Korean J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg.
2016 Feb;20(1):32-37. 10.14701/kjhbps.2016.20.1.32.
Benefit of pyloroplasty to prevent gastric stasis in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma patients undergoing extensive left-sided lymph node dissection
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. shwang@amc.seoul.kr
- KMID: 2243029
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14701/kjhbps.2016.20.1.32
Abstract
- BACKGROUNDS/AIMS
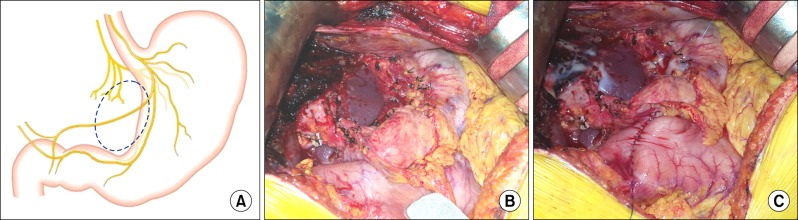
Intrahepatic cholangiocacinoma (IHCC) can result in spread of tumor cells to the lymph nodes (LNs) around the gastric lesser curvature. Extensive dissection of the gastric lesser curvature can induce injury to the extragastric vagus nerve branches that control motility of the pyloric sphincter and result in intractable gastric stasis. Herein, we presented our experience of preventive pyloroplasty added to resection of IHCC to address dissection-induced gastric stasis in 6 patients during 15-years.
METHODS
We analyzed the survival outcomes of 54 IHCC patients presenting left-sided LN metastasis. Nine study patients who underwent extended left-sided LN dissection including lesser curvature LN dissection were selected and divided into 2 groups according to performance of preventive pyloroplasty and the incidence of gastric stasis was analyzed.
RESULTS
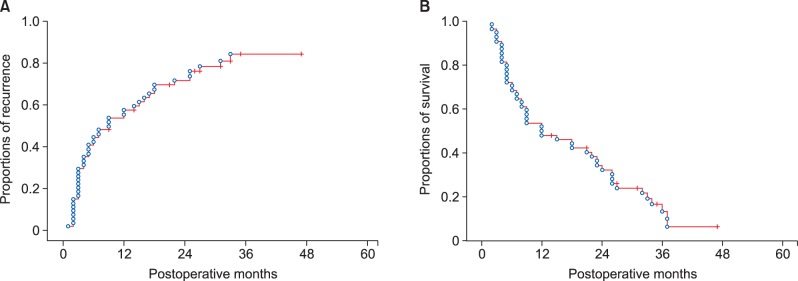
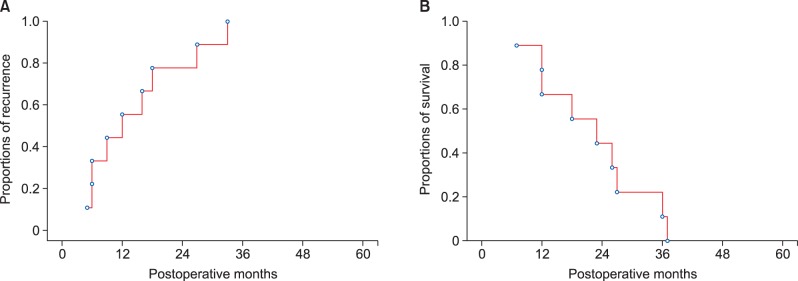
All 54 patients were classified as stage IV due to T1-3N1M0 stage. The tumor recurrence rate were 56.4% at 1 year, 84.3% at 3 years and 84.3% at 5 years; and the overall patient survival rate were 51.9% at 1 year, 13.6% at 3 years and 6.8% at 5 years. In all 3 study patients who did not receive pyloroplasty, overt postoperative gastric stasis persisted for >10 days leading to prolonged hospital stay. In contrast, none of the 6 study patients who underwent pyloroplasty suffered from gastric stasis.
CONCLUSIONS
Pyloroplasty is a useful surgical option to prevent gastric stasis when extensive left-sided LN dissection is required in IHCC patients with LN metastasis who have very poor post-resection prognosis.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Preemptive pyloroplasty for iatrogenic vagus nerve injury in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma patients undergoing extensive left-sided lymph node dissection: a retrospective observational study
Shin Hwang, Dong-Hwan Jung, Eun-Kyoung Jwa, Yumi Kim
J Yeungnam Med Sci. 2021;39(3):235-243. doi: 10.12701/yujm.2021.01550.
Reference
-
1. Tsuji T, Hiraoka T, Kanemitsu K, Takamori H, Tanabe D, Tashiro S. Lymphatic spreading pattern of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Surgery. 2001; 129:401–407. PMID: 11283529.
Article2. Morine Y, Shimada M, Utsunomiya T, Imura S, Ikemoto T, Mori H, et al. Clinical impact of lymph node dissection in surgery for peripheral-type intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Surg Today. 2012; 42:147–151. PMID: 22124809.
Article3. Edge SB, Byrd DR, Compton CC, Fritz AG, Greene FL, Trotti A 3rd. AJCC cancer staging manual. 7th ed. New York: Springer;2010.4. Hwang S, Lee YJ, Song GW, Park KM, Kim KH, Ahn CS, et al. Prognostic impact of tumor growth type on 7th AJCC staging system for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: a single-center experience of 659 cases. J Gastrointest Surg. 2015; 19:1291–1304. PMID: 25820487.
Article5. Shafi MA, Pasricha PJ. Post-surgical and obstructive gastroparesis. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2007; 9:280–285. PMID: 17883974.
Article6. Lee A. Gastroparesis: what is the current state-of-the-art for evaluation and medical management? What are the results? J Gastrointest Surg. 2013; 17:1553–1556. PMID: 23801519.
Article7. Stevens JE, Jones KL, Rayner CK, Horowitz M. Pathophysiology and pharmacotherapy of gastroparesis: current and future perspectives. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2013; 14:1171–1186. PMID: 23663133.
Article8. Nathan H, Aloia TA, Vauthey JN, Abdalla EK, Zhu AX, Schulick RD, et al. A proposed staging system for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 2009; 16:14–22. PMID: 18987916.
Article9. Clark CJ, Wood-Wentz CM, Reid-Lombardo KM, Kendrick ML, Huebner M, Que FG. Lymphadenectomy in the staging and treatment of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: a population-based study using the National Cancer Institute SEER database. HPB (Oxford). 2011; 13:612–620. PMID: 21843261.
Article10. Adachi T, Eguchi S. Lymph node dissection for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: a critical review of the literature to date. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2014; 21:162–168. PMID: 24027075.
Article11. Ribero D, Pinna AD, Guglielmi A, Ponti A, Nuzzo G, Giulini SM, et al. Italian Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma Study Group. Surgical approach for long-term survival of patients with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: a multi-institutional analysis of 434 patients. Arch Surg. 2012; 147:1107–1113. PMID: 22910846.12. de Jong MC, Nathan H, Sotiropoulos GC, Paul A, Alexandrescu S, Marques H, et al. Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: an international multi-institutional analysis of prognostic factors and lymph node assessment. J Clin Oncol. 2011; 29:3140–3145. PMID: 21730269.
Article13. Becker HD, Herfarth C, Lierse W, Schreiber HW. Surgery of the stomach: indications, methods, complications. Berlin: Springer-Verlag;1986. p. 182–184.14. Lo CM. Complications and long-term outcome of living liver donors: a survey of 1,508 cases in five Asian centers. Transplantation. 2003; 75(3 Suppl):S12–S15. PMID: 12589131.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Preemptive pyloroplasty for iatrogenic vagus nerve injury in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma patients undergoing extensive left-sided lymph node dissection: a retrospective observational study
- Individualized Surgery for Gastric Cancer
- Advantages of Splenic Hilar Lymph Node Dissection in Proximal Gastric Cancer Surgery
- Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma Initially Presented as a Distant Metastatic Lymph Node without Demonstrable Hepatic Mass: A Case Report
- What Should Thoracic Surgeons Consider during Surgery for Ground-Glass Nodules?: Lymph Node Dissection