acute Renal Failure and Anaphylaxis
- Food allergies and food-induced anaphylaxis: role of cofactors
- Successful desensitization for cytarabine induced anaphylaxis