Korean J Hematol.
2011 Mar;46(1):49-51. 10.5045/kjh.2011.46.1.49.
Identification of a shared F8 mutation in the Korean patients with acquired hemophilia A
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Biological Science, College of Natural Sciences, Ajou University, Suwon, Korea. hsunkim@ajou.ac.kr
- 2Department of Hematology-Oncology, School of Medicine, Ajou University, Suwon, Korea.
- KMID: 2252020
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5045/kjh.2011.46.1.49
Abstract
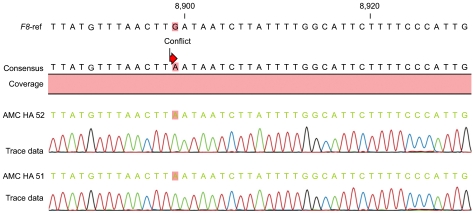
- Although uncommon, acquired hemophilia A (HA) is associated with a high rate of mortality due to severe bleeding. In spite of many hypotheses regarding the cause of acquired HA, there is as yet no established theory. In this study, we investigated the possibility that mutation(s) in the F8 gene may be correlated with the development of inhibitory autoantibodies. Direct sequencing analysis was performed on all 26 exons of the F8 gene of 2 patients exhibiting acquired HA. Both patients were found to share a common point mutation (c.8899G>A) in the 3'-untranslated region (3'-UTR) of exon 26. This is the first report on the genotyping of F8 in the context of acquired HA.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Delgado J, Jimenez-Yuste V, Hernandez-Navarro F, Villar A. Acquired haemophilia: review and meta-analysis focused on therapy and prognostic factors. Br J Haematol. 2003; 121:21–35. PMID: 12670328.
Article2. Boggio LN, Green D. Acquired hemophilia. Rev Clin Exp Hematol. 2001; 5:389–404. PMID: 11844135.
Article3. Collins PW, Hirsch S, Baglin TP, et al. Acquired hemophilia A in the United Kingdom: a 2-year national surveillance study by the United Kingdom Haemophilia Centre Doctors' Organisation. Blood. 2007; 109:1870–1877. PMID: 17047148.
Article4. Fidanci ID, Kavakli K, Uçar C, et al. Factor 8 (F8) gene mutation profile of Turkish hemophilia A patients with inhibitors. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 2008; 19:383–388. PMID: 18600086.
Article5. Oldenburg J, Pavlova A. Genetic risk factors for inhibitors to factors VIII and IX. Haemophilia. 2006; 12(Suppl 6):15–22. PMID: 17123389.
Article6. Hwang SH, Kim MJ, Lim JA, Kim HC, Kim HS. Profiling of factor VIII mutations in Korean haemophilia A. Haemophilia. 2009; 15:1311–1317. PMID: 19719548.7. Tiede A, Eisert R, Czwalinna A, Miesbach W, Scharrer I, Ganser A. Acquired haemophilia caused by non-haemophilic factor VIII gene variants. Ann Hematol. 2010; 89:607–612. PMID: 20054547.
Article8. Deichmann K, Heinzmann A, Brüggenolte E, Forster J, Kuehr J. An Mse I RFLP in the human CTLA4 promotor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1996; 225:817–818. PMID: 8780695.
Article9. Ueda H, Howson JM, Esposito L, et al. Association of the T-cell regulatory gene CTLA4 with susceptibility to autoimmune disease. Nature. 2003; 423:506–511. PMID: 12724780.10. Donner H, Rau H, Walfish PG, et al. CTLA4 alanine-17 confers genetic susceptibility to Graves' disease and to type 1 diabetes mellitus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1997; 82:143–146. PMID: 8989248.
Article11. Oldenburg J, Zeitler H, Pavlova A. Genetic markers in acquired haemophilia. Haemophilia. 2010; 16(Suppl 3):41–45. PMID: 20586801.
Article12. Di Marco S, Hel Z, Lachance C, Furneaux H, Radzioch D. Polymorphism in the 3'-untranslated region of TNFalpha mRNA impairs binding of the post-transcriptional regulatory protein HuR to TNFalpha mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001; 29:863–871. PMID: 11160917.
Article13. Di Paola R, Frittitta L, Miscio G, et al. A variation in 3' UTR of hPTP1B increases specific gene expression and associates with insulin resistance. Am J Hum Genet. 2002; 70:806–812. PMID: 11833006.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Sequence variation data of F8 and F9 genes in functionally validated control individuals: implications on the molecular diagnosis of hemophilia
- Total Knee Arthroplasty-associated Acquired Hemophilia: A Case Report
- A Case of Hemophilia A Diagnosed in a Premature Infant
- Acquired Hemophilia in a Patient Presenting with Swollen Left Limb
- Genetic Risk Factors of Hemophilia A