Korean J Hematol.
2011 Sep;46(3):180-185. 10.5045/kjh.2011.46.3.180.
Fludarabine-containing chemotherapy for patients with previously untreated low-grade non-Hodgkin's lymphoma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Hematology-Oncology, Chonnam National University Hwasun Hospital, Hwasun, Korea. drjejung@chonnam.ac.kr
- 2The Brain Korea 21 Project, Center for Biomedical Human Resources at Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea.
- KMID: 2252001
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5045/kjh.2011.46.3.180
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
The clinical efficacy and safety of fludarabine combination chemotherapy was investigated for the treatment of previously untreated patients with low-grade (NHL).
METHODS
Twenty-five patients who were newly diagnosed as low-grade NHL were treated with fludarabine combination chemotherapy. Fludarabine combination regimens consisted of fludarabine, mitoxantrone and dexamethasone or fludarabine, cyclophosphamide and mitoxantrone with or without rituximab and repeated every 4 weeks.
RESULTS
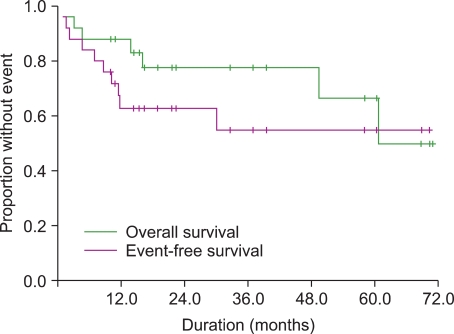
The median age was 60 years (range, 35-77 years), with 13 of 25 patients (52%) > or =60 years of age. Seven of 25 patients (28%) with an intermediate risk follicular lymphoma international prognostic index (FLIPI) and 9 of 25 patients (36%) with a high risk FLIPI were enrolled in this study. The delivered median number of chemotherapy was six (range, 2-9 cycles). The overall response rate with fludarabine-based treatment was 88%, including 52% complete remission and 36% partial remission. During the median follow-up of 19 months, the estimated 2-year event-free survival was 63+/-10% (95% CI, 43-83) and the 2-year overall survival was 78+/-9% (95% CI, 60-96). Fludarabine combination chemotherapy was frequently associated with grade 3 or 4 neutropenia in 84% patients. However, neutropenic infection was observed in only one (4%) patient. Four patients (16%) showed grade 3 or more non-hematologic toxicities, such as acute coronary syndrome, intracranial hemorrhage, anaphylaxis and gastric cancer.
CONCLUSION
Fludarabine-combination treatment was a highly active regimen with well toleration in untreated low-grade NHL.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Acute Coronary Syndrome
Anaphylaxis
Antibodies, Monoclonal, Murine-Derived
Cyclophosphamide
Dexamethasone
Disease-Free Survival
Drug Therapy, Combination
Follow-Up Studies
Humans
Intracranial Hemorrhages
Lymphoma
Lymphoma, Follicular
Lymphoma, Non-Hodgkin
Mitoxantrone
Neutropenia
Vidarabine
Rituximab
Antibodies, Monoclonal, Murine-Derived
Cyclophosphamide
Dexamethasone
Mitoxantrone
Vidarabine
Figure
Reference
-
1. Portlock CS. Management of the low-grade non-Hodgkin's lymphomas. Semin Oncol. 1990; 17:51–59. PMID: 2406918.2. Berger F, Felman P, Sonet A, et al. Nonfollicular small B-cell lymphomas: a heterogeneous group of patients with distinct clinical features and outcome. Blood. 1994; 83:2829–2835. PMID: 8180379.
Article3. Ardeshna KM, Smith P, Norton A, et al. Long-term effect of a watch and wait policy versus immediate systemic treatment for asymptomatic advanced-stage non-Hodgkin lymphoma: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2003; 362:516–522. PMID: 12932382.
Article4. Armitage JO. Staging non-Hodgkin lymphoma. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005; 55:368–376. PMID: 16282281.
Article5. Luthy SK, Ng AK, Silver B, et al. Response to low-dose involved-field radiotherapy in patients with non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Ann Oncol. 2008; 19:2043–2047. PMID: 18647962.
Article6. Berger F, Felman P, Thieblemont C, et al. Non-MALT marginal zone B-cell lymphomas: a description of clinical presentation and outcome in 124 patients. Blood. 2000; 95:1950–1956. PMID: 10706860.
Article7. Oh SY, Ryoo BY, Kim WS, et al. Nongastric marginal zone B-cell lymphoma: analysis of 247 cases. Am J Hematol. 2007; 82:446–452. PMID: 17266060.
Article8. Dana BW, Dahlberg S, Nathwani BN, et al. Long-term follow-up of patients with low-grade malignant lymphomas treated with doxorubicin-based chemotherapy or chemoimmunotherapy. J Clin Oncol. 1993; 11:644–651. PMID: 8478660.
Article9. Brandt L, Kimby E, Nygren P, et al. A systematic overview of chemotherapy effects in indolent non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Acta Oncol. 2001; 40:213–223. PMID: 11441933.
Article10. Klasa RJ, Meyer RM, Shustik C, et al. Randomized phase III study of fludarabine phosphate versus cyclophosphamide, vincristine, and prednisone in patients with recurrent low-grade non-Hodgkin's lymphoma previously treated with an alkylating agent or alkylator-containing regimen. J Clin Oncol. 2002; 20:4649–4654. PMID: 12488409.
Article11. Bellosillo B, Villamor N, Colomer D, Pons G, Montserrat E, Gil J. In vitro evaluation of fludarabine in combination with cyclophosphamide and/or mitoxantrone in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood. 1999; 94:2836–2843. PMID: 10515887.
Article12. Furlan A, Villanova F, Pietrogrande F, Celadin M, Sanzari M, Vianello F. Low-dose fludarabine increases rituximab cytotoxicity in B-CLL cells by triggering caspases activation in vitro. Leuk Lymphoma. 2010; 51:107–113. PMID: 20001234.13. Flinn IW, Neuberg DS, Grever MR, et al. Phase III trial of fludarabine plus cyclophosphamide compared with fludarabine for patients with previously untreated chronic lymphocytic leukemia: US Intergroup Trial E2997. J Clin Oncol. 2007; 25:793–798. PMID: 17283364.14. Fabbri A, Lenoci M, Gozzetti A, et al. Low-dose oral fludarabine plus cyclophosphamide as first-line treatment in elderly patients with indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Br J Haematol. 2007; 139:90–93. PMID: 17854311.
Article15. Ferrario A, Merli F, Luminari S, et al. Phase II fludarabine and cyclophosphamide for the treatment of indolent B cell non-follicular lymphomas: final results of the LL02 trial of the Gruppo Italiano per lo Studio dei Linfomi (GISL). Ann Hematol. 2011; 90:323–330. PMID: 20848104.16. Tam CS, Wolf M, Prince HM, et al. Fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab for the treatment of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia or indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Cancer. 2006; 106:2412–2420. PMID: 16649223.
Article17. Brown JR, Friedberg JW, Feng Y, et al. A phase 2 study of concurrent fludarabine and rituximab for the treatment of marginal zone lymphomas. Br J Haematol. 2009; 145:741–748. PMID: 19344412.
Article18. Zinzani PL, Pulsoni A, Perrotti A, et al. Fludarabine plus mitoxantrone with and without rituximab versus CHOP with and without rituximab as front-line treatment for patients with follicular lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2004; 22:2654–2661. PMID: 15159414.
Article19. Zinzani PL, Pulsoni A, Gentilini P, et al. Effectiveness of fludarabine, idarubicin and cyclophosphamide (FLUIC) combination regimen for young patients with untreated nonfollicular low-grade non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Leuk Lymphoma. 2004; 45:1815–1819. PMID: 15223641.
Article20. Peinert S, Carney D, Prince HM, Januszewicz EH, Seymour JF. Fludarabine combinations for patients with advanced marginal zone lymphomas--best treatment option or too toxic? Br J Haematol. 2009; 146:685–686. PMID: 19638019.21. Cheson BD, Pfistner B, Juweid ME, et al. Revised response criteria for malignant lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2007; 25:579–586. PMID: 17242396.22. Hagenbeek A, Eghbali H, Monfardini S, et al. Phase III intergroup study of fludarabine phosphate compared with cyclophosphamide, vincristine, and prednisone chemotherapy in newly diagnosed patients with stage III and IV low-grade malignant Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2006; 24:1590–1596. PMID: 16575010.
Article23. Velasquez WS, Lew D, Grogan TM, et al. Combination of fludarabine and mitoxantrone in untreated stages III and IV low-grade lymphoma: S9501. J Clin Oncol. 2003; 21:1996–2003. PMID: 12743154.
Article24. Dimopoulos MA, Fountzilas G, Papageorgiou E, et al. Primary treatment of low-grade non-Hodgkin's lymphoma with the combination of fludarabine and mitoxantrone: a phase II study of the Hellenic Cooperative Oncology Group. Leuk Lymphoma. 2002; 43:111–114. PMID: 11908713.
Article25. Lazzarino M, Orlandi E, Montillo M, et al. Fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and dexamethasone (FluCyD) combination is effective in pretreated low-grade non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Ann Oncol. 1999; 10:59–64. PMID: 10076723.
Article26. Zinzani PL, Magagnoli M, Bendandi M, et al. Efficacy of fludarabine and mitoxantrone (FN) combination regimen in untreated indolent non-Hodgkin's lymphomas. Ann Oncol. 2000; 11:363–365. PMID: 10811507.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Composite follicular lymphoma and classic Hodgkin lymphoma
- Primary Malignant Lymphoma of The Bilateral Orbit
- ProMACE/MOPP combination chemotherapy in advanced, intermediate and high grade non-Hodgkin's lymphoma
- A Rare Presentation of Follicular Lymphoma: Cerebellar Involvement, Successfully Treated with a Combination of Radiotherapy and Chemotherapy
- Hepatic candidiasis developed after high dose chemotherapy for non-hodgkin's lymphoma