Clin Orthop Surg.
2015 Sep;7(3):392-395. 10.4055/cios.2015.7.3.392.
Usefulness of the Medial Portal during Hip Arthroscopy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Chungnam National University Hospital, Daejeon, Korea. dshwang@cnu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2234096
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2015.7.3.392
Abstract
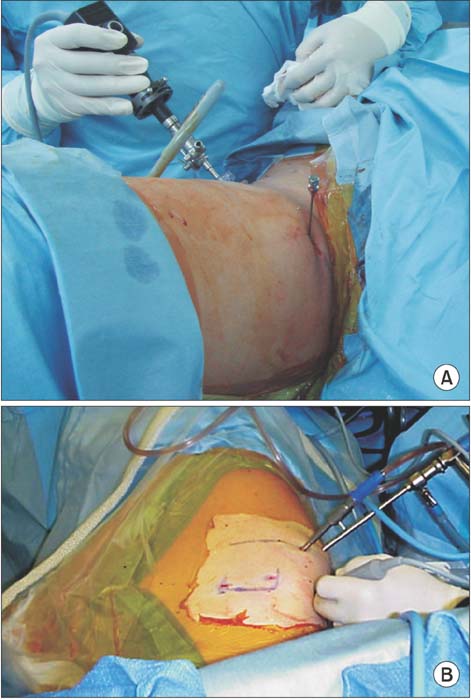
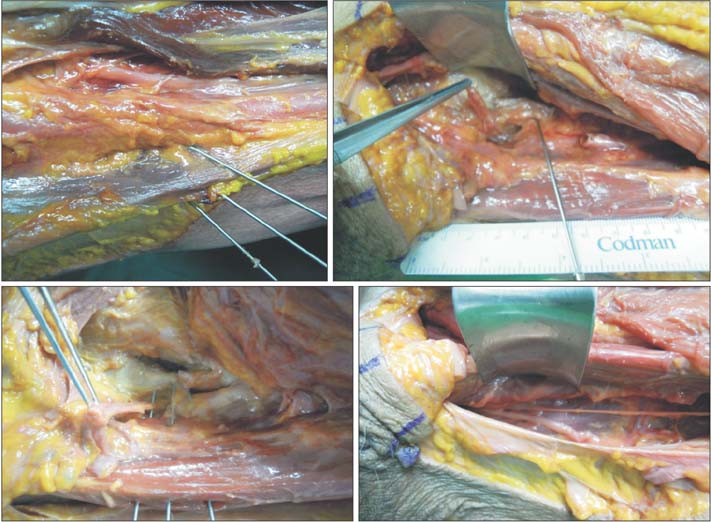
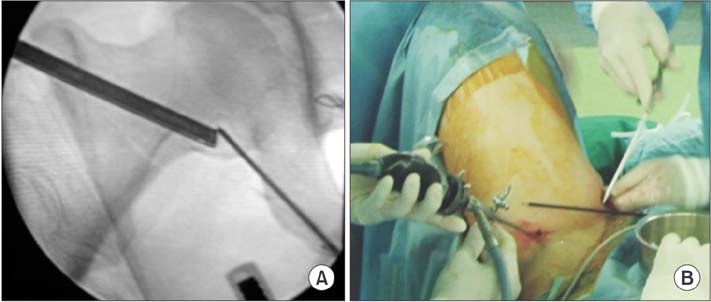
- The current conventional portals for hip arthroscopic surgery are the anterior, anterolateral, and posterolateral portals. For lesions in the medial anteroinferior or posteroinferior portion of the hip, these portals provide insufficient access to the lesion and consequently lead to incomplete treatment. Thus, in such a situation, a medial portal approach might be helpful. However, operators have avoided this procedure because of the risk of injury to the obturator, femoral neurovascular structures, and the medial femoral circumflex artery. Thus, to overcome the disadvantages of the conventional method for medial lesions of the hip, we performed a cadaveric study to evaluate the technique, usefulness, and risk of the medial portal technique.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Arthroscopic Treatment for Femoroacetabular Impingement with Extraspinal Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis
Jung-Mo Hwang, Deuk-Soo Hwang, Chan Kang, Woo-Yong Lee, Gi-Soo Lee, Jeong-Kil Lee, Yun-Ki Kim
Clin Orthop Surg. 2019;11(3):275-281. doi: 10.4055/cios.2019.11.3.275.
Reference
-
1. McCarthy JC, Busconi B. The role of hip arthroscopy in the diagnosis and treatment of hip disease. Can J Surg. 1995; 38:Suppl 1. S13–S17.
Article2. Botser IB, Smith TW Jr, Nasser R, Domb BG. Open surgical dislocation versus arthroscopy for femoroacetabular impingement: a comparison of clinical outcomes. Arthroscopy. 2011; 27(2):270–278.
Article3. Diulus CA, Krebs VE, Hanna G, Barsoum WK. Hip arthroscopy technique and indications. J Arthroplasty. 2006; 21:4 Suppl 1. 68–73.4. Beaule PE, Le Duff MJ, Zaragoza E. Quality of life following femoral head-neck osteochondroplasty for femoroacetabular impingement. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007; 89(4):773–779.
Article5. Mardones RM, Gonzalez C, Chen Q, Zobitz M, Kaufman KR, Trousdale RT. Surgical treatment of femoroacetabular impingement: evaluation of the effect of the size of the resection: surgical technique. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006; 88:Suppl 1 Pt 1. 84–91.
Article6. Funke EL, Munzinger U. Complications in hip arthroscopy. Arthroscopy. 1996; 12(2):156–159.
Article7. Dvorak M, Duncan CP, Day B. Arthroscopic anatomy of the hip. Arthroscopy. 1990; 6(4):264–273.
Article8. Sekiya JK, Wojtys EM, Loder RT, Hensinger RN. Hip arthroscopy using a limited anterior exposure: an alternative approach for arthroscopic access. Arthroscopy. 2000; 16(1):16–20.
Article9. Byrd JW, Pappas JN, Pedley MJ. Hip arthroscopy: an anatomic study of portal placement and relationship to the extra-articular structures. Arthroscopy. 1995; 11(4):418–423.
Article10. Gedouin JE. Arthroscopic treatment of femoroacetabular impingement: technical review. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2012; 98(5):583–596.
Article